
(a)
The critical speed of the trommel screen.
Answer to Problem 5.11P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The diameter of trommel screen is
The length of trommel screen is
The angle of inclination is
Concept Used:
Write theexpression to calculate the critical speed of trommel screen.
Here, the acceleration due to gravity is
Calculation:
Calculate the critical speed of trommel screen.
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the critical speed of trommel screen is
(b)
The type of movement of MSW in the trommel screen.
Answer to Problem 5.11P
The movement of MSW in trommel screen is cataracting.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The speed of trommelis
The feed rate is
Calculation:
The movement of MSW is determined by using the relation
Here,
Hence the movement of MSW is either cascading or cataracting.
The critical speed and the fraction of the screen occupied by the refuse are related which gives the process of movement of MSW.
Write the equation to calculate the bulk volume.
Here, the bulk volume of trommel screen is
Consider a single particle in the screen.
The following figure shows the force analysis diagram.
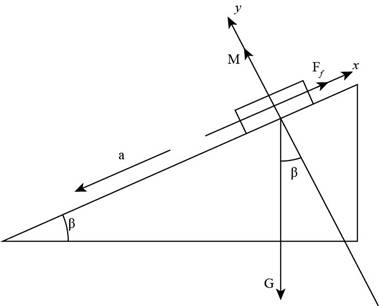
Figure-(1)
Here, gravity is
Write the equilibrium equation for the x and y axis as shown in Figure-(1).
Here, the coefficient of friction is
Write the equation to calculate acceleration.
Here, the acceleration is
Substitute
Calculate time for particle to move from end to end.
Here, the length is
Substitute
Calculate the volume occupied by the solids and the air spaces between the solids.
Here, the mass flow rate is
Convert the unit of
Convert the unit of time to
Substitute
Calculate the total volume inside the trommel screen.
Substitute
Calculate the bulk volume of trommel screen.
Substitute
The following graph shows critical speed and the fraction of the screen occupied by the refuse are related which gives the process of movement of MSW.
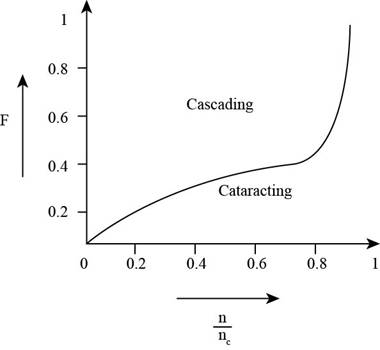
Figure-(2)
Since,
Conclusion:
The type of movement is calculated by equating time, bulk volume, mass flow, density, speed and feed rate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Solid Waste Engineering: A Global Perspective, Si Edition
- Q3: The scanning process was completed from point F to point G. The direction of the line Fl and the angles of deviation and interior are shown in the figure below. Find the direction of the remaining sides? Azimn = 60° F 52° 52° 72° R= 572.958/D ° T-R tan(A/2) • LC 2R sin (A/2) • E-R (sec(A/2)-1) • M-R (1-cos (A/2)) L= 10 A/D •C=2R sin(2D/2) • d=Dc/10 c' 2R sin (d/2) • Y= √√R2-X2-K • K= R2- K=R-M G H معادلات :مفيدةarrow_forwardPlease write me Background Reviews;arrow_forwardQ1/ The specific gravity of the soil is 1.41 percentage of water content by weight at field capacity and wilting point are 15% and 7% respectively calculate the equivalent moisture content as equivalent depth for 1.2m root zone : 1. at permanent wilting point 2. at field capacity 3. for ready available waterarrow_forward
- Kindy explain the pie chart percentage and give some related study and references about Value of travel time connected to the pie chartarrow_forwardConsider the specifications for an asphaltic concrete mixture and the results of a sieve analysis below. Coarse aggregates: Fine aggregates: Filler: 60% 35% 5% Percent of Weight of Aggregate or Filler Passing Sieve Designation Retained on Sieve Designation Coarse Aggregate Fine Aggregate Mineral Filler 3/4 in. (19 mm) 1/2 in. 6 1/2 in. (12.5 mm) 3/8 in. 15 3/8 in. (9.5 mm) No. 4 50 - No. 4 (4.75 mm) No. 10 20 1 No. 10 (2 mm) No. 40 (0.425 mm) No. 40 9 35 - No. 80 31 40 No. 80 (0.180 mm) No. 200 (0.075 mm) Total No. 200 - 33 - - 25 35 100 100 100 Determine the proportion of different aggregates to obtain the required gradation. Percent of Total Weight of Mixture Passing Sieve Designation Retained on Sieve Designation Coarse Aggregate Fine Aggregate 3/4 in. (19 mm) 1/2 in. (12.5 mm) 3/8 in. (9.5 mm) 1/2 in. 3/8 in. No. 4 No. 4 (4.75 mm) No. 10 No. 10 (2 mm) No. 40 No. 40 (0.425 mm) No. 80 No. 80 (0.180 mm) No. 200 No. 200 (0.075 mm) Total Need Help? Read It Mineral Filler Total 100arrow_forwardResults obtained from laboratory tests on a sample of RC-250 asphalt cement are given. Determine whether the properties of this material meet the Asphalt Institute specifications for this type of material; if not, note the differences. (For each specification, enter the minimum acceptab value in the same units as used in the test results.) • Kinematic viscosity at 140°F (60°C) = 230 centistokes • Flash point (Tagliabue open cup) = 89°F • Distillation test where distillate percent by volume of total distillate to 680°F (360ºC) • To 437°F (225°C) = 27% • To 500°F (260°C) = 69% • To 600°F (316°C) = 72% • Residue from distillation to 680°F (360°C) by volume percentage of sample by difference • Tests on Residue from Distillation: • Ductility at 77°F (25°C) = 92 cm • Absolute viscosity at 140°F (60°C) = 620 poises ⚫ Solubility = 90% Property Kinematic Viscosity = 74% Specification Test Results Were Specifications Met? centistokes 230 centistokes ---Select--- ✓ Flash Point °F 89°F…arrow_forward
- Problem 2 Two machines produce rivets for a factory job. The number of sub-standard rivets per hour by the two machines are random variables, denoted by X1 and X2. The bivariate PMF of X1 and X2, Px,x,(x1,x2), is given in the table below. X2=0 X2=1 X2=2 X2=3 X₁-0 0.07 0.05 0.02 0.01 X₁ =1 0.05 0.16 0.12 0.02 X₁ =2 0.02 0.12 0.17 0.05 X₁ =3 0.01 0.01 0.05 0.07arrow_forwardPlease provide a handwritten solution to the questionarrow_forwardPlease solve the question by hand with a detailed explanation of the steps.arrow_forward
- Please provide a handwritten solution to the questionarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardAS Q1/ The specific gravity of the soil is 1.41 percentage of water content by weight at field capacity and wilting point are 15% and 7% respectively calculate the equivalent moisture content as equivalent depth for 1.2m root zone : 1. at permanent wilting point 2. at field capacity 3. for ready available waterarrow_forward
 Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,
Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,





