
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780077687304
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.4, Problem 5.110P
An elbow for the duct of a ventilating system is made of s metal with a uniform thickness. Locate the center of gravi the elbow.
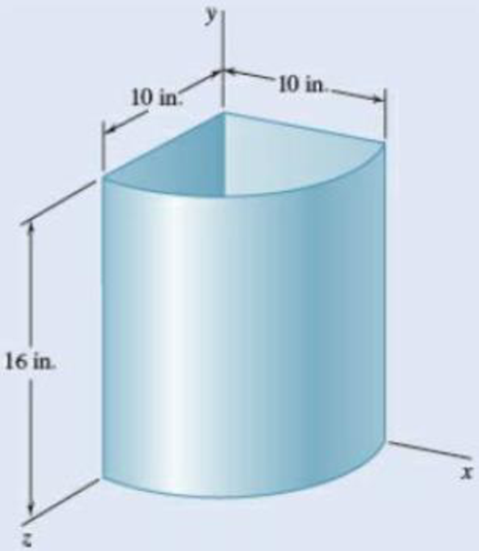
Fig. P5.110
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Qu 5 Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.30 wt% at a position 4 mm into an iron carbon alloy that initially contains 0.10 wt% C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 0.90 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1100°C. Use the data for the diffusion of
carbon into y-iron: Do = 2.3 x10-5 m2/s and Qd = 148,000 J/mol. Express your answer in hours to three significant figures.
show all work step by step problems formula material science
(Read Question)
In figure A, the homogeneous rod of constant cross section is attached to unyielding supports. In figure B, a homogeneous bar with a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2 is attached to rigid supports. The bar carries the axial loads P1 = 20 kN and P2 = 60 kN, as shown.1. In figure A, derive the expression that calculates the reaction R1 in terms of P, and the given dimensions.2. In figure B, calculate the reaction (kN) at A.3. In figure B, calculate the maximum axial stress (MPa) in the rod.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.
Ch. 5.1 - 5.10 through 5.15 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - 5.10 through 5.15 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - 5.10 through 5.15 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - 5.10 through 5.15 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - PROBLEM 5.16 Determine the y coordinate of the...Ch. 5.1 - Show that as r1 approaches r2, the location of the...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.18PCh. 5.1 - For the semiannular area of Prob. 5.12, determine...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.20PCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.21PCh. 5.1 - The horizontal x-axis is drawn through the...Ch. 5.1 - PROBLEM 5.23 The first moment of the shaded area...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.24PCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.25PCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.26PCh. 5.1 - A thin, homogeneous wire is bent to form the...Ch. 5.1 - The homogeneous wire ABC is bent into a...Ch. 5.1 - The frame for a sign is fabricated from thin, flat...Ch. 5.1 - The homogeneous wire ABCD is bent as shown and is...Ch. 5.1 - The homogeneous wire ABCD is bent as shown and is...Ch. 5.1 - Determine the distance h for which the centroid of...Ch. 5.1 - Knowing that the distance h has been selected to...Ch. 5.2 - 5.34 through 5.36 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.34 through 5.36 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.34 through 5.36 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.37 through 5.39 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.37 through 5.39 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.37 through 5.39 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.40 and 5.41 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - 5.40 and 5.41 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - Determine by direct integration the centroid of...Ch. 5.2 - 5.43 and 5.44 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - 5.43 and 5.44 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - 5.45 and 5.46 A homogeneous wire is bent into the...Ch. 5.2 - 5.45 and 5.46 A homogeneous wire is bent into the...Ch. 5.2 - A homogeneous wire is bent into the shape shown....Ch. 5.2 - 5.48 and 5.49 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 5.49PCh. 5.2 - Determine the centroid of the area shown in terms...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the centroid of the area shown when a =...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 5.52PCh. 5.2 - 5.53 Determine the volume and the surface area of...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the volume and the surface area of the...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 5.55PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 5.56PCh. 5.2 - Verify that the expressions for the volumes of the...Ch. 5.2 - Knowing that two equal caps have been removed from...Ch. 5.2 - Three different drive belt profiles are to be...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the capacity, in liters, of the punch...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the volume and total surface area of the...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the volume and weight of the solid brass...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the total surface area of the solid...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 5.64PCh. 5.2 - The shade for a wall-mounted light is formed from...Ch. 5.3 - 5.66 and 5.67 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 5.3 - 5.66 and 5.67 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.68PCh. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - Determine (a) the distance a so that the vertical...Ch. 5.3 - Determine (a) the distance a so that the reaction...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.76PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.77PCh. 5.3 - The beam AB supports two concentrated loads and...Ch. 5.3 - For the beam and loading of Prob. 5.78, determine...Ch. 5.3 - The cross section of a concrete dam is as shown....Ch. 5.3 - The cross section of a concrete dam is as shown....Ch. 5.3 - The dam for a lake is designed to withstand the...Ch. 5.3 - The base of a dam for a lake is designed to resist...Ch. 5.3 - 5.84 An automatic valve consists of a 9 × 9-in....Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.85PCh. 5.3 - The 3 4-m side AB of a tank is hinged at its...Ch. 5.3 - The 3 4-m side of an open tank is hinged at its...Ch. 5.3 - A 0.5 0.8-m gate AB is located at the bottom of a...Ch. 5.3 - A 0.5 0.8-m gate AB is located at the bottom of a...Ch. 5.3 - A 4 2-ft gate is hinged at A and is held in...Ch. 5.3 - Fig. P5.90 5.91 Solve Prob. 5.90 if the gate...Ch. 5.3 - A prismatically shaped gate placed at the end of a...Ch. 5.3 - A prismatically shaped gate placed at the end of a...Ch. 5.3 - A long trough is supported by a continuous hinge...Ch. 5.3 - The square gate AB is held in the position shown...Ch. 5.4 - Consider the composite body shown. Determine (a)...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.97PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.98PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.99PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.100PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.101PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.102PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.103PCh. 5.4 - For the machine element shown, locate the y...Ch. 5.4 - For the machine element shown, locate the x...Ch. 5.4 - 5.106 and 5.107 Locate the center of gravity of...Ch. 5.4 - 5.106 and 5.107 Locate the center of gravity of...Ch. 5.4 - A corner reflector for tracking by radar has two...Ch. 5.4 - A wastebasket, designed to fit in the corner of a...Ch. 5.4 - An elbow for the duct of a ventilating system is...Ch. 5.4 - A window awning is fabricated from sheet metal...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.112PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.113PCh. 5.4 - A thin steel wire with a uniform cross section is...Ch. 5.4 - The frame of a greenhouse is constructed from...Ch. 5.4 - Locate the center of gravity of the figure shown,...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.117PCh. 5.4 - A scratch awl has a plastic handle and a steel...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.117 A bronze bushing is mounted inside a...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.120 A brass collar, of length 2.5 in.,...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.121 The three legs of a small...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.122PCh. 5.4 - Determine by direct integration the values of x...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.124PCh. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.125 Locate the centroid of the volume...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.126PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.127PCh. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.128 Locate the centroid of the volume...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.129 Locate the centroid of the volume...Ch. 5.4 - Show that for a regular pyramid of height h and n...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.131 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.132 The sides and the base of a punch...Ch. 5.4 - Locate the centroid of the section shown, which...Ch. 5.4 - Locate the centroid of the section shown, which...Ch. 5.4 - Determine by direct integration the location of...Ch. 5.4 - Alter grading a lot, a builder places four stakes...Ch. 5 - 5.137 and 5.138 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5 - 5.137 and 5.138 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.139RPCh. 5 - Determine by direct integration the centroid of...Ch. 5 - Determine by direct integration the centroid of...Ch. 5 - The escutcheon (a decorative plate placed on a...Ch. 5 - Determine the reactions at the supports for the...Ch. 5 - A beam is subjected to a linearly distributed...Ch. 5 - A tank is divided into two sections by a 1 1-m...Ch. 5 - Determine the y coordinate of the centroid of the...Ch. 5 - An 8-in.-diameter cylindrical duct and a 4 8-in....Ch. 5 - Three brass plates are brazed to a steel pipe to...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Read image)arrow_forward(Read Image)arrow_forwardM16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1- Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the separation factor of safety. 19 mmarrow_forward
- Problem4. The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk. a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution. b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.) c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly. z R R 002 2R x Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec T 0.518 N-m =arrow_forwardProblem 3. The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes shown. Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k 3 m r b 2 C لا marrow_forwardOnly question 2arrow_forward
- Only question 1arrow_forwardOnly question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forward
- Describe at least 4 processes in engineering where control charts are (or should be) appliedarrow_forwardDescribe at least two (2) processes where control charts are (or should be) applied.arrow_forwardProblem 3: A cube-shaped spacecraft is in a circular Earth orbit. Let N (n,) be inertial and the spacecraft is denoted S (ŝ₁). The spacecraft is described such that ¯½º = J ŝ₁ŝ₁ + J ŝ₂§₂ + J §¸Ŝ3 Location of the spacecraft in the orbit is determined by the orbit-fixed unit vectors ê, that are oriented by the angle (Qt), where is a constant angular rate. 52 €3 3> 2t 55 Λ Из At the instant when Qt = 90°, the spacecraft S is oriented relative to the orbit such that 8₁ = 0° Space-three 1-2-3 angles 0₂ = 60° and ES = $₂ rad/s 0₁ = 135° (a) At this instant, determine the direction cosine matrix that describes the orientation of the spacecraft with respect to the inertial frame N.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanical Engineering: Centroids & Center of Gravity (1 of 35) What is Center of Gravity?; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tkyk-G1rDQg;License: Standard Youtube License