
Concept explainers
Functional-Based versus Activity-Based Costing
For years, Tamarindo Company produced only one product: backpacks. Recently, Tamarindo added a line of duffel bags. With this addition, the company began assigning
Josie, the marketing manager, and Steve, the production manager, both complained about the increase in the production cost of backpacks. Josie was concerned because the increase in unit costs led to pressure to increase the unit price of backpacks. She was resisting this pressure because she was certain that the increase would harm the company’s market share. Steve was receiving pressure to cut costs also, yet he was convinced that nothing different was being done in the way the backpacks were produced. After some discussion, the two managers decided that the problem had to be connected to the addition of the duffel-bag line.
Upon investigation, they were informed that the only real change in product-costing procedures was in the way overhead costs are assigned. A two-stage procedure was now in use. First, overhead costs are assigned to the two producing departments, Patterns and Finishing. Second, the costs accumulated in the producing departments are assigned to the two products by using direct labor hours as a driver (the rate in each department is based on direct labor hours). The managers were assured that great care was taken to associate overhead costs with individual products. So that they could construct their own example of overhead cost assignment, the controller provided them with the information necessary to show how accounting costs are assigned to products:
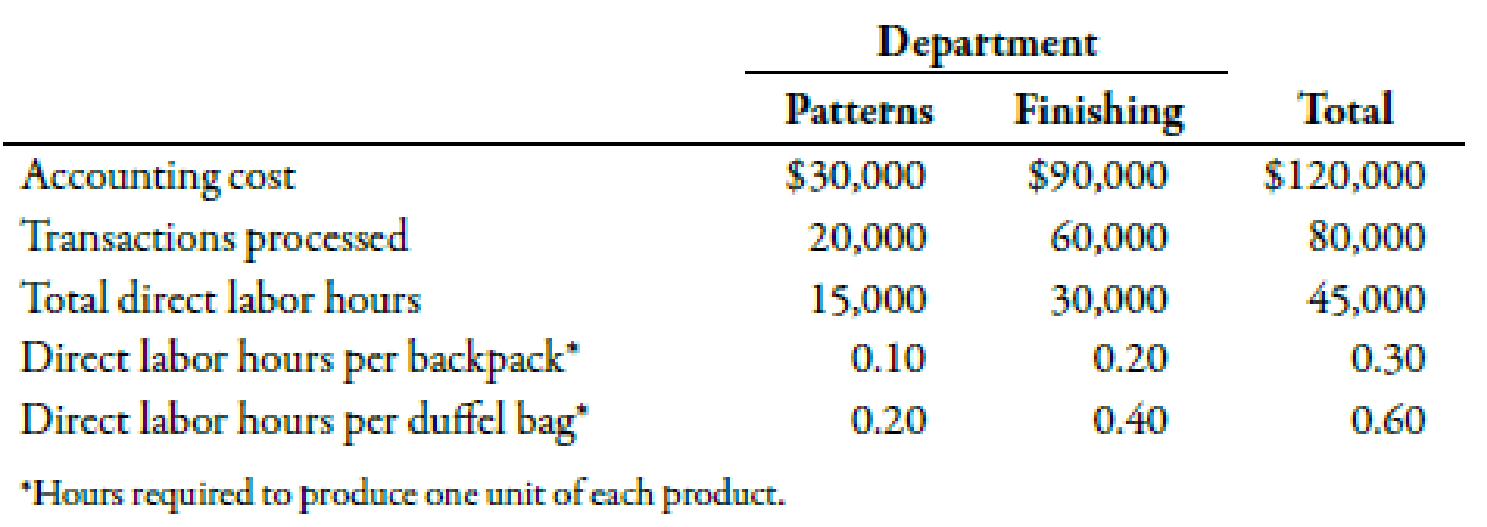
The controller remarked that the cost of operating the accounting department had doubled with the addition of the new product line. The increase came because of the need to process additional transactions, which had also doubled in number.
During the first year of producing duffel bags, the company produced and sold 100,000 backpacks and 25,000 duffel bags. The 100,000 backpacks matched the prior year’s output for that product.
Required:
(Note: Round rates and unit cost to the nearest cent.)
- 1. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compute the amount of accounting cost assigned to a backpack before the duffel-bag line was added by using a plantwide rate approach based on units produced. Is this assignment accurate? Explain.
- 2. Suppose that the company decided to assign the accounting costs directly to the product lines by using the number of transactions as the activity driver. What is the accounting cost per unit of backpacks? Per unit of duffel bags?
- 3. Compute the amount of accounting cost assigned to each backpack and duffel bag by using departmental rates based on direct labor hours.
- 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which way of assigning overhead does the best job—the functional-based approach by using departmental rates or the activity-based approach by using transactions processed for each product? Explain. Discuss the value of ABC before the duffel-bag line was added.
1.
Calculate the value of accounting costs which is apportioned to a backpack before the duffle-bag line was added with the help of plant wide rate approach. Also, identify whether this approach is accurate or not.
Answer to Problem 53P
Accounting costs before addition of duffel bags is $0.60 per unit.
Explanation of Solution
Activity Based Costing (ABC):
Activity based costing is an apportionment of costs that first considers the activity drivers that helps in the allocation of costs to various activities and then allocates costs to different cost objects by using the drivers.
Use the following formula to calculate accounting costs before addition of duffel bags:
Substitute $60,000 for accounting costs and 100,000 for units sold of backpacks in the above formula.
Therefore, accounting costs before addition of duffel bags is $0.60 per unit.
The assignment of costs is correct because all costs are related to single product.
Working Note:
1. Calculation of accounting costs:
2.
Calculate the accounting costs per unit of backpacks and per unit of duffle bags when the company decided to apportion the costs directly to the product lines with the help of number of transactions.
Answer to Problem 53P
Accounting costs of backpacks and duffel bags are $0.60 per unit and $2.4 per unit respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Use the following formula to calculate accounting costs per unit of backpacks:
Substitute $60,000 for overhead applied and 100,000 for units sold of backpacks in the above formula.
Therefore, accounting costs of backpacks is $0.60 per unit.
Use the following formula to calculate accounting costs per unit of duffle bags:
Substitute $60,000 for overhead applied and 25,000 for units sold of duffle bags in the above formula.
Therefore, accounting costs of duffle bags is $2.40 per unit.
Working Note:
1. Calculation of overhead applied:
First, the amount of activity rate is computed so as to calculate the overhead applied:
2. Calculation of overhead applied:
3.
Calculate the amount of accounting costs which is assigned to each backpack and duffel bags with the help of departmental rates.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of amount of costs:
| Activity | Rate(R) | Direct labor hours (D) |
Backpacks ($) |
Duffle bags ($) |
| (A)Patterns | 2.001 | 0.10 | 0.20 | |
| 2.001 | 0.20 | 0.40 | ||
| (B)Finishing | 3.002 | 0.20 | 0.60 | |
| 3.002 | 0.40 | 1.20 | ||
|
Total Cost | 0.80 | 1.60 |
Table (1)
Working Note:
1. Calculation of overhead rates of patterns:
2. Calculation of overhead rates of finishing:
4.
Discuss the best way of assigning the overhead costs. Also, explain the value of ABC before duffle bag line was added.
Explanation of Solution
The given problem allows the individual to determine the value of accounting costs per unit by including the costs of duffle bags or not including the costs of duffle bags. With the help of this calculation, it becomes easy to see the benefits of activity based approach as compared to the functional based approach. The activity based approach provides the same cost per unit as the single product setting. On the contrary, functional based approach uses the transaction number for apportion the costs to each producing department. Direct labor hours creates problem in allocation of the costs because direct labor hours do not show the pattern of consumption of individual products.
ABC approach offers no improvement in providing costing accuracy in a single product environment. On the other hand, in a single product environment there is a possibility to increase the accuracy of assignment of cost to other costs objects such as customers.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,



