
(a)
Interpretation:
Atomic percent of
Concept Introduction:
Fick's first law of equation is as follows:
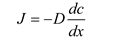
Answer to Problem 5.33P
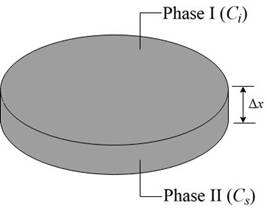
The concentration gradient in atomic percent
Explanation of Solution
The concentration gradient in atomic percent
Here,
The 1st phase composition in atomic percent
The 2nd phase composition in atomic percent is
The thickness of concentration gradient
Substitute the above value in the equaion
Hence, the concentration gradient in atomic percent
(b)
Interpretation:
The concentration gradient
Concept Introduction:
The concentration gradient can be calculated as follows:
Answer to Problem 5.33P
The value of concentration gradient in atomic
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the weight
The percentage of
The percentage of
Atomic weight of
Substitute the above value in equation
Substitute the above value of
Hence, the value of concentration gradient in atomic
Here minus sign indicates that flux is moving from higher concentration to lower concentration.
(c)
Interpretation:
The value of concentration gradient in
Concept Introduction:
The number of atoms of Zn per
Here, no. of atoms of
Answer to Problem 5.33P
The value of concentration gradient in
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the numbers of atoms per
Here no. of atoms of
The fraction of
Lattice parameter is
Substitute the above value in equation
Similarly,
Substitute the above value of
Hence, the value of concentration gradient in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering, SI Edition
- 1. Find the resolution, current and output voltage for a binary weighted resistor DAC of (applied binary word is (locoj), the resistor values R = 12 kQ, Rf = 6 k2 and VR = 12 V. 2. Convert the following 5-bit digital values (ble 10) to analog, using the R-2R ladder. Assume that the Vs = 10 V, R = Rf = 7 ksarrow_forward= = Q1/A cantilever sheet-pile wall penetrating a granular soil. Here, L₁= 3 m, L2 = 6 m, y 17.3kN/m³, Ysat 19.4 kN/m², and 0= 30. a. What is the theoretical depth of embedment, D? b. For a 30% increase in D, what should be the total length of the sheet piles? c. What should be the minimum section modulus of the sheet piles? Use σall = 172 MN/m².arrow_forwardK Q4/ For the unity-feedback system where G(s) = do the following: a. Plot the Nyquist diagram. (S+2)(S+4)(S+6) b. Use your Nyquist diagram to find the range of gain, K, for stabilityarrow_forward
- Q6/ Answer (two) of the following question A For the following G(s), find analytical expressions for the magnitude and phase response and make a plot of the logmagnitude and the phase, using log-frequency in rad/s as the ordinate. G(S)=- 1 (S+2)(S+4)arrow_forwardQ5 Given the system of Figure below, with dominant poles -5.415 t/10.57. design a PID controller so that the system can operate with a peak time that is two-thirds that of the uncompensated system at 20% overshoot to get and with zero steady-state error for a step input and KV= 5.7163sec and final K=4.6. R(s) + E(s) K(s + 8) (s+3)(x+6)(s + 10) C(s)arrow_forwardThe cardiovascular countercurrent heat exchnager mechanism is to warm venous blood from 28 degrees C to 35 degrees C at a mass flow rate of 2 g/s. The artery inflow temp is 37 degrees C at a mass flow rate of 5 g/s. The average diameter of the vein is 5 cm and the overall heat transfer coefficient is 125 W/m^2*K. Determine the overall blood vessel length needed too warm the venous blood to 35 degrees C if the specific heat of both arterial and venous blood is constant and equal to 3475 J/kg*K.arrow_forward
- 10.37 What is ffor the flow of water at 10°C through a 30-cm cast iron pipe with a mean velocity of 24 m/s?arrow_forward10.60 As shown, water (15°C) is draining from a tank through a galvanized iron pipe. The pipe length is L = 2 m, the tank depth is H = 1 m, and the pipe is a 0.5-inch NPS schedule 40. Calculate the velocity in the pipe. Neglect component head loss. H Pipe of diameter D L Problems 10.59 and 10.60arrow_forward(connection)? Q1: Define the BGP ? Ebgp vs I bgp, and how do I advertise? With a drawing example QT: Explain how to make messages in the BGP protocol. Q: What is concept the hot potato routing in BGP? Q: What are the criteria for BGP route selection? Qo: Define the concept of Spanning Tree Protocol. Explain in detail and draw the figures. Q1: What happens when STP is disabled? QV: Define the concept of broadcast storm. QA: List and explain the Steps to a Loop-Free Topology when using the Spanning Tree Algorithm and Spanning Tree Protocol in a four-step process. I want a typical and concise Solutionarrow_forward
- ".I need the correct answers with explanations" Answer True or False, then correct errors or explain if any: 1. The term pole in filter terminology refers to the feedback circuit. 2, A voltage shunt feedback with Ai-10, A-20, p 0.45, then Aif will be 1. 3. The integrator Op-Amp circuit can be used to produce square waves. 4. The equivalent circuit of the crystal oscillator is series and parallel (R, C) components. 5. The transistor in a class A power amplifier conducts for the entire input cycle. 6. Bypass capacitors in an amplifier determine the low and high-frequency responses. 7. The midrange voltage gain of an amplifier is 100. The input RC circuit has a lower critical frequency of 1 kHz. The actual voltage gain at f-100 Hz is 100. 8. The Bessel filter types produce almost ripple frequency response. 9. RC phase shift oscillators are based on both positive and negative feedback circuits. 10. In a high-pass filter, the roll-off region occurs above the critical frequency.arrow_forward10.53 Water is pumped through a vertical 10-cm new steel pipe to an elevated tank on the roof of a building. The pressure on the discharge side of the pump is 1.6 MPa. What pressure can be expected at a point in the pipe 110 m above the pump when the flow is 0.02 m³/s? Assume T = 20°C.arrow_forward".I need the correct answers with explanations" Answer True or False and correct errors if found: Marks) 1. The LC oscillator circuits are used to operate in low and moderate frequencies. 2. The voltage series feedback can increase both input and output impedances. 3. A two-pole Sallen-Key high-pass filter contains one capacitor and two resistors. 4. The main feature of a crystal oscillator is the high frequency operation that operates with optoelectronic effect. 5. The max. efficiency of the class B power amplifier is 50%. 6. The Q-point must be centered on the load line for maximum class AB output signal swing. 7. The differentiator Op-Amp can convert the triangle waveform into sinewave. 8. Class AB power amplifier eliminates crossover distortion found in pure class A. 9. RC-phase shift oscillators are based on positive feedback circuits. 10. Bypass capacitors in an amplifier determine the low and high-frequency responses.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





