
Mathematical Excursions (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305965584
Author: Richard N. Aufmann, Joanne Lockwood, Richard D. Nation, Daniel K. Clegg
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.2, Problem 9ES
Use trial and error to find two Hamiltonian circuits of different total weights, starting at vertex A in the weighted graph. Compute the total weight of each circuit.
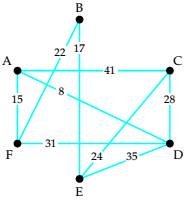
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Determine the volume and the surface area of the shape obtained by rotating the area of the figure about the x-axis and the y-axis.
I'm getting only chatgpt answer that are wrong
Plz don't use chatgpt answer will upvote .
Find xyz cordinates of center of gravity given z = 3.47 in
Chapter 5 Solutions
Mathematical Excursions (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 5.1 - A pen-tracing puzzle is given. See if you can find...Ch. 5.1 - A pen-tracing puzzle is given. See if you can find...Ch. 5.1 - A pen-tracing puzzle is given. See if you can find...Ch. 5.1 - A pen-tracing puzzle is given. See if you can find...Ch. 5.1 - Explain why the following pen-tracing puzzle is...Ch. 5.1 - Transportation An X in the table below indicates a...Ch. 5.1 - Transportation The table below shows the nonstop...Ch. 5.1 - Social Network A group of friends is represented...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 4ESCh. 5.1 - Determine (a) the number of edges in the graph,...
Ch. 5.1 - Determine (a) the number of edges in the graph,...Ch. 5.1 - Determine (a) the number of edges in the graph,...Ch. 5.1 - Determine (a) the number of edges in the graph,...Ch. 5.1 - Determine whether the two graphs are equivalent.Ch. 5.1 - Determine whether the two graphs are equivalent.Ch. 5.1 - Determine whether the two graphs are equivalent.Ch. 5.1 - Determine whether the two graphs are equivalent.Ch. 5.1 - Explain why the following two graphs cannot be...Ch. 5.1 - Label the vertices of the second graph so that it...Ch. 5.1 - (a) determine whether the graph is Eulerian. If it...Ch. 5.1 - (a) determine whether the graph is Eulerian. If it...Ch. 5.1 - (a) determine whether the graph is Eulerian. If it...Ch. 5.1 - (a) determine whether the graph is Eulerian. If it...Ch. 5.1 - (a) determine whether the graph is Eulerian. If it...Ch. 5.1 - (a) determine whether the graph is Eulerian. If it...Ch. 5.1 - (a) determine whether the graph is Eulerian. If it...Ch. 5.1 - (a) determine whether the graph is Eulerian. If it...Ch. 5.1 - Parks in Exercises 23 and 24, a map of a park is...Ch. 5.1 - Parks in Exercises 23 and 24, a map of a park is...Ch. 5.1 - Transportation For the train routes given in...Ch. 5.1 - Transportation For the direct air flights given in...Ch. 5.1 - Pets The diagram below shows the arrangement of a...Ch. 5.1 - Transportation A subway map is shown below. Is it...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 29ESCh. 5.1 - Prob. 30ESCh. 5.1 - Degrees of Separation In the graph below, an edge...Ch. 5.1 - Social Network In the graph below, an edge...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 33ESCh. 5.1 - Travel A map of South America is shown at the...Ch. 5.2 - Continue investigating Hamiltonian circuits in...Ch. 5.2 - Use the greedy algorithm and the weighted graph...Ch. 5.2 - Use the edge-picking algorithm to find a...Ch. 5.2 - Use Dirac's theorem to verify that the graph is...Ch. 5.2 - Use Dirac's theorem to verify that the graph is...Ch. 5.2 - Use Dirac's theorem to verify that the graph is...Ch. 5.2 - Use Dirac's theorem to verify that the graph is...Ch. 5.2 - Transportation For the train routes given in...Ch. 5.2 - Transportation For the direct air flights given in...Ch. 5.2 - Use trial and error to find two Hamiltonian...Ch. 5.2 - Use trial and error to find two Hamiltonian...Ch. 5.2 - Use trial and error to find two Hamiltonian...Ch. 5.2 - Use trial and error to find two Hamiltonian...Ch. 5.2 - Use the greedy algorithm to find a Hamiltonian...Ch. 5.2 - Use the greedy algorithm to find a Hamiltonian...Ch. 5.2 - Use the greedy algorithm to find a Hamiltonian...Ch. 5.2 - Use the greedy algorithm to find a Hamiltonian...Ch. 5.2 - Use the edge-picking algorithm to find a...Ch. 5.2 - Use the edge-picking algorithm to find a...Ch. 5.2 - Use the edge-picking algorithm to find a...Ch. 5.2 - Use the edge-picking algorithm to find a...Ch. 5.2 - Travel A company representative lives in...Ch. 5.2 - Travel A tourist is staying in Toronto, Canada,...Ch. 5.2 - Travel Use the edge-picking algorithm to design a...Ch. 5.2 - Travel Use the edge-picking algorithm to design a...Ch. 5.2 - Travel Nicole wants to tour Asia. She will start...Ch. 5.2 - Travel The prices for traveling between five...Ch. 5.2 - Travel Use the edge-picking algorithm to find a...Ch. 5.2 - Travel Use the edge-picking algorithm to find a...Ch. 5.2 - Route Planning Brian needs to visit the pet store,...Ch. 5.2 - Route Planning A bike messenger needs to deliver...Ch. 5.2 - Scheduling A research company has a large...Ch. 5.2 - Computer Networks A small office wishes to network...Ch. 5.2 - Route Planning A security officer patrolling a...Ch. 5.2 - Route Planning A city engineer needs to inspect...Ch. 5.2 - Draw a connected graph with six vertices that has...Ch. 5.2 - Assign weights to the edges of the following...Ch. 5.3 - The tetrahedron in figure 5.20 consists of four...Ch. 5.3 - The following graph is the projection of one ofthe...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 3EECh. 5.3 - Give a reason why the graph below Cannot be the...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 1ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 2ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 3ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 4ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 6ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 7ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 8ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 9ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 10ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 11ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 12ESCh. 5.3 - Show that the following graph contracts to K5.Ch. 5.3 - Show that the following graph contracts to the...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 15ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 16ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 17ESCh. 5.3 - Count the number of vertices, edges, and faces,...Ch. 5.3 - Count the number of vertices, edges, and faces,...Ch. 5.3 - Count the number of vertices, edges, and faces,...Ch. 5.3 - Count the number of vertices, edges, and faces,...Ch. 5.3 - Count the number of vertices, edges, and faces,...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 23ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 24ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 25ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 26ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 27ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 28ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 29ESCh. 5.3 - Prob. 30ESCh. 5.4 - A one-way road ends at a two-way street. The...Ch. 5.4 - A one-way road intersects a two-way road in a...Ch. 5.4 - A two-way road intersects another two-way road in...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 1ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 2ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 3ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 4ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 5ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 6ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 7ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 8ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 9ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 10ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 11ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 12ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 13ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 14ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 15ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 16ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 17ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 18ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 19ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 20ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 21ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 22ESCh. 5.4 - Scheduling Six different groups of children would...Ch. 5.4 - Scheduling Five different charity organizations...Ch. 5.4 - Scheduling Students in a film class have...Ch. 5.4 - Animal Housing A researcher has discovered six new...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 27ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 28ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 29ESCh. 5.4 - Prob. 30ESCh. 5.4 - Scheduling Edge colorings, as explained in...Ch. 5 - (a) determine the number of edges in the graph,...Ch. 5 - (a) determine the number of edges in the graph,...Ch. 5 - Soccer In the table below, an X indicates teams...Ch. 5 - Each vertex in the graph at the left represents a...Ch. 5 - Determine whether the two graphs are equivalent.Ch. 5 - Determine whether the two graphs are equivalent.Ch. 5 - Find an Euler path if possible, and (b) find an...Ch. 5 - Find an Euler path if possible, and (b) find an...Ch. 5 - Find an Euler path if possible, and (b) find an...Ch. 5 - Prob. 10RECh. 5 - Prob. 11RECh. 5 - Architecture The floor plan of a sculpture gallery...Ch. 5 - Use Dirac's theorem to verify that the graph is...Ch. 5 - Use Dirac's theorem to verify that the graph is...Ch. 5 - Prob. 15RECh. 5 - Prob. 16RECh. 5 - Use the greedy algorithm to find a Hamiltonian...Ch. 5 - Use the greedy algorithm to find a Hamiltonian...Ch. 5 - Use the edge-picking algorithm to find a...Ch. 5 - Use the edge-picking algorithm to find a...Ch. 5 - Efficient Route The distances, in miles, between...Ch. 5 - Computer Networking A small office needs to...Ch. 5 - Prob. 23RECh. 5 - Prob. 24RECh. 5 - Prob. 25RECh. 5 - Prob. 26RECh. 5 - Count the number of vertices, edges, and faces in...Ch. 5 - Count the number of vertices, edges, and faces in...Ch. 5 - Prob. 29RECh. 5 - Prob. 30RECh. 5 - Prob. 31RECh. 5 - Prob. 32RECh. 5 - Prob. 33RECh. 5 - Prob. 34RECh. 5 - Scheduling A company has scheduled a retreat at a...Ch. 5 - Social Network Each vertex in the graph at the...Ch. 5 - Determine whether the following two graphs are...Ch. 5 - Answer the following questions for the graph shown...Ch. 5 - Recreation The illustration below depicts bridges...Ch. 5 - a. What does Dirac's theorem state? Explain how it...Ch. 5 - Low-Cost Route The table below shows the cost of...Ch. 5 - Use the greedy algorithm to find a Hamiltonian...Ch. 5 - Prob. 8TCh. 5 - Answer the following questions for the graph shown...Ch. 5 - Prob. 10TCh. 5 - Prob. 11TCh. 5 - A group of eight friends is planning a vacation in...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, subject and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The graph of f', the derivative of f, is shown in the graph below. If f(-9) = -5, what is the value of f(-1)? y 87 19 6 LO 5 4 3 1 Graph of f' x -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 564%arrow_forwardFind the geometric center of shapearrow_forwardLet S = be a set of k vectors in R^, with karrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305071742
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305658004
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Graph Theory: Euler Paths and Euler Circuits; Author: Mathispower4u;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5M-m62qTR-s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
WALK,TRIAL,CIRCUIT,PATH,CYCLE IN GRAPH THEORY; Author: DIVVELA SRINIVASA RAO;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iYVltZtnAik;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY