
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781118992661
Author: Irwin, J. David, NELMS, R. M., 1939-
Publisher: Wiley,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 63P
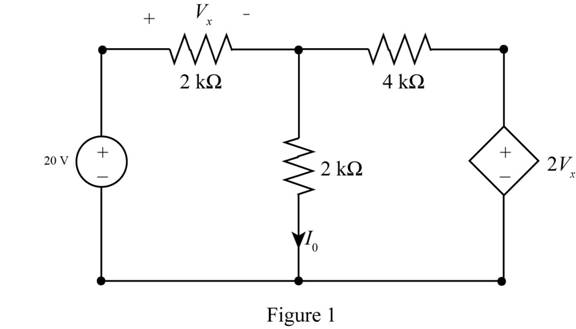
Use ThĂ©venin’s theorem to find 10 in the circuit in Fig. P5.63.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
3. What is the function of LM565 pin 6?
4. What is the purpose of the multistage low-pass filter between the LM565
output and the comparator input?
C10.1μ
FSK
Input
w₁
R2
100k
-o+5V(Vcc)
VR1
10k
C4
C5:
0.1 μ.
0.1μ
0.1 μ
8
10
R3
R4
D₁
FSK
Phase
Rx 7
10K
10K
Detector
www
ww
ww
1N4004
+
Demodulated
Output
6
AMP
R₁
6
100k
3
C₂
0.05 μ
VCO
4
5
9
U1
-5V
LM565
-0-5V(VEE)
Fig. 14-2 FSK demodulator
U2
R6
μ4741
10k
1. What components determine the free-running frequency of the VCO in
LM565 of Fig. 14-2?
2. What is the purpose of μA741 in Fig. 14-2?
C10.1μ
FSK
Input
-o+5V(Vcc)
VR1
10k
C4
C5:
0.1 μ.
0.1 μ
0.1 μ
8
10
R3
R4
R5
Phase
Rx 7
10K
10K
10k
D₁
FSK
Detector
www
ww
ww
ww
1N4004
+
Demodulated
Output
AMP
6
R₁
6
100k
w₁
R2
100k
3
C₂
0.05 μ
VCO
4
5
9
U1
-5V
LM565
-0-5V(VEE)
Fig. 14-2 FSK demodulator
U2
R6
μ4741
10k
When troubleshooting power and control circuits, approximate meter readings should be anticipated if the meter readings are going to be used to help determine circuit problems. Determine the expected DMM reading if the ciircuit is working properly. The expected reading of DMM 1 with the motor on is what VAC? And the expected reading of DMM 2 with the motor is on is what VAC? And The expected reading of DMM 3 with the motor on is What mA?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.1 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.2 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.3 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.4 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.5 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.6 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.7 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.8 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.9 using...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.l0, find using...
Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.11 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.12 using...Ch. 5 - Find IA in the network in Fig. P5.13 using...Ch. 5 - Using superposition, find IA in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find IA in the network in Fig. P5.15 using...Ch. 5 - Using superposition, find Vo in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.20 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.21 using...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use superposition to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the network...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the network...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.28 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.28 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find 10 in the network...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.31 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.32 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.33 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.34 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.35 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.36 using...Ch. 5 - Using Thévenins theorem, find IA in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.38 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.39 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.40 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.41 using...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.42 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in Fig. P5.43 using Thévenins theorem.Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in Fig. P5.45.Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.46 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in the network...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Given the linear circuit in Fig. P5.49, it is...Ch. 5 - If an 8-k load is connected to the terminals of...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.52 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.55 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.57 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.59 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.62, find Vo using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find 10 in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.64 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.66 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.69 using...Ch. 5 - Use Nortons theorem to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.71 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.72 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.73 using Nortons...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find the power supplied...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P5.75 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.76 using...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.77 using...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find I2 in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the circuit...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Io in the network...Ch. 5 - Use Thévenins theorem to find Vo in the network...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent of the network in...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent of the network in...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent of the network in...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit of the...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.88 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.89 using source...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Vo in the...Ch. 5 - Find 10 in the network in Fig. P5.91 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.92 using source...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Io in the...Ch. 5 - Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit of the...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P5.95 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.96 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.97 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P5.98 using source...Ch. 5 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P5.99 using source...Ch. 5 - Find in the circuit in Fig. P5.100 using source...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Io in the...Ch. 5 - Using source transformation, find Vo in the...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Io in the...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find Io in the...Ch. 5 - Use source transformation to find 10 in the...Ch. 5 - Using source transformation, find 10 in the...Ch. 5 - Use source exchange to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use a combination of Y- transformation and source...Ch. 5 - Use source exchange to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Use source exchange to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Use source exchange to find Io in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find RL in the network in Fig. P5.112 in order to...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.113, find RL for maximum...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Determine the value of RL in the network in Fig....Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL in the network in Fig. P5.120...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL for maximum power transfer...Ch. 5 - Find the maximum power that can be transferred to...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.123, find the value of...Ch. 5 - In the network in Fig. P5.124, find the value of...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL in Fig. P5.125 for maximum...Ch. 5 - Calculate the maximum power that can be...Ch. 5 - Find RL for maximum power transfer and the maximum...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL in Fig. P5.128 for maximum...Ch. 5 - A cell phone antenna picks up a call. If the...Ch. 5 - Some young engineers at the local electrical...Ch. 5 - Determine the maximum power that can be delivered...Ch. 5 - Find the value of the load RL in the network in...Ch. 5 - Find the value of RL in the network in fig. 5PFE-3...Ch. 5 - What is the current I in Fig. 5PFE4? a. 8 Ac. 0 A...Ch. 5 - What is the open-circuit voltage Voc at terminals...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How is a problem usually reduced with a recursive method?
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
In grinding, what is infeed versus cross feed?
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Explain the term cursor.
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Write an evaluation of some programming language you know, using the criteria described in this chapter.
Concepts Of Programming Languages
For the circuit shown, find (a) the voltage υ, (b) the power delivered to the circuit by the current source, an...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Running the Race Write a program that asks for the names of three runners and the time it took each of them to ...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- DU 1. Describe the operations of Q1, Q2 and LM566. 2. Describe the functions of VR1 and VR2. R6 lk R3 BRUD 3. If the input frequency is higher than the FSK frequency, does the FSK modulator operate normally? 0+12V R10 5.6k 6 10k VRI 500k U₁ LM566 3 VCO output 7 Digital input R₁ VR2 10k ww 1k Qi C945 C945 C5 I 0.1 uF C6 luF C₁ 0.01μ R2 10k ww R$ 100k C3 +12V 0.01μ R9 100k +12V 6 R710k Rs 100k 6 R4 100k P FSK output ww ww + www + 3 3 4 U U₂ 1000p -12V HA741 1000p-12V µА741 Fig. 13-2 FSK modulator CTS circuit.arrow_forward. 30-dB, right-circularly polarized antenna in a radio link radiates 5-W of power t 2 GHz. The input impedance of this antenna is 75 ohms, and it is attached ɔ a 50-ohm transmission line. The receiving antenna has an impedance mismatch at its terminals, - which leads to a VSWR of 2. The receiving antenna is about 95% efficient and has a field pattern near the beam maximum given by E, = (2âx + jây) F, (0, 0). The distance between the two antennas is 4,000 km, and the receiving antenna Directivity is 100. Determine the Minimum power Delivered to receiving antenna. 1arrow_forwardOpen plc - ladder logic To control traffic, we have red lights to stop cars and green lights to initiate entry/exit. If a car is in the lane, then the red lights turn ON. If no cars are in the lane, then the green lights turn ON. Upon turning ON the main switch button, the main switch indicator should turn ON and the system should start with green lights ON and red lights OFF?arrow_forward
- 3-4) 3.4-2 Signals g₁(t) = 104П(104) and g2(t) = 8(t) are applied at the inputs of the ideal low-pass filters H₁(f)=(f/20,000) and H2(f) = П(f/10,000) (Fig. P3.4-2). The outputs y₁ (t) and y2(t) of these filters are multiplied to obtain the signal y(t) = y1 (1)y2(t). (a) Sketch G1(f) and G2(f). (b) Sketch H₁(f) and H₂(f). (c) Sketch Y₁ (f) and Y2(f). (d) Find the bandwidths of y₁ (t), y2(t), and y(t). 8₁ (1) H₁(f) y, (t) y(t) = y₁ (1) y2 (1) 82(1) ½⁄2 (1) H₂(f)arrow_forwardsolve the differential equation y'' -2y'-3y=x³e^5x cos(3x) Don't use AI,I need it handwrittenarrow_forward3-3) Similar to Lathi & Ding prob. 3.3-7. The signals in the figure below are modulated signals with carrier cos(5t). Find the Fourier transforms of these signals using the appropriate properties of the Fourier transform and text Table 3.1. The sketch the magnitude and phase spectra for figure parts (a) and (b). Hint: these functions can be expressed in the form g(t) cos(2лfot) (a) 1 1 2π www. σπ (b) (c) όπarrow_forward
- 3-1) Similar to Lathi & Ding prob. 3.1-1. Use direct integration to find the Fourier transforms of the signals shown below. a) g₁(t) = II(t − 2) + 2 exp (−3|t|) b) g(t) = d(t+2)+3e¯u (t − 2)arrow_forward3-2) Lathi & Ding prob. 3.1-5. From the definition in eq. 3.1b, find the inverse Fourier transforms of the spectra in the figure below. G(f) COS лf 10 (a) G(f) 1 -B B (b)arrow_forwardFundamentals of Energy Systems HW 4 Q2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Current Divider Rule; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRU1mKWUehY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY