
A block of mass m = 2.00 kg rests on the left edge of a block of mass M = 8.00 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the two blocks is 0.300, and the surface on which the 8.00-kg block rests is frictionless. A constant horizontal force of magnitude F = 10.0 N is applied to the 2.00-kg block, setting it in motion as shown in Figure P5.103a. If the distance L that the leading edge of the smaller block, travels on the larger block is 3.00 m. (a) in what lime interval will the smaller block make it to the right side of the 8.00-kg block as shown in Figure P5.103b? (Note: Both blocks are set into motion when
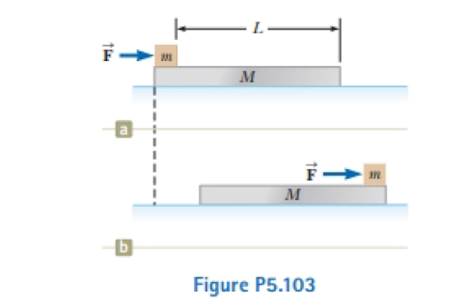
(a)
The time interval small block make it to the right of the larger block.
Answer to Problem 5.103CP
The time interval small block make it to the right of the larger block is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The mass of the smaller block is
The acceleration due to gravity is
The net force in
Here,
The frictional force between the smaller block and the larger block is,
Here,
Substitute
The net force in
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the acceleration of the smaller block is
For the larger block,
The net force in
The force
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the acceleration of the larger block is
Consider
From the second equation of motion the distance moved by the smaller block in time
The initial speed of the smaller block is
Substitute
From the second equation of motion the distance moved by the larger block in time
The initial speed of the larger block is
Substitute
For the smaller block to reach the right edge of the larger block,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange the above equation for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the time interval small block make it to the right of the larger block is
(b)
The distance the larger block moves in the process.
Answer to Problem 5.103CP
The larger block moves
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The mass of the smaller block is
The acceleration due to gravity is
From part (a) the distance the larger block moves in the process is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the larger block moves
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- Please solve this problem correctly please and be sure to provide explanation on each step so I can understand what's been done thank you. (preferrably type out everything)arrow_forwardUse a calculation to determine how far the fishing boat is from the water level .Determine distance Yarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forward
- 2. 1. Tube Rating Charts Name: Directions: For the given information state if the technique is safe or unsafe and why. 60 Hertz Stator Operation Effective Focal Spot Size- 0.6 mm Peak Kilovolts MA 2 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 2501 60 50 40 30 .01 .02 .04.06 .1 .2 .4.6 1 8 10 Maximum Exposure Time In Seconds Is an exposure of 80 kVp, 0.1 second and 200 mA within the limits of the single phase, 0.6 mm focal spot tube rating chart above? Is an exposure of 100 kVp, 0.9 second and 150 mA within the limits of the single phase, 0.6 mm focal spot tube rating chart above?arrow_forwardQ: You have a CO2 laser resonator (λ = 10.6 μm). It has two curved mirrors with R₁=10m, R2= 8m, and mirror separation /= 5m. Find: R2-10 m tl Z-O 12 R1-8 m 1. Confocal parameter. b= 21w2/2 =√1 (R1-1)(R2-1)(R1+R2-21)/R1+R2-21) 2. Beam waist at t₁ & t2- 3. Waist radius (wo). 4. 5. The radius of the laser beam outside the resonator and about 0.5m from R₂- Divergence angle. 6. Radius of curvature for phase front on the mirrors R₁ & R2-arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





