
Concept explainers
Starting from rest, a rectangular toy block with mass 300 g slides in 1.30 s all the way across a table 1.20 m in length that Zak has tilted at an angle of 42.0° to the horizontal. a. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the toy block? b. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table? c. What are the magnitude and direction of the friction force acting on the block? d. What is the speed of the block when it is at the end of the table, having slid a distance of 1.20 m?
(a)
Find the magnitude of acceleration of the toy block.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The magnitude of acceleration of the toy block is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for acceleration.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of acceleration of the toy block is
(b)
Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and table.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and table is
Explanation of Solution
From the given condition the free body diagram is given below.
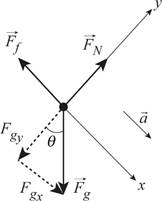
Here,
Here,
Write the equation for friction force.
Here,
Substitute equation II and III in equation IV.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and table is
(c)
Find the direction and magnitude of friction acting on the block.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The friction acting on the block is directed upward and its magnitude is
Explanation of Solution
Substitute equation III in IV.
Conclusion:
Substitute
The friction force is directed up in the incline.
Therefore, the friction acting on the block is directed upward and its magnitude is
(d)
Find the speed of the block when it is at the end of the table.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The speed of the block when it is at the end of the table is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation of motion.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the speed of the block when it is at the end of the table is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- 10. Imagine you have a system in which you have 54 grams of ice. You can melt this ice and then vaporize it all at 0 C. The melting and vaporization are done reversibly into a balloon held at a pressure of 0.250 bar. Here are some facts about water you may wish to know. The density of liquid water at 0 C is 1 g/cm³. The density of ice at 0 C is 0.917 g/cm³. The enthalpy of vaporization of liquid water is 2.496 kJ/gram and the enthalpy of fusion of solid water is 333.55 J/gram.arrow_forwardConsider 1 mole of supercooled water at -10°C. Calculate the entropy change of the water when the supercooled water freezes at -10°C and 1 atm. Useful data: Cp (ice) = 38 J mol-1 K-1 Cp (water) 75J mol −1 K -1 Afus H (0°C) 6026 J mol −1 Assume Cp (ice) and Cp (water) to be independent of temperature.arrow_forwardThe molar enthalpy of vaporization of benzene at its normal boiling point (80.09°C) is 30.72 kJ/mol. Assuming that AvapH and AvapS stay constant at their values at 80.09°C, calculate the value of AvapG at 75.0°C, 80.09°C, and 85.0°C. Hint: Remember that the liquid and vapor phases will be in equilibrium at the normal boiling point.arrow_forward
- 3. The entropy of an ideal gas is S = Nkg In V. Entropy is a state function rather than a path function, and in this problem, you will show an example of the entropy change for an ideal gas being the same when you go between the same two states by two different pathways. A. Express ASV = S2 (V2) - S₁(V1), the change in entropy upon changing the volume from V₁to V2, at fixed particle number N and energy, U. B. Express ASN = S₂(N₂) - S₁ (N₁), the change in entropy upon changing the particle number from N₁ to N2, at fixed volume V and energy U. C. Write an expression for the entropy change, AS, for a two-step process (V₁, N₁) → (V2, N₁) → (V2, N₂) in which the volume changes first at fixed particle number, then the particle number changes at fixed volume. Again, assume energy is constant.arrow_forwardPlease don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forward6. We used the constant volume heat capacity, Cv, when we talked about thermodynamic cycles. It acts as a proportionality constant between energy and temperature: dU = C₁dT. You can also define a heat capacity for constant pressure processes, Cp. You can think of enthalpy playing a similar role to energy, but for constant pressure processes δαρ C = (37) - Sup Ср ат P = ат Starting from the definition of enthalpy, H = U + PV, find the relationship between Cy and Cp for an ideal gas.arrow_forward
- Pure membranes of dipalmitoyl lecithin phospholipids are models of biological membranes. They melt = 41°C. Reversible melting experiments indicate that at Tm AHm=37.7 kJ mol-1. Calculate: A. The entropy of melting, ASm- B. The Gibbs free energy of melting, AGm- C. Does the membrane become more or less ordered upon melting? D. There are 32 rotatable CH2 CH2 bonds in each molecule that can rotate more freely if the membrane melts. What is the increase in multiplicity on melting a mole of bonds?arrow_forward5. Heat capacity often has a temperature dependence for real molecules, particularly if you go over a large temperature range. The heat capacity for liquid n-butane can be fit to the equation Cp(T) = a + bT where a = 100 J K₁₁ mol¹ and b = 0.1067 J K² mol¹ from its freezing point (T = 140 K) to its boiling point (T₁ = 270 K). A. Compute AH for heating butane from 170 K to 270 K. B. Compute AS for the same temperature range.arrow_forward4. How much energy must be transferred as heat to cause the quasi-static isothermal expansion of one mole of an ideal gas at 300 K from PA = 1 bar to PB = 0.5 bar? A. What is VA? B. What is VB? C. What is AU for the process? D. What is AH for the process? E. What is AS for the process?arrow_forward
- 1. The diagram shows the tube used in the Thomson experiment. a. State the KE of the electrons. b. Draw the path of the electron beam in the gravitational field of the earth. C. If the electric field directed upwards, deduce the direction of the magnetic field so it would be possible to balance the forces. electron gun 1KVarrow_forwardas a hiker in glacier national park, you need to keep the bears from getting at your food supply. You find a campground that is near an outcropping of ice. Part of the outcropping forms a feta=51.5* slopeup that leads to a verticle cliff. You decide that this is an idea place to hang your food supply out of bear reach. You put all of your food into a burlap sack, tie a rope to the sack, and then tie a bag full of rocks to the other end of the rope to act as an anchor. You currently have 18.5 kg of food left for the rest of your trip, so you put 18.5 kg of rocks in the anchor bag to balance it out. what happens when you lower the food bag over the edge and let go of the anchor bag? Determine the acceleration magnitude a of the two-bag system when you let go of the anchor bag?arrow_forward2. A thin Nichrome wire is used in an experiment to test Ohm's law using a power supply ranging from 0 to 12 V in steps of 2 V. Why isn't the graph of I vs V linear? 1. Nichrome wire does obey Ohm's law. Explain how that can that be true given the results abovearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





