
The Heart of Mathematics: An Invitation to Effective Thinking
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781118156599
Author: Edward B. Burger, Michael Starbird
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.1, Problem 22MS
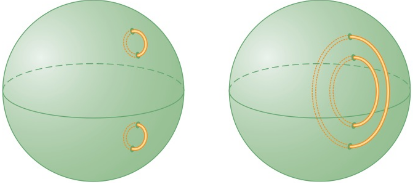
HoIy spheres. Consider the two spheres shown. Each has four holes on its surface. Ropes are looped through the holes in different ways. Is the first sphere with its two rope loops equivalent by distortion to the second sphere with its rope loops?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Calculs Insights
πT
| cos x |³ dx
59
2
2. Consider the ODE
u' = ƒ (u) = u² + r
where r is a parameter that can take the values r = −1, −0.5, -0.1, 0.1. For each value of r:
(a) Sketch ƒ(u) = u² + r and determine the equilibrium points.
(b) Draw the phase line.
(d) Determine the stability of the equilibrium points.
(d) Plot the direction field and some sample solutions,i.e., u(t)
(e) Describe how location of the equilibrium points and their stability change as you increase the
parameter r.
(f) Using the matlab program phaseline.m generate a solution for each value of r and the initial
condition u(0) = 0.9. Print and turn in your result for r = −1. Do not forget to add a figure caption.
(g) In the matlab program phaseline.m set the initial condition to u(0) = 1.1 and simulate the ode
over the time interval t = [0, 10] for different values of r. What happens? Why? You do not need to
turn in a plot for (g), just describe what happens.
The following are suggested designs for group sequential studies. Using PROCSEQDESIGN, provide the following for the design O’Brien Fleming and Pocock.• The critical boundary values for each analysis of the data• The expected sample sizes at each interim analysisAssume the standardized Z score method for calculating boundaries.Investigators are evaluating the success rate of a novel drug for treating a certain type ofbacterial wound infection. Since no existing treatment exists, they have planned a one-armstudy. They wish to test whether the success rate of the drug is better than 50%, whichthey have defined as the null success rate. Preliminary testing has estimated the successrate of the drug at 55%. The investigators are eager to get the drug into production andwould like to plan for 9 interim analyses (10 analyzes in total) of the data. Assume thesignificance level is 5% and power is 90%.Besides, draw a combined boundary plot (OBF, POC, and HP)
Chapter 5 Solutions
The Heart of Mathematics: An Invitation to Effective Thinking
Ch. 5.1 - Describing distortion. What does it mean to say...Ch. 5.1 - Your last sheet. Youre in your bathroom reading...Ch. 5.1 - Rubber polygons. Find a large rubber band and...Ch. 5.1 - Out, out red spot. Remove the red spot from the...Ch. 5.1 - That theta (S). Does there exist a pair of points...Ch. 5.1 - Your ABCs (H). Consider the following letters made...Ch. 5.1 - Half dollar and a straw. Suppose we drill a hole...Ch. 5.1 - Drop them. Is it possible to take off your...Ch. 5.1 - Coffee and doughnuts (H). Is a standard coffee mug...Ch. 5.1 - Lasting ties. Tie a thin rope around a friends...
Ch. 5.1 - Will you spill? (S). Suppose you rest a glass of...Ch. 5.1 - Grabbing the brass ring. Suppose a string attached...Ch. 5.1 - Hair care. Is a regular comb equivalent by...Ch. 5.1 - Three two-folds. Take three pieces of paper and...Ch. 5.1 - Equivalent objects. Group the objects in this...Ch. 5.1 - Clips. Is a paper clip equivalent to a circle? If...Ch. 5.1 - Pennies plus. Consider the two objects pictured...Ch. 5.1 - Starry-eyed. Consider the two stars below. Are...Ch. 5.1 - Learning the ropes. Pictured below are two ropes,...Ch. 5.1 - HoIy spheres. Consider the two spheres shown. Each...Ch. 5.1 - From sphere to torus. The following sequence of...Ch. 5.1 - Half full, half empty. One glass is half filled...Ch. 5.1 - Male versus female. Consider the male and female...Ch. 5.1 - Holey tori. Are these two objects equivalent by...Ch. 5.1 - More holey tori (H). Are these two objects...Ch. 5.1 - Last holey tori. Are these two objects equivalent...Ch. 5.1 - Beyond the holey inner tube. Suppose you are given...Ch. 5.1 - Heavy metal. Carefully examine this picture of a...Ch. 5.1 - The disk and the inner tube (ExH). Suppose you...Ch. 5.1 - Building a torus (S). Suppose you are given a...Ch. 5.1 - Lasso that hole. Consider the first two tori on...Ch. 5.1 - Knots in dougtnuts. We are given two solid...Ch. 5.1 - From knots to glasses (ExH). Take the thickened...Ch. 5.1 - More Jell-O. Suppose we take a cube of Jell-O,...Ch. 5.1 - Fixed spheres (H). We are given two spheres made...Ch. 5.1 - Holes. Is a torus equivalent to a two-holed torus?...Ch. 5.1 - More holes. Is a two-holed torus equivalent to a...Ch. 5.1 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.1 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.1 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.1 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.1 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.2 - One side to every story. What is a Mobius band?Ch. 5.2 - Maybe Mobius. How can you look at a loop of paper...Ch. 5.2 - Singin the blues. Take an ordinary strip of white...Ch. 5.2 - Whos blue now? Take an ordinary strip of white...Ch. 5.2 - Twisted sister. Your sister holds a strip of...Ch. 5.2 - Two twists. Take a strip of paper, put two half...Ch. 5.2 - Two twists again. Take a strip of paper, put two...Ch. 5.2 - Three twists (H). Take a strip of paper, put three...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 11MSCh. 5.2 - Möbius lengths. Use the edge identification...Ch. 5.2 - Squash and cut. Take a Möbius band and squash it...Ch. 5.2 - Two at once. Take two strips of paper and put them...Ch. 5.2 - Parallel Möbius. Is it possible to have two...Ch. 5.2 - Puzzling. Suppose you have a collection of jigsaw...Ch. 5.2 - Möbius triangle. Make a 1-inch-wide Möbius band,...Ch. 5.2 - Thickened Möbius. Imagine a Möbius band...Ch. 5.2 - Thickened faces. How many faces (sides) does a...Ch. 5.2 - Thick then thin. Suppose we take a Môbius band,...Ch. 5.2 - Drawing the band (ExH). Imagine you have a Möbius...Ch. 5.2 - Tubing (H). Suppose we take two Möbius bands and...Ch. 5.2 - Bug out (ExH). Suppose you are a ladybug on the...Ch. 5.2 - Open cider. Consider the Klein bottle half filled...Ch. 5.2 - Rubber Klein (S). Suppose you have a rectangular...Ch. 5.2 - One edge. Using the method on page 347 for...Ch. 5.2 - Twist of fate (S). Using the edge-identification...Ch. 5.2 - Linked together. Using the edge-identification...Ch. 5.2 - Count twists. Using the edge-identification...Ch. 5.2 - Dont cross. Can you draw a curve that does not...Ch. 5.2 - Twisted up (H). Suppose you are given a band of...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 32MSCh. 5.2 - Find a band. Find a Möbius band on the surface of...Ch. 5.2 - Holy Klein. Show that the figure on the left is...Ch. 5.2 - Möbius Möbius. Show that the Klein bottle is two...Ch. 5.2 - Attaching tubes. Consider a Möbius band with two...Ch. 5.2 - Möbius map (H). Using felt-tip color pens that...Ch. 5.2 - Thick slices. Thicken a Môbius band and then...Ch. 5.2 - Bagel slices. If we take a bagel and slice it in...Ch. 5.2 - Gluing and cutting. Consider a rectangular sheet...Ch. 5.2 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.2 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.2 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.2 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.2 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.3 - Knotty start. Which of the followign knots are...Ch. 5.3 - The not knot. What is the unknot?Ch. 5.3 - Crossing count. Count the crossings in each knot...Ch. 5.3 - Tangled up. Is the figure below a knot or a link?Ch. 5.3 - Ringing endorsement. What are the Borromean rings?Ch. 5.3 - Human trefoil. What is the minimum number of...Ch. 5.3 - Human figure eight. What is the minimum number of...Ch. 5.3 - Stick number (ExH). What is the smallest number...Ch. 5.3 - More Möbius. Make a Möbius band with three half...Ch. 5.3 - Slinky (H). Take a Slinky, lengthen one of its...Ch. 5.3 - More slink. Take a Slinky, and this time weave an...Ch. 5.3 - Make it. Use a piece of string or an extenstion...Ch. 5.3 - Knotted (S). Take an unknotted loop. Tie a knot in...Ch. 5.3 - Slip. Take an unknotted loop and put a slip knot...Ch. 5.3 - Dollar link. Take two paper clips and a dollar and...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 18MSCh. 5.3 - Unknotting knots (H). In each of the two knots at...Ch. 5.3 - Alternating. A picture of a knot is alternating...Ch. 5.3 - Making it alternating. Consider the knot on the...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 22MSCh. 5.3 - One cross (H). Prove that any loop with exactly...Ch. 5.3 - Two loops (S). Is there a picture of two linked...Ch. 5.3 - Hold the phone. Disconnect the wire from the phone...Ch. 5.3 - More unknotting knots. In these two knots, find...Ch. 5.3 - Unknotting pictures (S). Suppose you are given a...Ch. 5.3 - Twisted. Suppose we are given a figure consisting...Ch. 5.3 - More alternating. First reread Mindscape 20. For...Ch. 5.3 - Crossing numbers. Suppose you are given pictures...Ch. 5.3 - Lots of crossings. Suppose you arc given a picture...Ch. 5.3 - Torus knots (H). Can you draw a trefoil knot on a...Ch. 5.3 - Two crosses. Prove that any loop with exactly two...Ch. 5.3 - Hoop it up. Show that every knot can be positioned...Ch. 5.3 - The switcheroo. Pictured below is a way of...Ch. 5.3 - 4D washout. Why is the study of knots and links...Ch. 5.3 - Brunnian links (H). Link four loops together in...Ch. 5.3 - Fire drill (ExH). A fire starts in your...Ch. 5.3 - Fixed spheres again. We are given two spheres that...Ch. 5.3 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.3 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.3 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.3 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.3 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.4 - Fixed things first. What does the Brouwer Fixed...Ch. 5.4 - Say cheese. Youre making an open-faced cheese...Ch. 5.4 - Fixed flapjacks. Youre making pancakes and...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 4MSCh. 5.4 - Loop around. What does the Hot Loop Theorem...Ch. 5.4 - Fixed on a square. Does the Brouwer Fixed Point...Ch. 5.4 - Fixed on a circle. Does the Brouwer Fixed Point...Ch. 5.4 - Winding arrows. In each drawing below we have a...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 10MSCh. 5.4 - Prob. 11MSCh. 5.4 - Home heating (H). Prove that there are two points...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 13MSCh. 5.4 - Prob. 14MSCh. 5.4 - Prob. 15MSCh. 5.4 - Lining up (H). Suppose we have two line segments...Ch. 5.4 - A nice temp. Must there be two antipodal points on...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 18MSCh. 5.4 - Diet drill. Suppose someone weighs 160 lbs. and...Ch. 5.4 - Speedy (S). You enter a tollway and are given a...Ch. 5.4 - The cut core. Suppose we have the red and blue...Ch. 5.4 - Fixed without boundary. Do you think that the...Ch. 5.4 - Take a hike (ExH). A hiker decides to climb up...Ch. 5.4 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.4 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.4 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.4 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...Ch. 5.4 - Here we celebrate the power of algebra as a...
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Interpreting a Decision In Exercises 43–48, determine whether the claim represents the null hypothesis or the a...
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
A Bloomberg Businessweek subscriber study asked, In the past 12 months, when travelling for business, what type...
STATISTICS F/BUSINESS+ECONOMICS-TEXT
CHECK POINT I You deposit $1000 in a saving account at a bank that has a rate of 4%. a. Find the amount, A, of ...
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Explain the meaning of the term “statistically significant difference” in statistics terminology.
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Infinite limits at infinity Determine the following limits. 19. limx(3x129x7)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, subject and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. Solve the system of equations and express your solution using vectors. 2x1 +5x2+x3 + 3x4 = 9 -x2+x3 + x4 = 1 -x1-6x2+3x3 + 2x4 = -1arrow_forward3. Simplify the matrix expression A(A-B) - (A+B)B-2(A - B)2 + (A + B) 2arrow_forward[2 pts] 1. Let A = [. 1 -1 0 -343 and B = 05 5 -7 304 Compute (7A - 3B) - 4(2A - B).arrow_forward
- 20 2. Let A = = [ -2 0 1 3 ] and B = 2 3 -1 2 For each of the following, calculate the product or indicate why it is undefined: (a) AB (b) BAarrow_forwardTrue or False and whyarrow_forward10 5 Obtain by multiplying matrices the composite coordinate transformation of two transformations, first x' = (x + y√√2+2)/2 y' = z' (x√√2-2√2)/2 z = (-x+y√√2-2)/2 followed by x" = (x'√√2+z'√√2)/2 y" = (-x'y'√√2+2')/2 z" = (x'y'√√2-2')/2.arrow_forward
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forward4 The plane 2x+3y+ 6z = 6 intersects the coordinate axes at P, Q, and R, forming a triangle. Draw a figure and identify the three points on it. Also find vectors PQ and PR. Write a vector formula for the area of the triangle PQR and find its value.arrow_forward3.1 Limits 1. If lim f(x)=-6 and lim f(x)=5, then lim f(x). Explain your choice. x+3° x+3* x+3 (a) Is 5 (c) Does not exist (b) is 6 (d) is infinitearrow_forward
- 1 pts Let F and G be vector fields such that ▼ × F(0, 0, 0) = (0.76, -9.78, 3.29), G(0, 0, 0) = (−3.99, 6.15, 2.94), and G is irrotational. Then sin(5V (F × G)) at (0, 0, 0) is Question 1 -0.246 0.072 -0.934 0.478 -0.914 -0.855 0.710 0.262 .arrow_forwardAnswer the number questions with the following answers +/- 2 sqrt(2) +/- i sqrt(6) (-3 +/-3 i sqrt(3))/4 +/-1 +/- sqrt(6) +/- 2/3 sqrt(3) 4 -3 +/- 3 i sqrt(3)arrow_forward2. Answer the following questions. (A) [50%] Given the vector field F(x, y, z) = (x²y, e", yz²), verify the differential identity Vx (VF) V(V •F) - V²F (B) [50%] Remark. You are confined to use the differential identities. Let u and v be scalar fields, and F be a vector field given by F = (Vu) x (Vv) (i) Show that F is solenoidal (or incompressible). (ii) Show that G = (uvv – vVu) is a vector potential for F.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305658004
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...
Algebra
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Area Between The Curve Problem No 1 - Applications Of Definite Integration - Diploma Maths II; Author: Ekeeda;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q3ZU0GnGaxA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY