
Mechanics of Materials, SI Edition
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093354
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.12.12P
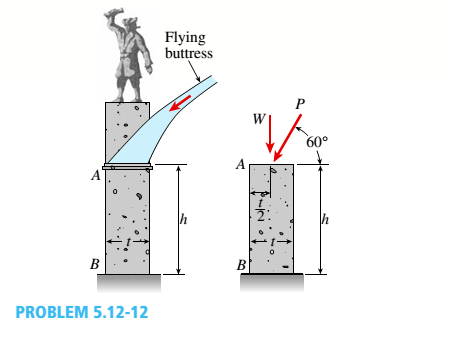
A flying but tress transmit s a load P = 25 kN, acting at an angle of 60º to the horizontal, to the top of a vertical buttress AB (see figure). The vertical buttress has height h = 5.0 m and rectangular cross section of thickness t = 1.5 m and width b = 1.0 m (perpendicular to the plane of the figure). The stone used in the construction weighs y = 26 kN/m3.
What is the required weight W of the pedestal and statue above the vertical buttress (that is, above section A) to avoid any tensile stresses in the vertical buttress?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Airplanes A and B, flying at constant velocity and at the same altitude, are tracking the eye
of hurricane C. The relative velocity of C with respect to A is 300 kph 65.0° South of West,
and the relative velocity of C with respect to B is 375 kph 50.0° South of East.
A
120.0 km
B
1N
1. Determine the relative velocity of B with respect to A.
A ground-based radar indicates that hurricane C is moving
at a speed of 40.0 kph due north.
2. Determine the velocity of airplane A.
3. Determine the velocity of airplane B.
Consider that at the start of the tracking expedition, the
distance between the planes is 120.0 km and their initial
positions are horizontally collinear.
4. Given the velocities obtained in items 2 and 3, should
the pilots of planes A and B be concerned whether the
planes will collide at any given time? Prove using
pertinent calculations. (Hint: x = x + vt)
0
Only 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okk don't use guidelines or ai answers okk will dislike okkk.
Solve this probem and show all of the work
Chapter 5 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, SI Edition
Ch. 5 - A steel wire with a diameter of d = 1/16 in. is...Ch. 5 - A copper wire having a diameter ofd = 4 mm is bent...Ch. 5 - A 4.75-in, outside diameter polyethylene pipe...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB is loaded by a couple M0at...Ch. 5 - A thin strip of steel with a length of L =19 in....Ch. 5 - A bar of rectangular cross section is loaded and...Ch. 5 - A simply supported beam with a length L = 10 ft...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam is subjected to a concentrated...Ch. 5 - A thin strip of hard copper (E = 16,000 ksi)...Ch. 5 - A steel wire (E = 200 GPa) of a diameter d = L25...
Ch. 5 - A thin, high-strength steel rule (E = 30 x 10ft...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam AB with a span length...Ch. 5 - Beam ABC has simple supports at A and B and an...Ch. 5 - A simply supported beam is subjected to a in early...Ch. 5 - Each girder of the lift bridge (sec figure) is 180...Ch. 5 - A freight-car axle AS is loaded approximately as...Ch. 5 - A seesaw weighing 3 lb/ft of length is occupied by...Ch. 5 - During construction of a highway bridge, the main...Ch. 5 - The horizontal beam ABC of an oil-well pump has...Ch. 5 - A railroad tie (or sleeper) is subjected to two...Ch. 5 - A fiberglass pipe is lifted by a sling, as shown...Ch. 5 - A small dam of height h = 2.0 m is constructed of...Ch. 5 - Determine the maximum tensile stress (7, (due to...Ch. 5 - Determine the maximum bending stress emaxdue to...Ch. 5 - A simple beam A B of a span length L = 24 ft is...Ch. 5 - Determine the maximum tensile stress erand maximum...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam A3, loaded by a uniform load and...Ch. 5 - A canti lever beam A B of a n isosceles t...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam, a C12 x 30 section, is...Ch. 5 - A frame ABC travels horizontally with an...Ch. 5 - A beam ABC with an overhang from B to C supports a...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB with a rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A beam with a T-section is supported and loaded as...Ch. 5 - Consider the compound beam with segments AB and...Ch. 5 - A small dam of a height h = 6 ft is constructed of...Ch. 5 - A foot bridge on a hiking trail is constructed...Ch. 5 - A steel post (E=30×106) having thickness t = 1/8...Ch. 5 - Beam ABCDE has a moment release just right of...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam having a span length...Ch. 5 - A simply supported beam (L = 4.5 m) must support...Ch. 5 - The cross section of a narrow-gage railway bridge...Ch. 5 - A fiberglass bracket A BCD with a solid circular...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beanie B is loaded by a uniform load...Ch. 5 - A simple beam of length L = 5 m carries a uniform...Ch. 5 - A simple beam AB is loaded as shown in the figure....Ch. 5 - A pontoon bridge (see figure) is constructed of...Ch. 5 - A floor system in a small building consists of...Ch. 5 - The wood joists supporting a plank Floor (see...Ch. 5 - A beam ABC with an overhang from B to C is...Ch. 5 - -12 A "trapeze bar" in a hospital room provides a...Ch. 5 - A two-axle carriage that is part of an over head...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB with a circular cross section...Ch. 5 - A propped cantilever beam A BC (see figure) has a...Ch. 5 - A small balcony constructed of wood is supported...Ch. 5 - A beam having a cross section in the form of an un...Ch. 5 - A beam having a cross section in the form of a...Ch. 5 - Determine the ratios of the weights of four beams...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.6.20PCh. 5 - A steel plate (called a cover ploie) having...Ch. 5 - A steel beam ABC is simply supported at A and...Ch. 5 - A retaining wall 6 ft high is constructed of...Ch. 5 - A retaining wall (Fig. a) is constructed using...Ch. 5 - A beam of square cross section (a = length of each...Ch. 5 - The cross section of a rectangular beam having a...Ch. 5 - A tapered cantilever beam A B of length L has...Ch. 5 - .2 A ligmio.irc ii supported by two vorlical beams...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.7.3PCh. 5 - Prob. 5.7.4PCh. 5 - Prob. 5.7.5PCh. 5 - A cantilever beam AB with rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A simple beam ABC having rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB having rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - The shear stresses t in a rectangular beam arc...Ch. 5 - .2 Calculate the maximum shear stress tmaxand the...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam is subjected to...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam with overhang is...Ch. 5 - Two wood beams, each of rectangular cross section...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam of length L = 2 m supports a...Ch. 5 - A steel beam of length L = 16 in. and...Ch. 5 - A beam of rectangular cross section (width/) and...Ch. 5 - A laminated wood beam on simple supports (figure...Ch. 5 - A laminated plastic beam of square cross section...Ch. 5 - A wood beam AB on simple supports with span length...Ch. 5 - A simply supported wood beam of rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A square wood platform is 8 ft × 8 ft in area and...Ch. 5 - A wood beam ABC with simple supports at A and B...Ch. 5 - A wood pole with a solid circular cross section (d...Ch. 5 - A simple log bridge in a remote area consists of...Ch. 5 - A vertical pole consisting of a circular tube of...Ch. 5 - A circular pole is subjected to linearly varying...Ch. 5 - A sign for an automobile service station is...Ch. 5 - A steel pipe is subjected to a quadratic...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - -1 through 5.10-6 A wide-flange beam (see figure)...Ch. 5 - A cantilever beam AB of length L = 6.5 ft supports...Ch. 5 - A bridge girder A B on a simple span of length L =...Ch. 5 - A simple beam with an overhang supports a uniform...Ch. 5 - A hollow steel box beam has the rectangular cross...Ch. 5 - A hollow aluminum box beam has the square cross...Ch. 5 - The T-beam shown in the figure has cross-sectional...Ch. 5 - Calculate the maximum shear stress tmax. in the...Ch. 5 - A prefabricated wood I-beam serving as a floor...Ch. 5 - A welded steel gird crhaving the erass section...Ch. 5 - A welded steel girder having the cross section...Ch. 5 - A wood box beam is constructed of two 260 mm × 50...Ch. 5 - A box beam is constructed of four wood boards as...Ch. 5 - Two wood box beams (beams A and B) have the same...Ch. 5 - A hollow wood beam with plywood webs has the...Ch. 5 - A beam of a T cross section is formed by nailing...Ch. 5 - The T-beam shown in the figure is fabricated by...Ch. 5 - A steel beam is built up from a W 410 × 85 wide...Ch. 5 - The three beams shown have approximately the same...Ch. 5 - Two W 310 × 74 Steel wide-flange beams are bolted...Ch. 5 - A pole is fixed at the base and is subjected to a...Ch. 5 - A solid circular pole is subjected to linearly...Ch. 5 - While drilling a hole with a brace and bit, you...Ch. 5 - An aluminum pole for a street light weighs 4600 N...Ch. 5 - A curved bar ABC having a circular axis (radius r...Ch. 5 - A rigid Trame ABC is formed by welding two steel...Ch. 5 - A palm tree weighing 1000 lb is inclined at an...Ch. 5 - A vertical pole of aluminum is fixed at the base...Ch. 5 - Because of foundation settlement, a circular tower...Ch. 5 - A steel bracket of solid circular cross section is...Ch. 5 - A cylindrical brick chimney of height H weighs w =...Ch. 5 - A flying but tress transmit s a load P = 25 kN,...Ch. 5 - A plain concrete wall (i.e., a wall with no steel...Ch. 5 - A circular post, a rectangular post, and a post of...Ch. 5 - Two cables, each carrying a tensile force P = 1200...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.12.16PCh. 5 - A short column constructed of a W 12 × 35...Ch. 5 - A short column with a wide-flange shape is...Ch. 5 - A tension member constructed of an L inch angle...Ch. 5 - A short length of a C 200 × 17.1 channel is...Ch. 5 - The beams shown in the figure are subjected to...Ch. 5 - The beams shown in the figure are subjected to...Ch. 5 - A rectangular beam with semicircular notches, as...Ch. 5 - A rectangular beam with semicircular notches, as...Ch. 5 - A rectangular beam with notches and a hole (see...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: WRITE OUT SOLUTION DO NOT USE A COPIED SOLUTION Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe?arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardDetermine the minimum applied force P required to move wedge A to the right. The spring is compressed a distance of 175 mm. Neglect the weight of A and B. The coefficient of static friction for all contacting surface is μs = 0.35. Neglect friction at the rollers. k = = 15 kN/m P A B 10°arrow_forward
- DO NOT COPY SOLUTION- will report The differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe?arrow_forwarda box shaped barge 37m long, 6.4 m beam, floats at an even keel draught of 2.5 m in water density 1.025 kg/m3. If a mass is added and the vessel moves into water density 1000 kg/m3, determine the magnitude of this mass if the fore end and aft end draughts are 2.4m and 3.8m respectively.arrow_forwarda ship 125m long and 17.5m beam floats in seawater of 1.025 t/m3 at a draught of 8m. the waterplane coefficient is 0.83, block coefficient 0.759 and midship section area coefficient 0.98. calculate i) prismatic coefficient ii) TPC iii) change in mean draught if the vessel moves into water of 1.016 t/m3arrow_forward
- c. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40) handplot only, and solve for eacharrow_forwardA ship of 9000 tonne displacement floats in fresh water of 1.000 t/m3 at a draught 50 mm below the sea water line. The waterplane area is 1650 m2. Calculate the mass of cargo which must be added so that when entering seawater of 1.025 t/m3 it floats at the seawater line.arrow_forwardA ship of 15000 tonne displacement floats at a draught of 7 metres in water of 1.000t/cub. Metre.It is required to load the maximum amount of oil to give the ship a draught of 7.0 metre in seawater ofdensity 1.025 t/cub.metre. If the waterplane area is 2150 square metre, calculate the massof oil requiredarrow_forward
- A ship of 8000 tonne displacement floats in seawater of 1.025 t/m3 and has a TPC of 14. The vessel moves into fresh water of 1.000 t/m3 and loads 300 tonne of oil fuel. Calculate the change in mean draught.arrow_forwardAuto Controls DONT COPY ANSWERS - will report Perform the partial fraction expansion of the following transfer function and find the impulse response: G(s) = (s/2 + 5/3) / (s^2 + 4s + 6) G(s) =( 6s^2 + 50) / (s+3)(s^2 +4)arrow_forwardI submitted the below question and received the answer i copied into this question as well. Im unsure if it is correct, so looking for a checkover. i am stuck on the part tan-1 (0.05) = 0.04996 radians. Just unsure where the value for the radians came from. Just need to know how they got that answer and how it is correct before moving on to the next part. If any of the below information is wrong, please feel free to give me a new answer or an entire new explanation. An Inclining experiment done on a ship thats 6500 t, a mass of 30t was moved 6.0 m transvesly causing a 30 cm deflection in a 6m pendulum, calculate the transverse meta centre height. Here is the step-by-step explanation: Given: Displacement of the ship (W) = 6500 tonnes = 6500×1000=6,500,000kg Mass moved transversely (w) = 30 tonnes=30×1000=30,000kg The transverse shift of mass (d) = 6.0 meters Pendulum length (L) = 6.0 meters Pendulum deflection (x) = 30 cm = 0.30 meters Step 1: Formula for Metacentric Height…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License