1 Physics And Measurement 2 Motion In One Dimension 3 Vectors 4 Motion In Two Dimensions 5 The Laws Of Motion 6 Circular Motion And Other Applications Of Newton's Laws 7 Energy Of A System 8 Conservation Of Energy 9 Linear Momentum And Collisions 10 Rotation Of A Rigid Object About A Fixed Axis 11 Angular Momentum 12 Static Equilibrium And Elasticity 13 Universal Gravitation 14 Fluid Mechanics 15 Oscillatory Motion 16 Wave Motion 17 Sound Waves 18 Superposition And Standing Waves 19 Temperature 20 The First Law Of Thermodynamics 21 The Kinetic Theory Of Gases 22 Heat Engines, Entropy, And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics 23 Electric Fields 24 Gauss’s Law 25 Electric Potential 26 Capacitance And Dielectrics 27 Current And Resistance 28 Direct-current Circuits 29 Magnetic Fields 30 Sources Of The Magnetic Field 31 Faraday's Law 32 Inductance 33 Alternating-current Circuits 34 Electromagnetic Waves 35 The Nature Of Light And The Principles Of Ray Optics 36 Image Fonnation 37 Wave Optics 38 Diffraction Patterns And Polarization 39 Relativity 40 Introduction To Quantum Physics 41 Quantum Mechanics 42 Atomic Physics 43 Molecules And Solids 44 Nuclear Structure 45 Applications Of Nuclear Physics 46 Particle Physics And Cosmology expand_more
5.1 The Concept Of Force 5.2 Newton's First Law And Inertial Frames 5.3 Mass 5.4 Newton's Second Law 5.5 The Gravitational Force And Weight 5.6 Newton's Third Law 5.7 Analysis Models Using Newton's Second Law 5.8 Force Of Friction Chapter Questions expand_more
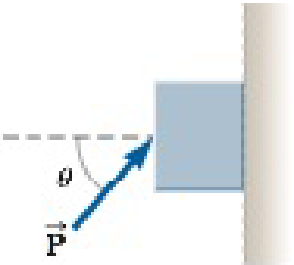
Problem 1OQ: The driver of a speeding empty truck slams on the brakes and skids to a stop through a distance d.... Problem 2OQ: In Figure OQ5.2, a locomotive has broken through the wall of a train station. During the collision,... Problem 3OQ Problem 4OQ Problem 5OQ Problem 6OQ: The manager of a department store is pushing horizontally with a force of magnitude 200 N on a box... Problem 7OQ: Two objects are connected by a string that passes over a frictionless pulley as in Figure 5.14a,... Problem 8OQ Problem 9OQ: A truck loaded with sand accelerates along a highway. The driving force on the truck remains... Problem 10OQ: A large crate of mass m is place on the flatbed of a truck but not tied down. As the truck... Problem 11OQ: If an object is in equilibrium, which of the following statements is not true? (a) The speed of the... Problem 12OQ: A crate remains stationary after it has been placed on a ramp inclined at an angle with the... Problem 13OQ: An object of mass m moves with acceleration a down a rough incline. Which of the following forces... Problem 1CQ Problem 2CQ: Your hands are wet, and the restroom towel dispenser is empty. What do you do to get drops of water... Problem 3CQ: In the motion picture It Happened One Night (Columbia Pictures, 1934), Clark Gable is standing... Problem 4CQ: If a car is traveling due westward with a constant speed of 20 m/s, what is the resultant force... Problem 5CQ: A passenger sitting in the rear of a bus claims that she was injured when the driver slammed on the... Problem 6CQ: A child tosses a ball straight up. She says that the ball is moving away from her hand because the... Problem 7CQ: A person holds a ball in her hand. (a) Identify all the external forces acting on the ball and the... Problem 8CQ Problem 9CQ Problem 10CQ: Twenty people participate in a tug-of-war. The two teams of ten people are so evenly matched that... Problem 11CQ Problem 12CQ Problem 13CQ: A weightlifter stands on a bathroom scale. He pumps a barbell up and down. What happens to the... Problem 14CQ Problem 15CQ: Suppose you are driving a classic car. Why should you avoid slamming on your brakes when you want to... Problem 16CQ Problem 17CQ: Describe two examples in which the force of friction exerted on an object is in the direction of... Problem 18CQ: The mayor of a city reprimands some city employees because they will not remove the obvious sags... Problem 19CQ: Give reasons for the answers to each of the following questions: (a) Can a normal force be... Problem 20CQ Problem 21CQ: Identify actionreaction pairs in the following situations: (a) a man takes a step (b) a snowball... Problem 22CQ Problem 23CQ Problem 1P: A certain orthodontist uses a wire brace to align a patients crooked tooth as in Figure P5.1. The... Problem 2P: If a man weighs 900 N on the Earth, what would he weigh on Jupiter, where the free-fall acceleration... Problem 3P: A 3.00-kg object undergoes an acceleration given by a=(2.00i+5.00j)m/s2. Find (a) the resultant... Problem 4P Problem 5P Problem 6P: The average speed of a nitrogen molecule in air is about 6.70 102 m/s, and its mass is 4.68 1026... Problem 7P Problem 8P Problem 9P: Review. The gravitational force exerted on a baseball is 2.21 N down. A pitcher throws the ball... Problem 10P: Review. The gravitational force exerted on a baseball is Fgj. A pitcher throws the ball with... Problem 11P: Review. An electron of mass 9. 11 1031 kg has an initial speed of 3.00 105 m/s. It travels in a... Problem 12P Problem 13P: One or more external forces, large enough to be easily measured, are exerted on each object enclosed... Problem 14P: A brick of mass M has been placed on a rubber cushion of mass m. Together they are sliding to the... Problem 15P: Two forces, F1=(6.00i4.00j)N and F2=(3.00i+7.00j)N, act on a particle of mass 2.00 kg that is... Problem 16P Problem 17P Problem 18P Problem 19P Problem 20P: You stand on the seat of a chair and then hop off. (a) During the time interval you are in flight... Problem 21P Problem 22P: Review. Three forces acting on an object are given by F1=(2.00i2.00j)N, and F1=(5.00i3.00j)N, and... Problem 23P Problem 24P Problem 25P: Review. Figure P5.15 shows a worker poling a boata very efficient mode of transportation across a... Problem 26P: An iron bolt of mass 65.0 g hangs from a string 35.7 cm long. The top end of the string is fixed.... Problem 27P Problem 28P: The systems shown in Figure P5.28 are in equilibrium. If the spring scales are calibrated in... Problem 29P Problem 30P: A block slides down a frictionless plane having an inclination of 15.0. The block starts from rest... Problem 31P: The distance between two telephone poles is 50.0 m. When a 1.00-kg bird lands on the telephone wire... Problem 32P: A 3.00-kg object is moving in a plane, with its x and y coordinates given by x = 5t2 1 and y = 3t3... Problem 33P: A bag of cement weighing 325 N hangs in equilibrium from three wires as suggested in Figure P5.33.... Problem 34P: A bag of cement whose weight is Fg hangs in equilibrium from three wires as shown in Figure P5.18.... Problem 35P Problem 36P Problem 37P: An object of mass m = 1.00 kg is observed to have an acceleration awith a magnitude of 10.0 m/s2 in... Problem 38P Problem 39P Problem 40P: An object of mass m1 = 5.00 kg placed on a frictionless, horizontal table is connected to a string... Problem 41P Problem 42P: Two objects are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley as shown in... Problem 43P Problem 44P Problem 45P: In the system shown in Figure P5.23, a horizontal force Facts on an object of mass m2 = 8.00 kg. The... Problem 46P: An object of mass m1 hangs from a string that passes over a very light fixed pulley P1 as shown in... Problem 47P: A block is given an initial velocity of 5.00 m/s up a frictionless incline of angle = 20.0 (Fig.... Problem 48P: A car is stuck in the mud. A tow truck pulls on the car with the arrangement shown in Figure P5.24.... Problem 49P Problem 50P Problem 51P: In Example 5.8, we investigated the apparent weight of a fish in an elevator. Now consider a 72.0-kg... Problem 52P: Consider a large truck carrying a heavy load, such as steel beams. A significant hazard for the... Problem 53P Problem 54P Problem 55P: A 25.0-kg block is initially at rest on a horizontal surface. A horizontal force of 75.0 N is... Problem 56P: Why is the following situation impassible? Your 3.80-kg physics book is placed next to you on the... Problem 57P Problem 58P: Before 1960m people believed that the maximum attainable coefficient of static friction for an... Problem 59P Problem 60P: A woman at an airport is towing her 20.0-kg suitcase at constant speed by pulling on a strap at an... Problem 61P: Review. A 3.00-kg block starts from rest at the top of a 30.0 incline and slides a distance of 2.00... Problem 62P: The person in Figure P5.30 weighs 170 lb. As seen from the front, each light crutch makes an angle... Problem 63P: A 9.00-kg hanging object is connected by a light, in extensible cord over a light, frictionless... Problem 64P: Three objects are connected on a table as shown in Figure P5.31. The coefficient of kinetic friction... Problem 65P Problem 66P: A block of mass 3.00 kg is pushed up against a wall by a force P that makes an angle of = 50.0 with... Problem 67P Problem 68P Problem 69P Problem 70P: A 5.00-kg block is placed on top of a 10.0-kg block (Fig. P5.36). A horizontal force of 45.0 N is... Problem 71P Problem 72AP: A black aluminum glider floats on a film of air above a level aluminum air track. Aluminum feels... Problem 73AP Problem 74AP: Why is the following situation impossible? A book sits on an inclined plane on the surface of the... Problem 75AP Problem 76AP: A 1.00-kg glider on a horizontal air track is pulled by a string at an angle . The taut string runs... Problem 77AP Problem 78AP Problem 79AP: Two blocks of masses m1 and m2, are placed on a table in contact with each other as discussed in... Problem 80AP Problem 81AP: An inventive child named Nick wants to reach an apple in a tree without climbing the tree. Sitting... Problem 82AP Problem 83AP Problem 84AP: An aluminum block of mass m1 = 2.00 kg and a copper block of mass m2 = 6.00 kg are connected by a... Problem 85AP Problem 86AP Problem 87AP Problem 88AP Problem 89AP: A crate of weight Fg is pushed by a force P on a horizontal floor as shown in Figure P5.45. The... Problem 90AP Problem 91AP: A flat cushion of mass m is released from rest at the corner of the roof of a building, at height h.... Problem 92AP: In Figure P5.46, the pulleys and pulleys the cord are light, all surfaces are frictionless, and the... Problem 93AP: What horizontal force must be applied to a large block of mass M shown in Figure P5.49 so that the... Problem 94AP Problem 95AP: A car accelerates down a hill (Fig. P5.95), going from rest to 30.0 m/s in 6.00 s. A toy inside the... Problem 96CP Problem 97CP Problem 98CP: Initially, the system of objects shown in Figure P5.49 is held motionless. The pulley and all... Problem 99CP: A block of mass 2.20 kg is accelerated across a rough surface by a light cord passing over a small... Problem 100CP Problem 101CP Problem 102CP: In Figure P5.55, the incline has mass M and is fastened to the stationary horizontal tabletop. The... Problem 103CP Problem 104CP format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning




