
Concept explainers
Perpetual: Alternative cost flows
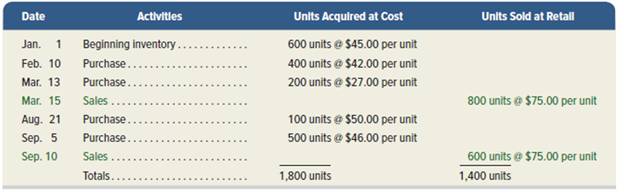
Montoure Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following calendar-year purchases and sales transactions. (For specific identification, units sold consist of 600 units from beginning inventory, 300 from the February 10 purchase, 200 from the March 13 purchase, 50 from the August 21 purchase, and 250 from the September 5 purchase.)
Required
- Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale.
- Compute the number of units in ending inventory.
- Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using(a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification.(Round all amounts to cents.)
Check (3) Ending inventory: FIFO, $18,400; LIFO, $18,000; WA, $17,760 - Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3.
(4) LIFO gross profit, $45,800 Analysis Component
- The company's manager earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit. Which method of inventory costing produces the highest bonus for the manager?
Inventory:
Inventory refers to the stock or goods which will be sold in the near future and thus is an asset for the company. It comprises of the raw materials which are yet to be processed, the stock which is still going through the process of production and it also includes completed products that are ready for sale. Thus inventory is the biggest and the important source of income and profit for the business.
Perpetual Inventory System:
In perpetual inventory system there is a continuous recording of transactions as and when they take place that is purchase and sale transactions are recorded whenever they occur.
Cost of Goods Available for Sale:
It basically includes the cost of inventory which is ready for sale within an accounting period. It mainly includes the cost of beginning inventory as well as the stock purchased in that year and the production within that period (if any).
Cost of Goods Sold:
Cost of goods sold is the total expenses or the cost incurred by the business during the process of manufacturing of goods and is directly related to the production. It generally includes the cost of raw material, labor and other manufacturing support costs.
Gross Profit:
The profit made after subtracting or debiting the costs related to the goods sold from the total revenue earned or made through sales in a fiscal year is the gross profit.
First in First out:
In case of first in, first out method, also known as FIFO method, the inventory which was bought first will also be the first one to be taken out.
Last in First out:
In case of last in, first out, also known as LIFO method, the inventory which was bought in the last will be taken out first.
Weighted Average Cost Method:
In this method the weighted average cost is evaluated after any purchases have been made and transactions are recorded as when purchase or sales take place.
Specific Identification Method:
Under this method, there is a continuous tracking of the inventory and the inventory cost at the time of purchase on the basis of unique identity which thus helps in the valuation of the ending inventory as well as the cost of goods sold. This method is used generally when the company is involved in limited expensive goods which are easily identifiable.
To compute: 1. Cost of goods available for sale and number of units available for sale.
2. Number of units in ending inventory.
3. Cost of ending inventory under the following methods
(a) FIFO
(b)LIFO
(c) Weighted average
(d) Specific identification
4. Gross profit for each of the four methods in part
5. The inventory costing method suitable incase of bonus earned on gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Given info,
| Date | Particulars | Units acquired | Cost per unit ($) | Units sold | Retail price per unit ($) |
| Jan 1 | Beginning inventory | 600 | 45 | ||
| Feb 10 | Purchase | 400 | 42 | ||
| Mar 13 | Purchase | 200 | 27 | 800 | 75 |
| Mar 15 | Sales | ||||
| Aug 21 | Purchase | 100 | 50 | ||
| Sept 5 | Purchase | 500 | 46 | 600 | 75 |
| Sept 10 | Sales | ||||
| Total | 1,800 | 1,400 |
Table (1)
Given,
The ending inventory has,
100 units are from Feb 10,
50 units are from August 21 and
250 units are from September 5.
1.
Cost of goods available for sale
Formula to calculate Cost of goods available for sale is,
Cost and units of goods available for sale:
| Particulars | Number of units | Cost per unit($) | Amount($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 600 | 45 | 27,000 |
| Purchases: | |||
| Feb 10 | 400 | 42 | 16,800 |
| March 13 | 200 | 27 | 5,400 |
| August 21 | 100 | 50 | 5,000 |
| September 5 | 500 | 46 | 23,000 |
| Total Purchases | 1,200 | 50,200 | |
| Available for sale | 1,800 | 77,200 |
Table (2)
The cost of goods available for sale is $77,200 and the number of units available for sale is 1,800 units.
2.
Number of units in ending inventory
| Particulars | Number of units |
| Number of units available for sale (given) | 1,800 |
| Less: units sold (given) | 1,400 |
| Number of units in ending inventory | 400 |
Table (3)
The number of units in ending inventory is 400 units.
(a)
First in, First out method (FIFO)
Ending inventory
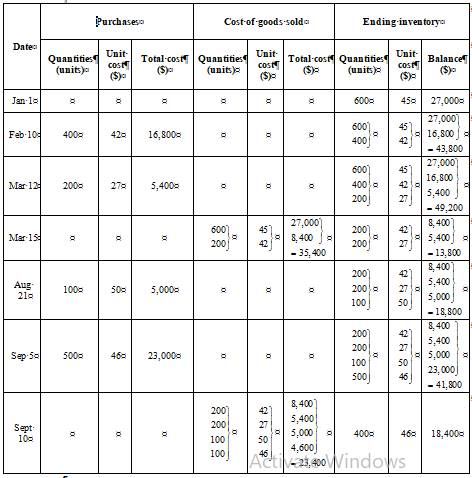
Table (4)
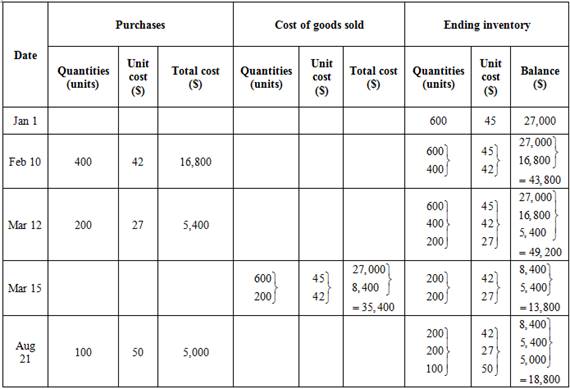
Table (5)
Cost of goods sold
Formula to calculate cost of goods sold is,
Substitute $77,200 for cost of goods available for sale (calculated in part (1)) and $18,400 for cost of ending inventory (as calculated above in the table) in the above formula.
Under FIFO method, the amount of ending inventory is $18,400 and cost of goods sold is $58,800.
(b)
Last in, first out method (LIFO)
Ending inventory
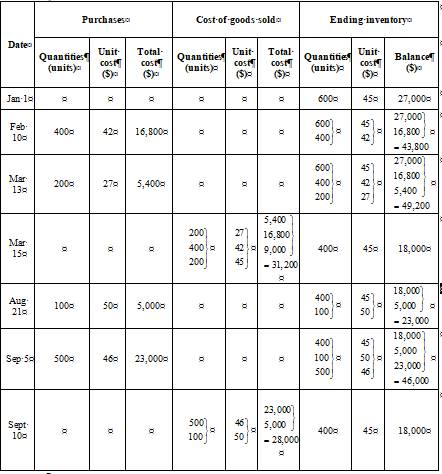
Table (6)
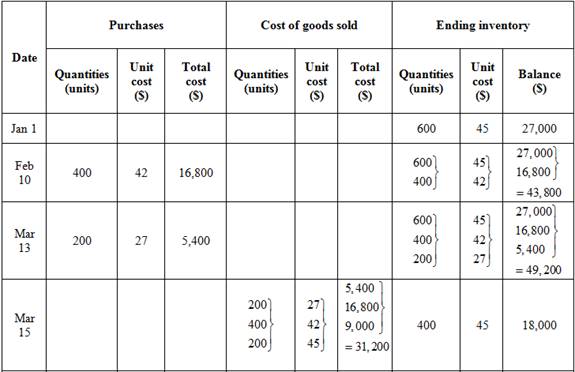
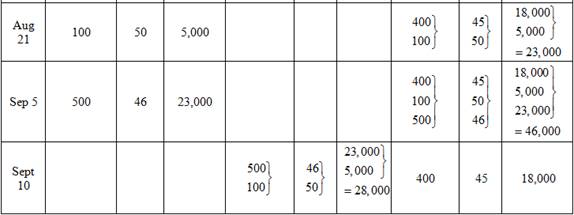
Table (7)
Cost of goods sold
Formula to calculate cost of goods sold is,
Substitute $77,200 for cost of goods available for sale (calculated in part (1)) and $18,000 for cost of ending inventory (as calculated above in the table) in the above formula.
Under FIFO method, the amount of ending inventory is $18,000 and cost of goods sold is $59,200.
(c)
Weighted average method
Ending inventory
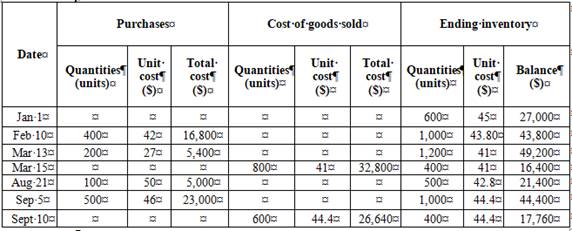
Table (8)
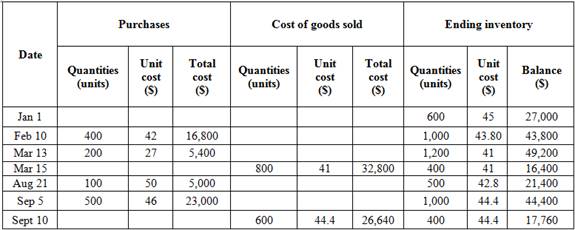
Table (9)
Working notes:
Calculation of weighted average cost per unit,
Cost of goods sold
Formula to calculate cost of goods sold is,
Substitute $77,200 for cost of goods available for sale (calculated in part (1)) and $17,760 for cost of ending inventory (as calculated above in the table) in the above formula.
Under weighted average method, the amount of ending inventory is $17,760 and cost of goods sold is $59,440.
(d)
Specific identification method
Cost of Ending Inventory
| Date of Purchase | Number of units(A) | Cost per unit($)(B) | Amount($) |
| Feb 10 | 100 | 42 | 4,200 |
| August 21 | 50 | 50 | 2,500 |
| September 5 | 250 | 46 | 11,500 |
| Cost of Ending Inventory | 18,200 |
Table (10)
Cost of goods sold
Formula to calculate cost of goods sold is,
Substitute $77,200 for cost of goods available for sale (calculated in part (1)) and $18,200 for cost of ending inventory (calculated above in the table) in the above formula.
The cost of ending inventory is $18,200 and the cost of goods sold is $59,000.
(4)
Sales are $105,000 (working notes).
Cost of goods sold in case of FIFO is $58,800. (Calculated in part (3(a))
Cost of goods sold in case LIFO is $59,200. (Calculated in part (3(b))
Cost of goods sold in case of weighted average is $59,440 and (Calculated in part (3(c))
Cost of goods sold in case of specific identification is 59,000. (Calculated in part (3(d))
Gross Profit
Formula to calculate gross profit is,
| Particulars | FIFO($) | LIFO($) | Weighted average($) | Specific identification($) |
| Sales(working notes) | 105,000 | 105,000 | 105,000 | 105,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | 58,800 | 59,200 | 59,440 | 59,000 |
| Gross profit | 46,200 | 45,800 | 45,560 | 46,000 |
Table (11)
Working notes:
Calculation of sales,
The gross profit in case of FIFO it is $46,200, of LIFO it is $45,800, of weighted average it is $45,560 and of specific identification it is $46,000.
5.
FIFO inventory method resulted in highest gross profit that is $46,200 as compared to other four methods. The bonus will be more on the highest gross profit made by the company and herein it is the FIFO method which resulted in the highest gross profit.
Thus, the FIFO method is the best to earn more bonus on the gross profit.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCT.FUND.(LOOSELEAF)
- I need help finding the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardPlease explain the accurate process for solving this financial accounting question with proper principles.arrow_forwardI need guidance with this financial accounting problem using the right financial principles.arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardPlease show me the correct way to solve this financial accounting problem with accurate methods.arrow_forwardI need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning





