![OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months)](https://www.bartleby.com/isbn_cover_images/9781305863170/9781305863170_largeCoverImage.jpg)
Concept explainers
The following figure shows three 1.00-L bulbs connected by valves. Each bulb contains argon gas with amounts proportional to the number of circles pictorially represented in the chamber. All three bulbs are maintained at the same temperature. Unless stated otherwise, assume that the valves connecting the bulbs are closed and seal the gases in their respective chambers. Assume also that the volume between each bulb is negligible.
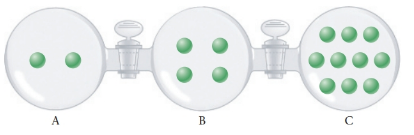
(a) Which bulb has the highest pressure?
(b) If the pressure in bulb A is 0.500 atm, what is the pressure in bulb C?
(c) If the pressure in bulb A is 0.500 atm, what is the total pressure?
(d) If the pressure in bulb A is 0.500 arm, and the valve between bulbs A and B is opened, redraw the figure shown above to accurately represent the gas atoms in all three bulbs. What is
(e) Follow the instructions of part (d) but now open only the valve between bulbs B and C.
(a)
Interpretation:
The bulb with the highest pressure needs to be identified based on the given description.
Concept introduction:
The ideal gas equation is a thermodynamic equation of state which relates the pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n) and temperature (T) of an ideal gas through the following expression:
where R is the universal gas constant = 0.0821 L.atm/mol-K
Answer to Problem 86QAP
Bulb C has the highest pressure.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Volume (V) of bulb A = B = C = 1.0 L
Temperature (T) of bulb A = B = C
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in A = 2
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in B = 4
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in C = 10
Calculation:
Based on equation (1), the pressure (P) in each of the bulbs can de deduced by substituting the values of n in bulbs A, B and C and volume, V = 1.0 L
Now, pressure (P) is directly proportional to the number of moles (n). Therefore, under constant temperature, bulb C will have the highest pressure.
(b)
Interpretation:
The pressure in bulb C needs to be deduced if the pressure in bulb A is 0.500 atm.
Concept introduction:
The ideal gas equation is a thermodynamic equation of state which relates the pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n) and temperature (T) of an ideal gas through the following expression:
where R is the universal gas constant = 0.0821 L.atm/mol-K
Answer to Problem 86QAP
Pressure in Bulb C is 2.5 atm
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Volume (V) of bulb A = B = C = 1.0 L
Temperature (T) of bulb A = B = C
Pressure (P) in bulb A = 0.500 atm
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in A = 2
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in C = 10
Calculation:
Based on equation (1), the pressure (P) in bulbs A and C can be deduced by substituting the given values of n, V and P under constant T
(c)
Interpretation:
The total pressure needs to be deduced if the pressure in bulb A is 0.500 atm.
Concept introduction:
The ideal gas equation is a thermodynamic equation of state which relates the pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n) and temperature (T) of an ideal gas through the following expression:
where R is the universal gas constant = 0.0821 L.atm/mol-K
As per Dalton’s law, the total pressure exerted by a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of the individual gases.
Answer to Problem 86QAP
Total pressure = 4.00 atm
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Volume (V) of bulb A = B = C = 1.0 L
Temperature (T) of bulb A = B = C
Pressure (P) in bulb A = 0.500 atm
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in A = 2
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in B = 4
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in C = 10
Calculation:
Based on equation (1), the pressure (P) in bulbs A and B can be deduced by substituting the given values of n, V and P under constant T
(d)
Interpretation:
The total pressure needs to be deduced after the valve between A and B is opened.
Concept introduction:
The ideal gas equation is a thermodynamic equation of state which relates the pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n) and temperature (T) of an ideal gas through the following expression:
where R is the universal gas constant = 0.0821 L.atm/mol-K
As per Dalton’s law, the total pressure exerted by a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of the individual gases.
Answer to Problem 86QAP
Total pressure after the valve between A and B is opened in 8.50 atm
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Volume (V) of bulb A = B = C = 1.0 L
Temperature (T) of bulb A = B = C
Pressure (P) in bulb A = 0.500 atm
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in A = 2
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in B = 4
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in C = 10
Calculation:
When the valve between A and B is opened the Ar gas will diffuse from the region of high pressure i.e. bulb B to A until equilibrium is established.
Now the total number of moles (atoms) of Ar = 2 + 4 = 6. The final pressure in each bulb will be due to 6 moles (atoms) of Ar
Step 1: Calculate the final pressure in bulb A after mixing:
The initial pressure in bulb A = Pi = 0.500 atm
Initial moles of Ar gas in A = ni = 2
Final moles in A = nf = 6
The final pressure in bulb A = Pf
Under constant V and T, the ratio of the initial and final pressures would be:
Step 2: Calculate the final pressure in bulb B after mixing:
The initial pressure in bulb B = Pi = 1.50 atm
Initial moles of Ar gas in A = ni = 2
Final moles in A = nf = 6
The final pressure in bulb A = Pf
Under constant V and T, the ratio of the initial and final pressures would be:
Step 3: Calculate the total pressure after mixing:
The total pressure after the valve between A and B is opened is higher than that when the valve is closed.
(d)
Interpretation:
The total pressure needs to be deduced after the valve between B and C is opened.
Concept introduction:
The ideal gas equation is a thermodynamic equation of state which relates the pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n) and temperature (T) of an ideal gas through the following expression:
where R is the universal gas constant = 0.0821 L.atm/mol-K
As per Dalton’s law, the total pressure exerted by a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of the individual gases.
Answer to Problem 86QAP
Total pressure after the valve between B and C is opened in 9.25 atm
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Volume (V) of bulb A = B = C = 1.0 L
Temperature (T) of bulb A = B = C
Pressure (P) in bulb A = 0.500 atm
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in A = 2
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in B = 4
Number of moles (n) of Ar gas in C = 10
Calculation:
When the valve between B and C is opened the Ar gas will diffuse from the region of high pressure i.e. bulb C to B until equilibrium is established.
Now the total number of moles (atoms) of Ar = 4 + 10 = 14. The final pressure in each bulb will be due to 14 moles (atoms) of Ar
Step 1: Calculate the final pressure in bulb B after mixing:
The initial pressure in bulb B = Pi = 1.50 atm
Initial moles of Ar gas in B = ni = 4
Final moles in A = nf = 10
The final pressure in bulb B = Pf
Under constant V and T, the ratio of the initial and final pressures would be:
Step 2: Calculate the final pressure in bulb C after mixing:
The initial pressure in bulb C = Pi = 2.50 atm
Initial moles of Ar gas in C = ni = 10
Final moles in C = nf = 14
The final pressure in bulb A = Pf
Under constant V and T, the ratio of the initial and final pressures would be:
Step 3: Calculate the total pressure after mixing:
The total pressure after the valve between B and C is opened is higher than that when the valve is closed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months)
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solution and correct answerarrow_forwardH R Part: 1/2 :CI: is a/an electrophile Part 2 of 2 Draw the skeletal structure of the product(s) for the Lewis acid-base reaction. Include lone pairs and formal charges (if applicable) on the structures. 4-7: H ö- H Skip Part Check X :C1: $ % L Fi Click and drag to start drawing a structure. MacBook Pro & ㅁ x G 0: P Add or increase positive formal cha Save For Later Submit ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forwardDraw the friedel-crafts acylation mechanism of m-Xylenearrow_forward
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward1. Base on this experimental results, how do you know that the product which you are turning in is methyl 3-nitrobenzoate(meta substituted product ) rather than either of the other two products? 2. What observation suggests that at least a small amount of one or both of the other two isomers are in the mother liquor?arrow_forwardExplain Huckel's rule.arrow_forward
- here is my question can u help me please!arrow_forwardSo I need help with understanding how to solve these types of problems. I'm very confused on how to do them and what it is exactly, bonds and so forth that I'm drawing. Can you please help me with this and thank you very much!arrow_forwardSo I need help with this problem, can you help me please and thank you!arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





