
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134382593
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.5, Problem 61P
The platform scale consists of a combination of third and first class levers so that the load on one lever becomes the effort that moves the next lever. Through this arrangement a small weight can balance a massive object. If x = 450 mm, and the mass of the counterweight S is 2 kg, determine the mass of the load L required to maintain the balance.
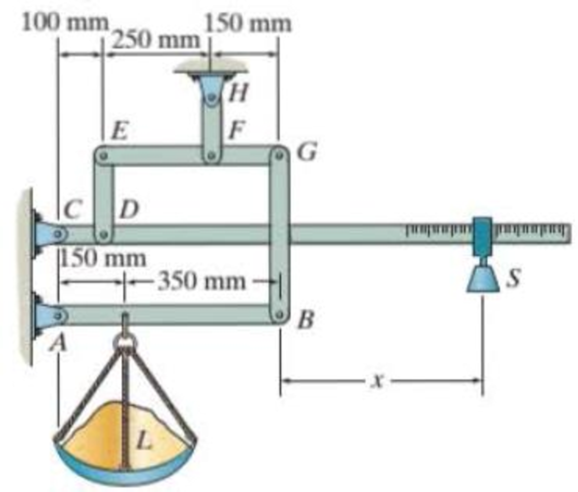
Probs. 5-60/61
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 6. The circular plate shown rotates about its vertical diameter. At the instant shown, the
angular velocity ₁ of the plate is 10 rad/s and is decreasing at the rate of 25 rad/s². The disk lies
in the XY plane and Point D of strap CD moves upward. The relative speed u of Point D of strap
CD is 1.5 m/s and is decreasing at the rate of 3 m/s².
Determine (a) the velocity of D, (b) the acceleration of D.
Answers: =0.75 +1.299]-1.732k m/s a=-28.6 +3.03-10.67k m/s²
200 mm
x
Z
Problem 1. The flywheel A has an angular velocity o 5 rad/s. Link AB is connected via ball
and socket joints to the flywheel at A and a slider at B. Find the angular velocity of link AB and
the velocity of slider B at this instant. (Partial Answer: @ABN = -2î + 2.25; red
Z
-1.2 ft
C
-7 Y
-1.5 ft-
B
2.0 ft
Need help please
Chapter 5 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Ch. 5.3 - In each ease, calculate the support reactions and...Ch. 5.3 - Identify the zero-force members in each truss....Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the greatest load P that can be applied...Ch. 5.3 - Identify the zero-force members in the truss....Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...
Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 5.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 5.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - If the maximum force that any member can support...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CF, and FE and...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members LK, KC, and CD of...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members KJ, KD, and CD of...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC of...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members GF, GD, and CD of...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HI, and JI of...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HC and HI of...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members ED, EH, and GH of...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members HG, HE, and DE of...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members CD, HI, and CH of...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, KJ, and DJ...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 22PCh. 5.4 - The Howe truss is subjected to the loading shown....Ch. 5.4 - The Howe truss is subjected to the loading shown....Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC, and...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force in members AF, BF, and BC, and...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 27PCh. 5.4 - Determine the force in members BC, BE, and EF of...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 29PCh. 5.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CF, and CG and...Ch. 5.4 - Determine the force developed in members FE, EB,...Ch. 5.5 - In each ease, identify any two-force members, and...Ch. 5.5 - F5-13. Determine the force P needed to hold the...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5.5 - If a 100-N force is applied to the handles of the...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the force P required to hold the 100-lb...Ch. 5.5 - In each case, determine the force P required to...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the force P required to hold the 50-kg...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the force P required to hold the 150-kg...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, C, and...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the resultant force at pins A, B, and C...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the reactions at the supports at A, E,...Ch. 5.5 - The wall crane supports a load of 700 lb....Ch. 5.5 - The wall crane supports a load of 700 lb....Ch. 5.5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the force in members FD and DB of the...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the force that the smooth 20-kg cylinder...Ch. 5.5 - The three power lines exert the forces shown on...Ch. 5.5 - The pumping unit is used to recover oil. When the...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 47PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 48PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 49PCh. 5.5 - Determine the force created in the hydraulic...Ch. 5.5 - The hydraulic crane is used to lift the 1400-lb...Ch. 5.5 - Determine force P on the cable if the spring is...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 53PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 54PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 55PCh. 5.5 - Determine the force P on the cable if the spring...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 57PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 58PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 59PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 60PCh. 5.5 - The platform scale consists of a combination of...Ch. 5 - All the problems solutions must include FBDs....Ch. 5 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 5 - Determine the force in member GJ and GC of the...Ch. 5 - Determine the force in members GF, FB, and BC of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5RPCh. 5 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 5 - Prob. 7RPCh. 5 - Determine the resultant forces at pins B and C on...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PROBLEM 15.225 The bent rod shown rotates at the constant rate @₁ = 5 rad/s and collar C moves toward point B at a constant relative speed u = 39 in./s. Knowing that collar C is halfway between points B and D at the instant shown, determine its velocity and acceleration. Answers: v=-45 +36.6)-31.2 k in./s āc = -2911-270} in./s² 6 in 20.8 in. 14.4 in.arrow_forwardNeed help, please show all work, steps, units and please box out and round answers to 3 significant figures. Thank you!..arrow_forwardNeed help, please show all work, steps, units and please box out and round answers to 3 significant figures. Thank you!...arrow_forward
- FL y b C Z Determine the moment about O due to the force F shown, the magnitude of the force F = 76.0 lbs. Note: Pay attention to the axis. Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 1.90 ft b 2.80 ft с 2.60 ft d 2.30 ft Mo 144 ft-lb = -212 × 1 + xk) ☑+212arrow_forward20 in. PROBLEM 15.206 Rod AB is connected by ball-and-socket joints to collar A and to the 16-in.-diameter disk C. Knowing that disk C rotates counterclockwise at the constant rate ₁ =3 rad/s in the zx plane, determine the velocity of collar A for the position shown. 25 in. B 8 in. Answer: -30 in/s =arrow_forwardB Z 001 2.5 ft PROBLEM 15.236 The arm AB of length 16 ft is used to provide an elevated platform for construction workers. In the position shown, arm AB is being raised at the constant rate de/dt = 0.25 rad/s; simultaneously, the unit is being rotated about the Y axis at the constant rate ₁ =0.15 rad/s. Knowing that 20°, determine the velocity and acceleration of Point B. Answers: 1.371 +3.76)+1.88k ft/s a=1.22 -0.342)-0.410k ft/s² Xarrow_forward
- F1 3 5 4 P F2 F2 Ꮎ Ꮎ b P 3 4 5 F1 The electric pole is subject to the forces shown. Force F1 245 N and force F2 = 310 N with an angle = 20.2°. Determine the moment about point P of all forces. Take counterclockwise moments to be positive. = Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 2.50 m b 11.3 m C 13.0 m The moment about point P is 3,414 m. × N- If the moment about point P sums up to be zero. Determine the distance c while all other values remained the same. 1.26 m.arrow_forwardZ 0.2 m B PROBLEM 15.224 Rod AB is welded to the 0.3-m-radius plate, which rotates at the constant rate ₁ = 6 rad/s. Knowing that collar D moves toward end B of the rod at a constant speed u = 1.3 m, determine, for the position shown, (a) the velocity of D, (b) the acceleration of D. Answers: 1.2 +0.5-1.2k m/s a=-7.21-14.4k m/s² A 0.25 m 0.3 marrow_forwardI am trying to code in MATLAB the equations of motion for malankovich orbitlal elements. But, I am having a problem with the B matrix. Since f matrix is 7x1 and a_d matrix has to be 3x1, the B matrix has to be 7x3. I don't know how that is possible. Can you break down the B matrix for me and let me know what size it is?arrow_forward
- I am trying to code the solution to the problem in the image in MATLAB. I wanted to know what is the milankovich constraint equation that is talked about in part b.arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardAir modeled as an ideal gas enters an insulated compressor at a temperature of 300 K and 100 kPa, and leaves at 600 kPa. The mass flowrate of air entering the compressor is 50 kg/hr, and the power consumed by the compressor is 3 kW. (Rair = 0.287 kJ/kg-K, k = 1.4, cp = 1.0045 kJ/kg-K, cv = 0.718 kJ/kg-K) Determine the isentropic exit temperature (Te,s) of the air in [K]. Determine the actual exit temperature (Te) of the air in [K]. Determine the isentropic efficiency of the compressor. (Answer: ηc,s = 93.3%) Determine the rate of entropy generated through the compressor in [kW/K]. (Answer: Ṡgen = 0.000397 kW/K)arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License