
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780077687304
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.2, Problem 5.54P
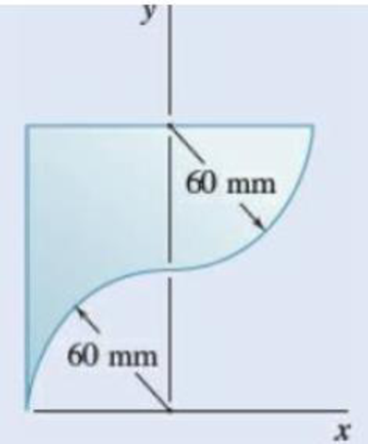
Determine the volume and the surface area of the solid obtained by rotating the area of Prob. 5.6 about (a) the line x = -60 mm, (b) the line y = 120 mm.
Fig. P5.6
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
You are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of
lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (µ = 0.001 kg m¯¹ s¯¹) can be approximated
as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates.
The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed,
U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by
a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By
applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that
end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be
U
y = +h
У
2h = 1 cm
1
x1
y=-h
u(y)
=
1 dP
2μ dx
-y² + Ay + B
moving plate
-
U
stationary plate
2
I2
L = 10 cm
Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm,
into the page.
(a) By considering the appropriate boundary conditions, show that the constants take
the following forms:
A =
U
2h
U
1 dP…
Question 2
You are an engineer working in the propulsion team for a supersonic civil transport
aircraft driven by a turbojet engine, where you have oversight of the design for the
engine intake and the exhaust nozzle, indicated in Figure Q2a. The turbojet engine can
operate when provided with air flow in the Mach number range, 0.60 to 0.80. You are
asked to analyse a condition where the aircraft is flying at 472 m/s at an altitude of
14,000 m. For all parts of the question, you can assume that the flow path of air through
the engine has a circular cross section.
(a)
normal
shock
472 m/s
A B
(b)
intake
engine
altitude: 14,000 m
D
exhaust nozzle→
exit to
atmosphere
472 m/s
50 m/s
B
diameter: DE = 0.30 m
EX
diameter: DF = 0.66 m
Figure Q2: Propulsion system for a supersonic aircraft.
F
a) When the aircraft is at an altitude of 14,000 m, use the International Standard
Atmosphere in the Module Data Book to state the local air pressure and tempera-
ture. Thus show that the aircraft speed of…
given below:
A rectangular wing with wing twist yields the spanwise circulation distribution
kbV1
roy) = kbv. (2)
where k is a constant, b is the span length and V. is the free-stream velocity. The wing has an
aspect ratio of 4. For all wing sections, the lift curve slope (ag) is 2 and the zero-lift angle of
attack (a=0) is 0.
a. Derive expressions for the downwash (w) and induced angle of attack a distributions
along the span.
b. Derive an expression for the induced drag coefficient.
c. Calculate the span efficiency factor.
d. Calculate the value of k if the wing has a washout and the difference between the
geometric angles of attack of the root (y = 0) and the tip (y = tb/2) is:
a(y = 0) a(y = ±b/2) = /18
Hint: Use the coordinate transformation y = cos (0)
Chapter 5 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - 5.1 through 5.9 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.
Ch. 5.1 - 5.10 through 5.15 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - Locate the centroid of the plane area shown.Ch. 5.1 - 5.10 through 5.15 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - 5.10 through 5.15 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - 5.10 through 5.15 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5.1 - PROBLEM 5.16 Determine the y coordinate of the...Ch. 5.1 - Show that as r1 approaches r2, the location of the...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.18PCh. 5.1 - For the semiannular area of Prob. 5.12, determine...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.20PCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.21PCh. 5.1 - The horizontal x-axis is drawn through the...Ch. 5.1 - PROBLEM 5.23 The first moment of the shaded area...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 5.24PCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.25PCh. 5.1 - Prob. 5.26PCh. 5.1 - A thin, homogeneous wire is bent to form the...Ch. 5.1 - The homogeneous wire ABC is bent into a...Ch. 5.1 - The frame for a sign is fabricated from thin, flat...Ch. 5.1 - The homogeneous wire ABCD is bent as shown and is...Ch. 5.1 - The homogeneous wire ABCD is bent as shown and is...Ch. 5.1 - Determine the distance h for which the centroid of...Ch. 5.1 - Knowing that the distance h has been selected to...Ch. 5.2 - 5.34 through 5.36 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.34 through 5.36 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.34 through 5.36 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.37 through 5.39 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.37 through 5.39 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.37 through 5.39 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 5.2 - 5.40 and 5.41 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - 5.40 and 5.41 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - Determine by direct integration the centroid of...Ch. 5.2 - 5.43 and 5.44 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - 5.43 and 5.44 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - 5.45 and 5.46 A homogeneous wire is bent into the...Ch. 5.2 - 5.45 and 5.46 A homogeneous wire is bent into the...Ch. 5.2 - A homogeneous wire is bent into the shape shown....Ch. 5.2 - 5.48 and 5.49 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 5.49PCh. 5.2 - Determine the centroid of the area shown in terms...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the centroid of the area shown when a =...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 5.52PCh. 5.2 - 5.53 Determine the volume and the surface area of...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the volume and the surface area of the...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 5.55PCh. 5.2 - Prob. 5.56PCh. 5.2 - Verify that the expressions for the volumes of the...Ch. 5.2 - Knowing that two equal caps have been removed from...Ch. 5.2 - Three different drive belt profiles are to be...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the capacity, in liters, of the punch...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the volume and total surface area of the...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the volume and weight of the solid brass...Ch. 5.2 - Determine the total surface area of the solid...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 5.64PCh. 5.2 - The shade for a wall-mounted light is formed from...Ch. 5.3 - 5.66 and 5.67 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 5.3 - 5.66 and 5.67 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.68PCh. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - 5.68 through 5.73 Determine the reactions at the...Ch. 5.3 - Determine (a) the distance a so that the vertical...Ch. 5.3 - Determine (a) the distance a so that the reaction...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.76PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5.77PCh. 5.3 - The beam AB supports two concentrated loads and...Ch. 5.3 - For the beam and loading of Prob. 5.78, determine...Ch. 5.3 - The cross section of a concrete dam is as shown....Ch. 5.3 - The cross section of a concrete dam is as shown....Ch. 5.3 - The dam for a lake is designed to withstand the...Ch. 5.3 - The base of a dam for a lake is designed to resist...Ch. 5.3 - 5.84 An automatic valve consists of a 9 × 9-in....Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.85PCh. 5.3 - The 3 4-m side AB of a tank is hinged at its...Ch. 5.3 - The 3 4-m side of an open tank is hinged at its...Ch. 5.3 - A 0.5 0.8-m gate AB is located at the bottom of a...Ch. 5.3 - A 0.5 0.8-m gate AB is located at the bottom of a...Ch. 5.3 - A 4 2-ft gate is hinged at A and is held in...Ch. 5.3 - Fig. P5.90 5.91 Solve Prob. 5.90 if the gate...Ch. 5.3 - A prismatically shaped gate placed at the end of a...Ch. 5.3 - A prismatically shaped gate placed at the end of a...Ch. 5.3 - A long trough is supported by a continuous hinge...Ch. 5.3 - The square gate AB is held in the position shown...Ch. 5.4 - Consider the composite body shown. Determine (a)...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.97PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.98PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.99PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.100PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.101PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.102PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.103PCh. 5.4 - For the machine element shown, locate the y...Ch. 5.4 - For the machine element shown, locate the x...Ch. 5.4 - 5.106 and 5.107 Locate the center of gravity of...Ch. 5.4 - 5.106 and 5.107 Locate the center of gravity of...Ch. 5.4 - A corner reflector for tracking by radar has two...Ch. 5.4 - A wastebasket, designed to fit in the corner of a...Ch. 5.4 - An elbow for the duct of a ventilating system is...Ch. 5.4 - A window awning is fabricated from sheet metal...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.112PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.113PCh. 5.4 - A thin steel wire with a uniform cross section is...Ch. 5.4 - The frame of a greenhouse is constructed from...Ch. 5.4 - Locate the center of gravity of the figure shown,...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.117PCh. 5.4 - A scratch awl has a plastic handle and a steel...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.117 A bronze bushing is mounted inside a...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.120 A brass collar, of length 2.5 in.,...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.121 The three legs of a small...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.122PCh. 5.4 - Determine by direct integration the values of x...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.124PCh. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.125 Locate the centroid of the volume...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 5.126PCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.127PCh. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.128 Locate the centroid of the volume...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.129 Locate the centroid of the volume...Ch. 5.4 - Show that for a regular pyramid of height h and n...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.131 Determine by direct integration the...Ch. 5.4 - PROBLEM 5.132 The sides and the base of a punch...Ch. 5.4 - Locate the centroid of the section shown, which...Ch. 5.4 - Locate the centroid of the section shown, which...Ch. 5.4 - Determine by direct integration the location of...Ch. 5.4 - Alter grading a lot, a builder places four stakes...Ch. 5 - 5.137 and 5.138 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5 - 5.137 and 5.138 Locate the centroid of the plane...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.139RPCh. 5 - Determine by direct integration the centroid of...Ch. 5 - Determine by direct integration the centroid of...Ch. 5 - The escutcheon (a decorative plate placed on a...Ch. 5 - Determine the reactions at the supports for the...Ch. 5 - A beam is subjected to a linearly distributed...Ch. 5 - A tank is divided into two sections by a 1 1-m...Ch. 5 - Determine the y coordinate of the centroid of the...Ch. 5 - An 8-in.-diameter cylindrical duct and a 4 8-in....Ch. 5 - Three brass plates are brazed to a steel pipe to...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ۳/۱ العنوان O не شكا +91x PU + 96852 A heavy car plunges into a lake during an accident and lands at the bottom of the lake on its wheels as shown in figure. The door is 1.2 m high and I m wide, and the top edge of Deine the hadrostatic force on the Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm. = -20125 750 x2.01arrow_forwardPlot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm.arrow_forwardQ1/ A vertical, circular gate with water on one side as shown. Determine the total resultant force acting on the gate and the location of the center of pressure, use water specific weight 9.81 kN/m³ 1 m 4 marrow_forward
- I need handwritten solution with sketches for eacharrow_forwardGiven answers to be: i) 14.65 kN; 6.16 kN; 8.46 kN ii) 8.63 kN; 9.88 kN iii) Bearing 6315 for B1 & B2, or Bearing 6215 for B1arrow_forward(b) A steel 'hot rolled structural hollow section' column of length 5.75 m, has the cross-section shown in Figure Q.5(b) and supports a load of 750 kN. During service, it is subjected to axial compression loading where one end of the column is effectively restrained in position and direction (fixed) and the other is effectively held in position but not in direction (pinned). i) Given that the steel has a design strength of 275 MN/m², determine the load factor for the structural member based upon the BS5950 design approach using Datasheet Q.5(b). [11] ii) Determine the axial load that can be supported by the column using the Rankine-Gordon formula, given that the yield strength of the material is 280 MN/m² and the constant *a* is 1/30000. [6] 300 600 2-300 mm wide x 5 mm thick plates. Figure Q.5(b) L=5.75m Pinned Fixedarrow_forward
- Q1: For the following force system, find the moments with respect to axes x, y, and zarrow_forwardQ10) Body A weighs 600 lb contact with smooth surfaces at D and E. Determine the tension in the cord and the forces acting on C on member BD, also calculate the reaction at B and F. Cable 6' 3' wwwarrow_forwardHelp ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License