
Concept explainers
(a)
If the crate resting on the bed of a decelerating truck would slide during the braking period.
Answer to Problem 77QAP
The crate will not slide, since the acceleration it experiences due to the truck's deceleration is less than the acceleration it experiences due to the force of static friction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of the crate
Initial velocity of the truck
Final velocity of the truck
Time during which the truck comes to a stop
Coefficient of static friction between the truck and the crate
Formula used:
To find if the crate would slide or not, a free body diagram is drawn for the crate and the force equations for equilibrium and for motion of the crate are determined.
The free body diagram for the crate is shown below:
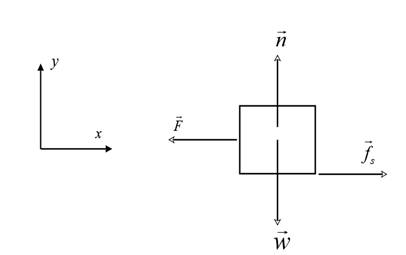
The weight of the block
The block is in equilibrium along the vertical ( y ) direction.
Therefore,
Since,
Therefore,
If
If the force of friction produces an acceleration,
Write an expression for the acceleration due to the force of friction using equations (1) and (2).
The expression for the acceleration produced by the truck is given by,
Calculation:
Calculate the acceleration
Express the initial velocity of the crate in m/s.
Calculate the acceleration a experienced by the crate due to the truck's decoration by substituting the values of the variables in equation (4).
This acceleration acts along the −x direction.
The crate slides if a >af.
Conclusion:
It can be seen that the acceleration in the +x direction is 6.419 m/s2 and that along the −x direction is 1.158 m/s2. Since
(b)
The minimum stopping time for the truck, that prevents the crate from sliding.
Answer to Problem 77QAP
For the crate to not slide on the bed of the truck, the minimum stopping time of the truck is 2.16 s.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Acceleration produced by the
Initial velocity of the truck
Final velocity of the truck
Formula used:
The crate will just remain in equilibrium, if the acceleration acting on it along the −x direction due to the truck's deceleration is equal to the acceleration along the +x direction due to the force of friction.
Calculation:
Rewrite the expression for
Substitute the values of the variables in the equation and solve for
Conclusion:
Thus, for the crate to not slide on the bed of the truck, the minimum stopping time of the truck is 2.16 s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS-ACHIEVE AC (1-TERM)
- A man slides two boxes up a slope. The two boxes A and B have a mass of 75 kg and 50 kg, respectively. (a) Draw the free body diagram (FBD) of the two crates. (b) Determine the tension in the cable that the man must exert to cause imminent movement from rest of the two boxes. Static friction coefficient USA = 0.25 HSB = 0.35 Kinetic friction coefficient HkA = 0.20 HkB = 0.25 M₁ = 75 kg MB = 50 kg P 35° Figure 3 B 200arrow_forwardA golf ball is struck with a velocity of 20 m/s at point A as shown below (Figure 4). (a) Determine the distance "d" and the time of flight from A to B; (b) Determine the magnitude and the direction of the speed at which the ball strikes the ground at B. 10° V₁ = 20m/s 35º Figure 4 d Barrow_forwardThe rectangular loop of wire shown in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 0.18 g per centimeter of length and is pivoted about side ab on a frictionless axis. The current in the wire is 8.5 A in the direction shown. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane. Find the direction of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane.arrow_forward
- A particle with a charge of − 5.20 nC is moving in a uniform magnetic field of (B→=−( 1.22 T )k^. The magnetic force on the particle is measured to be (F→=−( 3.50×10−7 N )i^+( 7.60×10−7 N )j^. Calculate the y and z component of the velocity of the particle.arrow_forwardneed answer asap please thank youarrow_forward3. a. Determine the potential difference between points A and B. b. Why does point A have a higher potential energy? Q = +1.0 C 3.2 cm 4.8 cm Aarrow_forward
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





