
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Whether the indicated cyclohexane derivative is chiral or not should be identified.
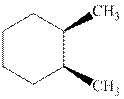
Concept introduction: Four kinds of symmetry elements that may be present are tabulated as follows:
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(b)
Interpretation: Whether the indicated cyclohexane derivative is chiral or not should be identified.
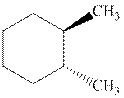
Concept introduction: Four kinds of symmetry elements that may be present are tabulated as follows:
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(c)
Interpretation: Whether the indicated cyclohexane derivative is chiral or not should be identified.
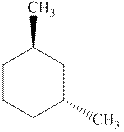
Concept introduction: Four kinds of symmetry elements that may be present are tabulated as follows:
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(d)
Interpretation: Whether the indicated cyclohexane derivative is chiral or not should be identified.
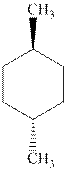
Concept introduction: Four kinds of symmetry elements that may be present are tabulated as follows:
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-PACKAGE
- Which synthesis of a Grignard reagent would fail to occur as written? Why is the correct answer D? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the major organic product(s) of the reaction. H3C 1. DIBAH, toluene -CH3 + 2. H3O DIBAH = diisobutylaluminum hydride, [(CH3)2CHCH2]2AIHarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not an intermediate of the reaction below? Why is the correct answer C? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forward
- Which of the following is the product of the reaction between acetone, CH3COCH3 and methyl amine, CH3NH2? Why is the correct answer A? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the reaction shown below? Why is the correct answer D? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure name П O ☐ O ☐ Oarrow_forward
- The 13C NMR signal for which of the indicated carbons will occur at the frequency (most deshielded)? Why is the correct answer E? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation needed to understand the or question.arrow_forwardWhich of the following reagents best achieves the reaction shown below? Why is the correct answer B? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction sequence? Why is the correct answer D? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forwardThe reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide (C6H5MgBr) with propanal (CH3CH2CHO)3 followed by hydrolysis yields. A. 2-phenyl-1-propanol B. 1-phenyl-1propanol C. 3-phenyl-2-propanol D. 3-phenyl-1-propanol Why is the correct answer B? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and/or a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the reaction sequence below? Why is the correct answer D? Please explain what is happening. Please include a detailed explanation and a drawing of steps needed to understand the reaction or question. The part that is under the pen in the image is (1) CH3CHO (2) H3O+arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

