
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The volume of each solution that contains the given amount and strength of the solute that is 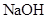 have to determine.
have to determine.
Concept introduction:
The concentration of any solution is mean the amount of solute present in the specific volume of the solvent. Now the amount of solute present in the solution is expressed by different units like: gram, gram-equivalent, gram-mole or mole etc. The amount of solvent to prepare the solution can be expressed in terms of weight or volume. The different unit of expression the concentration of a solution are- percentage strength, normality, molarity, molality, formality, gram per litter, mole fraction, parts per million etc.
- Molarity: In per litter (1000 mL or 1000 cc) volume of any solution the amount of solute present in gram-mole is called the molarity of the solution. It is expressed by ‘M’. Like- If in 1 L of H2SO4 solution 2 gm-mole of the pure H2SO4 is present then the strength of the solution will be 2M. It can be expressed as-
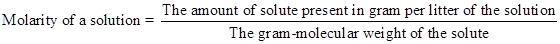
The equation can be simplified as,

The equation can be rewritten as-
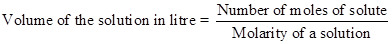
(b)
Interpretation:
The volume of each solution contains the given amount and strength of the solute that is 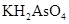 have to determine.
have to determine.
Concept introduction:
The concentration of any solution is mean the amount of solute present in the specific volume of the solvent. Now the amount of solute present in the solution is expressed by different units like: gram, gram-equivalent, gram-mole or mole etc. The amount of solvent to prepare the solution can be expressed in terms of weight or volume. The different unit of expression the concentration of a solution are- percentage strength, normality, molarity, molality, formality, gram per litter, mole fraction, parts per million etc.
- Molarity: In per litter (1000 mL or 1000 cc) volume of any solution the amount of solute present in gram-mole is called the molarity of the solution. It is expressed by ‘M’. Like- If in 1 L of H2SO4 solution 2 gm-mole of the pure H2SO4 is present then the strength of the solution will be 2M. It can be expressed as-
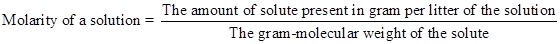
The equation can be alternatively written as- 
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry For Changing Times (14th Edition)
- a. OH H₂N-O -Ph H+ acyclic productarrow_forwardeks.com/aleksogi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS17Hd6m-HIl6n52njJN-TXdQA2X9yID-1SWQJTgnjARg30 111 States of Matter Understanding conceptual components of the enthalpy of solution 0/5 Ge A small amount of acetonitrile (CH, CN) is dissolved in a large amount of water. Imagine separating this process into the four stages sketched below. (These sketches show only a portion of the substances, so you can see the density and distribution of atoms and molecules in them.) CH,CN H₂O B 88 C Use these sketches to answer the questions in the table below. The enthalpy of solution AH is negative soln when CH3CN dissolves in water. Use this information to list the stages in order of increasing enthalpy. Would heat be absorbed or released if the system moved from Stage C to D? What force would oppose or favor the system moving from Stage C to D? Check all that apply. 1 absorbed O released neither absorbed nor released. none O ionic bonding force covalent bonding force…arrow_forwardIn a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of ŋ as a function of the current density: 1. at low fields is linear 2. at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law Find the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value as when calculated for cases 1 and 2 (maximum relative difference of 5% with respect to the behavior for higher fields). To which overpotential range does this correspond? Data: 10 = 1.5 mA cm², T = 300°C, ẞ = 0.64, R = 8.314 J K 1 mol¹ and F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forward
- Indicate 10.6 with only one significant figure.arrow_forwardIf I have 10 data points for variables x and y, when I represent y versus x I obtain a line with the equation y = mx + b. Is the slope m equal to dy/dx?arrow_forwardThe data for the potential difference of a battery and its temperature are given in the table. Calculate the entropy change in J mol-1 K-1 (indicate the formulas used).Data: F = 96485 C mol-1arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





