
Interpretation:
It is impossible that two adiabatic reversible processes can intersect on
Concept Introduction:
From the second law of
Answer to Problem 5.1P
Hence, it is impossible that two adiabatic reversible processes can intersect on
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
It is given that two adiabatic reversible processes do intersect and complete the cycle on
From the given data, we plot a diagram on
Thus, AB is isothermal process; BC and AC are adiabatic reversible processes. This forms a cycle ABC where area inside the cycle is given as work.
Now, for the heat calculations, the adiabatic reversible processes have no heat transfer, so heat given by both process BC and AC are zero. So, heat transfer takes place only by the isothermal process which has only one single temperature
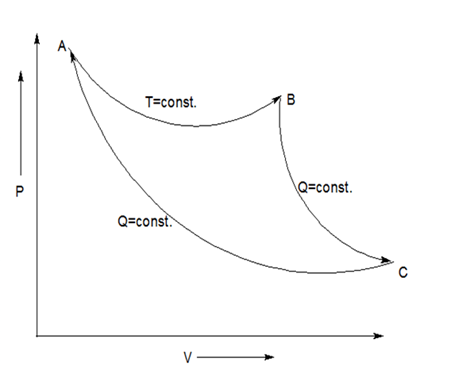
Two thermodynamic curves of same kind (isothermal, adiabatic, polytropic) never intersect each other on
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
- 2.) A mixture with 4% n-pentane, 40% n-hexane, 50% n-heptane, and 6% n-octane is to be distilled at 14.7 lb/in² with 98% of the hexane and 1% of the heptane recovered in the distillate. If the feed is a saturated liquid (q = 1), the top and bottom temperature are 149°F and 212°F respectively, calculate i.) The product compositions, ii.) Minimum reflux ratio (Rm), iii.) Minimum theoretical plates and iv.) Actual plate when the reflux ratio is 2Rm.arrow_forwardanswer choices 3. A. 0.18, B. 0.44, C. 0.01, D. 2 4. A. 0.2, B. 01, C. 0.4, D. 0.065 5.A. 1.43, B. 5.72, C. 0.93, D. 2.86 6. A. 1.0, B. 4.0, . 2.0, D. 0.65 7.A. 15.5, B. 8.0, C. 11.0, D. 58.5arrow_forwardDescribe with the aid of a labelled diagram how to seperate i) Acetone-water Azeotrope using solvent extractive distillation ii)Acetone-Methano azeotrope using salt effective extractive distillationarrow_forward
- H.W 1. A feed of 4535 kg/h of a 2.0 wt % salt solution at 311 K enters continuously a single-effect evaporator and is being concentrated to 3.0%. The evaporation is at atmospheric pressure and the area of the evaporator is 69.7m². Saturated steam at 383.2 K is supplied for heating. Since the solution is dilute, it can be assumed to have the same boiling point as water. The heat capacity of the feed can be taken as cp = 4.10 kJ/kg K. Calculate the amounts of vapor and liquid product, and the overall heat-transfer coefficient U?arrow_forwardThe switch in Fig.1 has been closed for a long time. It opens at t = Find i(t) for t > 0. 50 www 1.5 H m t=0 10 Ω 9A 0.arrow_forwarde a) 1) Indicate whether each statement below is True or False: Precipitates have a more regular structure than crystals. b) A protein will be more likely to precipitate when the surrounding pH is at its pl. c) Larger proteins are more likely to precipitate than smaller proteins. d) Precipitation nucleation typically follows a secondary nucleation mechanism. e) Precipitates in a CSTR are usually uniform in size. f) Crystallization nucleation usually follows a secondary nucleation mechanism. g) The most common scale-up method for precipitation and crystallization is constant P/V h) Evaporation is commonly carried out above atmospheric pressure. i) The boiling point of a solvent typically rises as the concentration of solute increases. j) Scale-up of evaporation units is usually carried out by increasing evaporator height. k) Unbound water is more difficult to remove than bound water when drying. 1) The most common convection dryer is a freeze dryer. m) Vacuum shelf dryers typically heat…arrow_forward
- 5) Wet insulin crystals containing 32 g water per 100 g of dry insulin need to be dried in air to a moisture level of 5 g water per 100 g of dry insulin. For your convenience, a graph of water content of insulin vs. relative humidity and a psychrometric chart are provided below. a) Determine the percentage of bound and unbound water in the wet crystals before drying. b) Determine the relative humidity of the air to accomplish the drying to 5 g water/100 g dry solids. c) For drying with air at 20°C, what should be the moisture content of the air (g moisture/g dry air)? Water content (g/100 g dry solids) 40 30 20 10 Cefazolin sodium tPA 20 40 Insulin 60 Relative humidity (%) 80 100arrow_forwardA power plant needs to evaporate 1500.0 lbm/h of water at 40.0 °F at 1 atm. Utility superheated steam at 1200 °F and 40 bar is available, but the steam cannot drop below 20 bar and 700 °F. Use the steam tables to determine the specific enthalpies of the four streams. The reference for the enthalpies should be water at the triple point. You may interpolate in Tables B6. and B7, and can also use external, automated sources. Determine the amount of superheated steam required to accomplish the evaporation for a superheated steam outlet of 700 °F and 20 bar. Assume no heat losses and use the steam tables to determine enthalpies.arrow_forwardRecitation 11 Problem 1 400 kg/min of steam enters a steam turbine at 300 °C and 80 bar through a 8.5-cm diameter line and exits at 100 °C and 10.0 bar through a 5.5-cm line. The exiting stream may be vapor, liquid, or "wet steam", a mist composed of saturated water vapor and entrained liquid droplets. Find how much power W (kW) is transferred from the turbine to the steam? The answer can be positive or negative. Neglect AE, but not AEK. What percentage (%) of the total power is due to kinetic energy changes?arrow_forward
- A 30.0-g block of iron at 200.0°C is dropped into a liter of water in an insulated flask at 25.0°C and 1 atm. The specific enthalpy of iron is given by the expression Ĥ(J/g) = 17.3 T(°C).arrow_forwardRecitation 11 Problem 2 Eight fluid ounces (1 qt = fl 32 oz) of a beverage in a glass at 23.0 °C is to be cooled by adding ice and stirring. The properties of the beverage may be taken to be those of liquid water. The enthalpy of the ice relative to liquid water at the triple point is -348 kJ/kg. Estimate the mass of ice (g) that must melt to bring the liquid temperature to 4.0 °C, neglecting energy losses to the surroundings. (Note: For this isobaric batch process, the energy balance reduces to Q = AH)arrow_forwardA solid slab of 5.15 wt% agar gel at 278 K is 6.00 mm thick and contains a uniform concentration of urea of 0.2 kmol/m3. Diffusion is only in the direction through two parallel flat surfaces 6.00 mm apart. The slab is suddenly immersed in pure turbulent water so that the surface resistance can be assumed to be negligible; i.e, the convective coefficient hm is very large. The diffusivity of urea in the agar is 4.72e-10 m2/s. a) Calculate the concentration at the midpoint of the slab and (b) 1.50 mm from the surface after 19 h. c) if the thickness of the slab is halved, what would be the midpoint concentration in 19 h.arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





