
Laboratory Experiments for Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780134566207
Author: Theodore E. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Bruce E. Bursten, Catherine Murphy, Patrick Woodward, Matthew E. Stoltzfus, John H. Nelson, Kenneth C. Kemp
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 65E
From the enthalpies of reaction
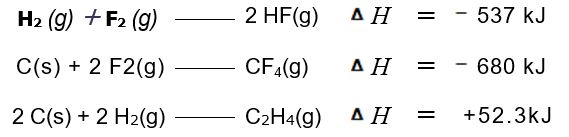
Calculate &£916;H for the reaction of ethylene with F2:
C2H4(g) + 6 F2(g)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Which molecule is the most stable? Please explain.
Please see photo
Complete the equation...see image
Chapter 5 Solutions
Laboratory Experiments for Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Ch. 5.2 - A mixture of gases A2 and B2 are introduced to a...Ch. 5.2 - Practice Exercise 2 Calculate the change in the...Ch. 5.3 - A solid sample of Zn(OH)2 is added to 0.350 L of...Ch. 5.3 -
Practice Exercise 2
Calculate the work, in J, if...Ch. 5.3 - Practice Exercise 1 A chemical reaction that gives...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 5.3.2PECh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.4.1PECh. 5.4 - Prob. 5.4.2PECh. 5.5 - The coinage metals (Group 1B) copper, silver, and...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 5.5.2PE
Ch. 5.5 - Practice Exercise 1 When 0.243 g of Mg metal is...Ch. 5.5 - Practical exercise 2 When 50.0 mL of 0.100MAgNO3...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 5.7.1PECh. 5.5 - Practice Exercise 2 A 0.5865-g sample of lactic...Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 5.8.1PECh. 5.6 - Prob. 5.8.2PECh. 5.6 - Calculate H for the reaction C(s)+...Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 5.9.2PECh. 5.7 - Prob. 5.10.1PECh. 5.7 - Prob. 5.10.2PECh. 5.7 - Prob. 5.11.1PECh. 5.7 - Prob. 5.11.2PECh. 5.7 -
Practice Exercise 1
Given 2SO2(g) + 02(g) —>...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 5.12.2PECh. 5.8 - Use the average bond enthalpies in Table 5.41to...Ch. 5.8 -
Use the average bond enthalpies in Table 5.4 to...Ch. 5.9 - Prob. 5.14.1PECh. 5.9 - Prob. 5.14.2PECh. 5 - One of the important ideas of thermodynamics is...Ch. 5 - Two positively charged spheres, each with a charge...Ch. 5 - SI The accompanying photo shows a pipevine...Ch. 5 - Consider the accompanying energy diagram. Does...Ch. 5 - The contents of the closed box in each of the...Ch. 5 - Imagine that you are climbing a mountain. Is the...Ch. 5 - The diagram shows four states of a system, each...Ch. 5 - You may have noticed that when you compress the...Ch. 5 - Imagine a container placed in a tub of water, as...Ch. 5 - In the accompanying cylinder diagram, a chemical...Ch. 5 - Prob. 10ECh. 5 - Consider the two diagrams that follow. Based on...Ch. 5 - Consider the conversion of compound A into...Ch. 5 - What is the electrostatic potential energy (in...Ch. 5 - What is the electrostatic potential energy (in...Ch. 5 - The electrostatic force (not energy) of attraction...Ch. 5 - Use the equations given in Problem 5.15 to...Ch. 5 - A sodium ion, Na+, with a charge of 1.6 x 10-19 C...Ch. 5 - A magnesium ion, Mg2+, with a charge of 3.2 x...Ch. 5 - Identify the force present and explain whether...Ch. 5 - Identify the force present and explain whether...Ch. 5 - Which of the following cannot leave or enter a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 22ECh. 5 - According to the first law of thermodynamics, what...Ch. 5 - Write an equation that expresses the first law of...Ch. 5 - Calculate AB and determine whether the process is...Ch. 5 - For the following processes, calculate the change...Ch. 5 - A gas is confined to a cylinder fitted with a...Ch. 5 - Consider a system consisting of two oppositely...Ch. 5 - What is meant by the term state function? Give an...Ch. 5 - Indicate which of the following is independent of...Ch. 5 - During a normal breath, our lungs expand about...Ch. 5 - How much work (in J) is involved in a chemical...Ch. 5 - Why is the change in enthalpy usually easier to...Ch. 5 - Under what condition will the enthalpy change of a...Ch. 5 - Assume that the following reaction occurs at...Ch. 5 - Suppose that the gas-phase reaction 2NO(g) + 02(g)...Ch. 5 - A gas is confined to a cylinder under constant...Ch. 5 - A gas is confined to a cylinder under constant...Ch. 5 - The complete combustion of ethanol, C2H5OH(l), to...Ch. 5 - The decomposition of Ca(OH)2(s) into CaO(s) and...Ch. 5 - Ozone, 03(9), is a form of elemental oxygen that...Ch. 5 -
5.42 Without referring to tables, predict which...Ch. 5 - Consider the following reaction: 2 Mg(s) + 02(g)2...Ch. 5 -
544 Consider the following reaction:
2...Ch. 5 - When solutions containing silver ions and chloride...Ch. 5 - At one time, a common means of forming small...Ch. 5 -
5.47 Consider the combustion of liquid methanol,...Ch. 5 -
5.48 Consider the decomposition of liquid...Ch. 5 - 5.49
a What are the units of molar heat...Ch. 5 - Two solid objects, A and B, are placed in boiling...Ch. 5 - What is the specific heat of liquid water? What is...Ch. 5 -
5.52
a. Which substance in Table 5.2 requires...Ch. 5 - The specific heat of octane, C8H18(l), is 2.22...Ch. 5 -
6.54 Consider the data about gold metal in...Ch. 5 - When a 6-50-g sample of solid sodium hydroxide...Ch. 5 -
5.56
a. When a 4 25-g sample of solid ammonium...Ch. 5 - A 2.200-g sample of quinone (C5H402) is burned in...Ch. 5 -
8.68 A 1.800-g sample of phenol (C6H5OH) was...Ch. 5 - Under constant-volume conditions, the heat of...Ch. 5 -
5.60 Under constant-volume conditions, the heat...Ch. 5 -
5.61 Can you use an approach similar to Hess's...Ch. 5 -
5.62 Consider the following hypothetical...Ch. 5 - Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction...Ch. 5 - From the enthalpies of reaction calculate H for...Ch. 5 - From the enthalpies of reaction Calculate H for...Ch. 5 - Given the data use Hess's law to calculate H for...Ch. 5 -
5.67
What is meant by the term standard...Ch. 5 - S
5.68
What is the value of the standard enthalpy...Ch. 5 - For each of the following compounds, write a...Ch. 5 - Write balanced equations that describe the...Ch. 5 - The following is known as the thermite reaction:...Ch. 5 -
5.72 Many portable gas heaters and grills use...Ch. 5 - Using values from Appendix C , calculate the...Ch. 5 -
5.74 Using values from Appendix C, calculate the...Ch. 5 - Complete combustion of 1 mol of acetone (C2H6O)...Ch. 5 - Calcium carbide (CaC2) reacts with water to form...Ch. 5 -
5.77 Gasoline is composed primarily of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 78ECh. 5 - Ethanol (C2H5OH) is blended with gasoline as an...Ch. 5 -
5.80 Methanol (CH3OH) is used as a fuel in race...Ch. 5 -
5.81 Without doing any calculations, predict the...Ch. 5 -
5.82 Without doing any calculations, predict...Ch. 5 - Use bond enthalpies in Table 5.4 Q to estimate for...Ch. 5 - Use bond enthalpies in Table 5.40 to estimate for...Ch. 5 - Use enthalpies of formation given in Appendix C to...Ch. 5 -
5.86
The nitrogen atoms in an N2 molecule are...Ch. 5 -
5.87 Consider the reaction 2H(g) + O2(g) ...Ch. 5 -
5.88 Consider the reaction H2(g) + I2(s) ...Ch. 5 -
5.89
What is meant by the term fuel value?
Which...Ch. 5 -
5.90
Which releases the most energy when...Ch. 5 -
5.91
A serving of a particular ready-to-serve...Ch. 5 -
5.92 A pound of plain M&M® candies contains 96 g...Ch. 5 -
5.93 The heat of combustion of fructose,...Ch. 5 -
5.94 The heat of combustion of ethanol,...Ch. 5 -
5.95 The standard enthalpies of formation of...Ch. 5 -
5.98 It is interesting to compare the ‘fuel...Ch. 5 - At the end of 2012, global population was about...Ch. 5 -
5.98 The automobile fuel called E85 consists of...Ch. 5 - The air bags that provide protection in...Ch. 5 -
5.100 An aluminum can of a soft drink is placed...Ch. 5 -
5.101 Consider a system consisting of the...Ch. 5 - A sample of gas is contained in a...Ch. 5 - Limestone stalactites and stalagmites are formed...Ch. 5 - Consider the systems shown in Figure 5.10. In one...Ch. 5 -
5.105 A house is designed to have passive solar...Ch. 5 -
5.108 A coffee-cup calorimeter of the type shown...Ch. 5 -
5.107
When a 0.235-9 sample of benzoic acid is...Ch. 5 -
5.108 Meals-ready-to-eat (MREs) are military...Ch. 5 - 5.109 Burning methane in oxygen can produce three...Ch. 5 - Prob. 110AECh. 5 -
5.111 From the following data for three...Ch. 5 - The hydrocarbons acetylene (C2H2) and benzene...Ch. 5 - Ammonia (NH3) boils at -33 °C; at this temperature...Ch. 5 -
5.114 Three common hydrocarbons that contain four...Ch. 5 -
5.115 A 201-lb man decides to add to his exercise...Ch. 5 -
5.116 TheSun supplies about 1.0 kilowatt of...Ch. 5 -
5.117 Itis estimated that the net amount of...Ch. 5 -
5.118 At 20 °C (approximately room temperature)...Ch. 5 - Suppose an Olympic diver who weighs 52.0 kg...Ch. 5 -
5.120 Consider the combustion of a single...Ch. 5 -
5.121 Consider the following unbalanced...Ch. 5 - Consider the following acid-neutralization...Ch. 5 -
5.123 Consider two solutions, the first being...Ch. 5 - The precipitation reaction between AgNO3(aq) and...Ch. 5 -
5.125 A sample of a hydrocarbon is combusted...Ch. 5 -
5.126 The methane molecule, CH4, has the geometry...Ch. 5 -
5.127 One of the best-selling light, or...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please see photoarrow_forward=Naming benzene derivatives Name these organic compounds: structure C1 CH3 name ☐ CH3 ப C1 × ☐arrow_forwardBlocking Group are use to put 2 large sterically repulsive group ortho. Show the correct sequence toconnect the reagent to product with the highest yield possible. * see image **NOTE: The compound on the left is the starting point, and the compound on the right is the final product. Please show the steps in between to get from start to final, please. These are not two different compounds that need to be worked.arrow_forward
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? What is the name of the intermediate complex? *See imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor” *see attachedarrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? *see imagearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax
Calorimetry Concept, Examples and Thermochemistry | How to Pass Chemistry; Author: Melissa Maribel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nSh29lUGj00;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY