
Concept explainers
A real estate agent is considering changing her cell phone plan. There are three plans to choose from, all of which involve a monthly service charge of $20. Plan A has a cost of $.45 a minute for daytime calls and $.20 a minute for evening calls. Plan B has a charge of $.55 a minute for daytime calls and $.15 a minute for evening calls. Plan C has a flat rate of $80 with 200 minutes of calls allowed per month and a charge of $.40 per minute beyond that, day or evening.
a. Determine that total charge under each plan for this case: 120 minutes of day calls and 40 minutes of evening calls in a month.
b. Prepare a graph that shows total monthly cost for each plan versus daytime call minutes.
c. If the agent will use the service for daytime calls, over what range of call minutes will each plan be optimal?
d. Suppose that the agent expects both daytime and evening calls. At what point (i.e., percentage of call minutes for daytime calls) would she be indifferent between plans A and B?
a)
To determine: The total charge of each plan for 120 minutes of day calls and 40 minutes of evening calls.
Introduction: Capacity planning is the process of planning the required production output based on the requirement or the demand that is predicted.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A real estate is considered changing her cell phone plan which incurs a monthly service charge of $20. There are three plans available.
Plan A: $0.45 per minute for a day calls and $0.20 per minute for evening calls.
Plan B: $0.55 per minute for a day calls and $0.15 per minute for evening calls.
Plan C: $80 for allowed 200 calls per month and $0.40 per minutes beyond that irrespective of day or evening
Calculate the total cost for Plan A:
It is calculated by adding the monthly service charge, the multiple of cost per minute of day calls and total minutes given for day calls, and the multiple of cost per minute of evening calls and total minutes given for evening calls.
Hence, the total cost for Plan A is $82.
Calculate the total cost for Plan B:
It is calculated by adding the monthly service charge, the multiple of cost per minute of day calls and total minutes given for day calls, and the multiple of cost per minute of evening calls and total minutes given for evening calls.
Hence, the total cost for Plan B is $92.
Calculate the total cost for Plan C:
It is calculated by adding monthly service charge, call cost for the allowed 200 minutes, and the multiple of call minutes beyond 200 and the cost per minutes. The total call minutes is 160 (120+40). As it does not exceed 200 minutes, there would 0 remaining minutes.
Hence, the total cost for Plan C is $100.
b)
To prepare: A graph for monthly charge for each plan versus day time minutes.
Introduction: Capacity planning is the process of planning the required production output based on the requirement or the demand that is predicted.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A real estate is considered changing her cellphone plan which incurs a monthly service charge of $20. There are three plans available.
Plan A: $0.45 per minute for a day calls and $0.20 per minute for evening calls.
Plan B: $0.55 per minute for a day calls and $0.15 per minute for evening calls.
Plan C: $80 for allowed 200 calls per month and $0.40 per minutes beyond that irrespective of day or evening
Prepare a graph of monthly charge for each plan versus day time minutes:
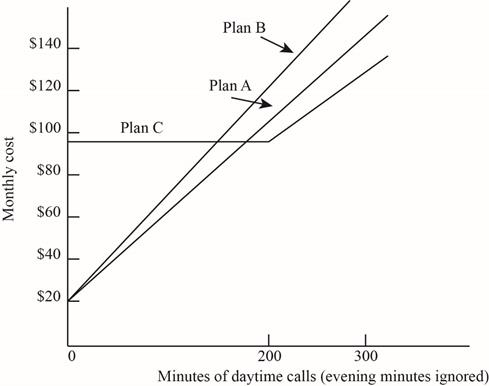
c)
To determine: The optimal call minutes for each plan if the agent would use only day calls.
Introduction: Capacity planning is the process of planning the required production output based on the requirement or the demand that is predicted.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A real estate is considered changing her cellphone plan which incurs a monthly service charge of $20. There are three plans available.
Plan A: $0.45 per minute for a day calls and $0.20 per minute for evening calls.
Plan B: $0.55 per minute for a day calls and $0.15 per minute for evening calls.
Plan C: $80 for allowed 200 calls per month and $0.40 per minutes beyond that irrespective of day or evening
Determine the optimal call minutes for each plan if the agent would use only day calls:
D refers to day time calls
The volume of Plan B is more than Plan A. Hence, it should be omitted, as it would obvious have high cost.
Calculate the total cost for Plan C:
It is calculated by adding monthly service charge, call cost for the allowed 200 minutes, and the multiple of call minutes beyond 200 and the cost per minutes. The total call minutes is 160 (120+40). As it does not exceed 200 minutes, there would 0 remaining minutes.
Hence, the total cost for Plan C is $100.
Determined the value of D in the equation of Plan A by comparing the equation with the total cost of Plan C:
The equation of Plan A (considering the day calls) should be compared with the total cost of Plan C.
Hence, the day call minutes are 177.78 minutes.
Conclusion: Plan A would be optimal when the day call minutes are less than 177.78 minutes and Plan C would be optional when it exceeds up to 200 minutes.
d)
To determine: The percentage of call minutes would be indifferent between Plan A and Plan B if the agent would both day calls and evening calls.
Introduction: Capacity planning is the process of planning the required production output based on the requirement or the demand that is predicted.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A real estate is considered changing her cellphone plan which incurs a monthly service charge of $20. There are three plans available.
Plan A: $0.45 per minute for a day calls and $0.20 per minute for evening calls.
Plan B: $0.55 per minute for a day calls and $0.15 per minute for evening calls.
Plan C: $80 for allowed 200 calls per month and $0.40 per minutes beyond that irrespective of day or evening
Determine the percentage of call minutes would be indifferent between Plan A and Plan B if the agent would both day calls and evening calls:
D refers to day time calls
E refers to evening calls
Compare the equations to solve D:
The equation of Plan A and Plan B considering both day and evening calls should be compared to determine the value of D.
It should that day calls are half of the evening calls.
For example: If E=100 minutes,
It states the following equations:
Hence, at 33.33% of total call time, the agent would be indifferent between the plans A and B.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- Solve the following Question 1. How do volume and variety affect the process selection and layout types? Discuss 2. How is the human resource aspect important to operation function? Discuss 3. Discuss the supply network design and its impact on the overall performance of the organization.arrow_forwardHelp with question?arrow_forwardWhat are some good examples of bullet points on a resume for a Christian Elementary School?arrow_forward
- What is an example of a cover letter for a Christian School Long-Term Substitute Teaching position?arrow_forwardThe supply chain is a conventional notion, but organizations are only really interested in making products that they can sell to customers. Provided they have reliable supplies of materials and reasonable transport for finished products, logistics is irrelevant. Do you think this is true? If yes, explain, and if no, clearly explain as well.arrow_forwardworking as a program operations managerarrow_forward
- 12 X1, X230 1 x =0x2 write the Following linear Programming model by 1- general Form Canonical Forms Canonical formY 2- Standard Form Max Z=35X+ 4 X 2 +6 X3 ST. X+2X2-5x3 = 40 3X, + 6X2 + 7x 3 = 30 7x, +lox2 x3 = 50 X3 X 2 X 3 <0arrow_forwarda/ a Minimum cost assign each worker for one job at Jobs J1 12 33 WI 2 4 6 W2 5 W3 5 33 6 7arrow_forwardوبة واضافة هذه القيمة الى القيم Ex: Assign each job for each worker at minimum total Cost عمل لكل عامل وبأقل كلفة ممكنة obs الأعمال Workors العمال J1 J2 J3 J4 W₁ 15 13 14 12 W2 11 12 15 13 W3 13 12 10 11 W4 15 17 14 16arrow_forward
- The average completion time (flow time) for the sequence developed using the FCFS rule = 11.75 days (round your response to two decimal places). The percentage utilization for the sequence developed using the FCFS rule = 42.55 % (enter your response as a percentage rounded to two decimal places). b) Using the SPT (shortest processing time) decision rule for sequencing the jobs, the order is (to resolve a tie, use the order in which the jobs were received): An Alabama lumberyard has four jobs on order, as shown in the following table. Today is day 205 on the yard's schedule. In what sequence would the jobs be ranked according to the decision rules on the left: Job Due Date A 212 B 209 C 208 D 210 Duration (days) 6 3 3 8 Sequence 1 Job B 2 3 4 A D The average tardiness (job lateness) for the sequence developed using the SPT rule = 5.00 days (round your response to two decimal places). The average completion time (flow time) for the sequence developed using the SPT rule = 10.25 days…arrow_forwardWith the aid of examples, fully discuss any five (5) political tactics used in organisations.arrow_forwarda. With the aid of examples, define discrimination. b. Fully discuss any four (4) types of discrimination in the workplacearrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
