
Concept explainers
(a)
To calculate:The exact value of the trigonometric function
(a)
Answer to Problem 9E
The exact value of the trigonometric function
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The figure is given as follows.
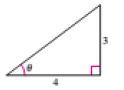
Formula Used:
Use the formula
Calculation:
From the figure,
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore the value of
Substitute these values in the formula
Therefore, the exact value of
(b)
To calculate:The exact value of the trigonometric function
(b)
Answer to Problem 9E
The exact value of the trigonometric function
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The figure is given as follows.
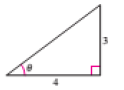
Formula Used:
Use the formula
Calculation:
From the figure,
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore the value of
Substitute these values in the formula
Therefore, the exact value of
(c)
To calculate:The exact value of the trigonometric function
(c)
Answer to Problem 9E
The exact value of the trigonometric function
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The figure is given as follows.
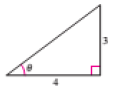
Formula Used:
Use the formula
Calculation:
From the figure,
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore the value of
Substitute these values in the formula
Therefore, the exact value of
(d)
To calculate:The exact value of the trigonometric function
(d)
Answer to Problem 9E
The exact value of the trigonometric function
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The figure is given as follows.
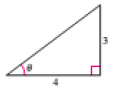
Formula Used:
Use the formula
Calculation:
From the given figure,
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore the value of
Substitute these values in the formula
Therefore, the exact value of
Substitute the values in the formula
Therefore the exact value of
Substitute both the values in the formula
Therefore the exact value of
(e)
To calculate:The exact value of the trigonometric function
(e)
Answer to Problem 9E
The exact value of the trigonometric function
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
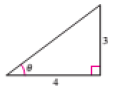
The figure is given as follows.
Formula Used:
Use the formula
Calculation:
From the above,
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore the value of
Substitute these values in the formula
Therefore, the exact value of
Substitute the value in the formula
Therefore the exact value of
(f)
To calculate:The exact value of the trigonometric function
(f)
Answer to Problem 9E
The exact value of the trigonometric function
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
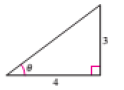
The figure is given as follows.
Formula Used:
Use the formula
Calculation:
From the given figure,
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore the value of
Substitute these values in the formula
Therefore, the exact value of
Substitute the value in the formula
Therefore the exact value of
Substitute
Therefore the exact value of
(g)
To calculate:The exact value of the trigonometric function
(g)
Answer to Problem 9E
The exact value of the trigonometric function
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
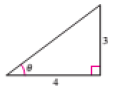
The figure is given as follows.
Formula Used:
Use the formula
Calculation:
From the given figure,
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore the value of
Substitute these values in the formula
Therefore, the exact value of
Substitute the values in the formula
Therefore the exact value of
Substitute both the values in the formula
Therefore the exact value of
Substitute this value in the formula
Therefore the exact value of
(h)
To calculate:The exact value of the trigonometric function
(h)
Answer to Problem 9E
The exact value of the trigonometric function
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
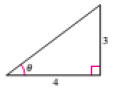
The figure is given as follows.
Formula Used:
Use the formula
Calculation:
From the given figure,
Apply the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore the value of
Substitute these values in the formula
Therefore, the exact value of
Substitute the value in the formula
Therefore the exact value of
Substitute this value in the formula
Therefore the exact value of
Chapter 5 Solutions
PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS:GRAPH.APPROACH(HS)
- (7) (12 points) Let F(x, y, z) = (y, x+z cos yz, y cos yz). Ꮖ (a) (4 points) Show that V x F = 0. (b) (4 points) Find a potential f for the vector field F. (c) (4 points) Let S be a surface in R3 for which the Stokes' Theorem is valid. Use Stokes' Theorem to calculate the line integral Jos F.ds; as denotes the boundary of S. Explain your answer.arrow_forward(3) (16 points) Consider z = uv, u = x+y, v=x-y. (a) (4 points) Express z in the form z = fog where g: R² R² and f: R² → R. (b) (4 points) Use the chain rule to calculate Vz = (2, 2). Show all intermediate steps otherwise no credit. (c) (4 points) Let S be the surface parametrized by T(x, y) = (x, y, ƒ (g(x, y)) (x, y) = R². Give a parametric description of the tangent plane to S at the point p = T(x, y). (d) (4 points) Calculate the second Taylor polynomial Q(x, y) (i.e. the quadratic approximation) of F = (fog) at a point (a, b). Verify that Q(x,y) F(a+x,b+y). =arrow_forward(6) (8 points) Change the order of integration and evaluate (z +4ry)drdy . So S√ ² 0arrow_forward
- (10) (16 points) Let R>0. Consider the truncated sphere S given as x² + y² + (z = √15R)² = R², z ≥0. where F(x, y, z) = −yi + xj . (a) (8 points) Consider the vector field V (x, y, z) = (▼ × F)(x, y, z) Think of S as a hot-air balloon where the vector field V is the velocity vector field measuring the hot gasses escaping through the porous surface S. The flux of V across S gives the volume flow rate of the gasses through S. Calculate this flux. Hint: Parametrize the boundary OS. Then use Stokes' Theorem. (b) (8 points) Calculate the surface area of the balloon. To calculate the surface area, do the following: Translate the balloon surface S by the vector (-15)k. The translated surface, call it S+ is part of the sphere x² + y²+z² = R². Why do S and S+ have the same area? ⚫ Calculate the area of S+. What is the natural spherical parametrization of S+?arrow_forward(1) (8 points) Let c(t) = (et, et sint, et cost). Reparametrize c as a unit speed curve starting from the point (1,0,1).arrow_forward(9) (16 points) Let F(x, y, z) = (x² + y − 4)i + 3xyj + (2x2 +z²)k = - = (x²+y4,3xy, 2x2 + 2²). (a) (4 points) Calculate the divergence and curl of F. (b) (6 points) Find the flux of V x F across the surface S given by x² + y²+2² = 16, z ≥ 0. (c) (6 points) Find the flux of F across the boundary of the unit cube E = [0,1] × [0,1] x [0,1].arrow_forward
- (8) (12 points) (a) (8 points) Let C be the circle x² + y² = 4. Let F(x, y) = (2y + e²)i + (x + sin(y²))j. Evaluate the line integral JF. F.ds. Hint: First calculate V x F. (b) (4 points) Let S be the surface r² + y² + z² = 4, z ≤0. Calculate the flux integral √(V × F) F).dS. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardDetermine whether the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines can be used to find another measure of the triangle. a = 13, b = 15, C = 68° Law of Sines Law of Cosines Then solve the triangle. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) C = 15.7449 A = 49.9288 B = 62.0712 × Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forward(4) (10 points) Evaluate √(x² + y² + z²)¹⁄² exp[}(x² + y² + z²)²] dV where D is the region defined by 1< x² + y²+ z² ≤4 and √√3(x² + y²) ≤ z. Note: exp(x² + y²+ 2²)²] means el (x²+ y²+=²)²]¸arrow_forward
- (2) (12 points) Let f(x,y) = x²e¯. (a) (4 points) Calculate Vf. (b) (4 points) Given x directional derivative 0, find the line of vectors u = D₁f(x, y) = 0. (u1, 2) such that the - (c) (4 points) Let u= (1+3√3). Show that Duƒ(1, 0) = ¦|▼ƒ(1,0)| . What is the angle between Vf(1,0) and the vector u? Explain.arrow_forwardFind the missing values by solving the parallelogram shown in the figure. (The lengths of the diagonals are given by c and d. Round your answers to two decimal places.) a b 29 39 66.50 C 17.40 d 0 54.0 126° a Ꮎ b darrow_forward(5) (10 points) Let D be the parallelogram in the xy-plane with vertices (0, 0), (1, 1), (1, 1), (0, -2). Let f(x,y) = xy/2. Use the linear change of variables T(u, v)=(u,u2v) = (x, y) 1 to calculate the integral f(x,y) dA= 0 ↓ The domain of T is a rectangle R. What is R? |ǝ(x, y) du dv. |ð(u, v)|arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





