
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 33P
What is the minimum downward force on the box in Figure P5.30 that will keep it from slipping? The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the box and the floor are 0.35 and 0.25, respectively.
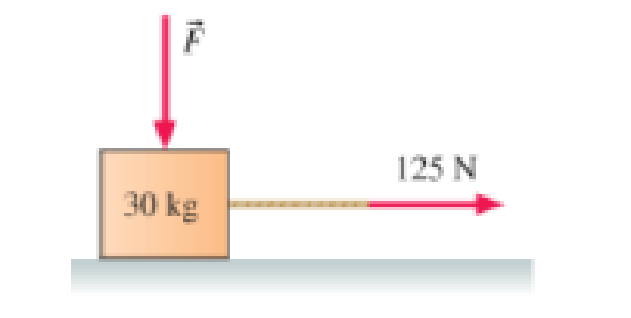
Figure P5.33
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
At what temperature would water boil if the outside pressure was only 19,900 Pa in degrees Celsius?
Which of these properties of a sound wave is associated with the pitch of the sound that we hear?
amplitudefrequency intensity levelintensity
A wave travels upward in a medium (vertical wave velocity). What is the direction of particle oscillation for the following?
(a)
a longitudinal wave
parallel to the direction of propagationperpendicular to the direction of propagation
Chapter 5 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 5 - An object is subject to two forces that do not...Ch. 5 - Are the objects described here in static...Ch. 5 - What forces are acting on you right now? What net...Ch. 5 - Decide whether each of the following is true or...Ch. 5 - An astronaut takes his bathroom scale to the moon...Ch. 5 - A light block of mass m and a heavy block of mass...Ch. 5 - a. Can the normal force on an object be directed...Ch. 5 - A ball is thrown straight up. Taking the drag...Ch. 5 - You are going sledding with your friends, sliding...Ch. 5 - Suppose you are holding a box in front of you and...
Ch. 5 - You are walking up an icy slope. Suddenly your...Ch. 5 - Three objects move through the air as shown in...Ch. 5 - A skydiver is falling at her terminal speed. Right...Ch. 5 - Raindrops can fall at different speeds; some fall...Ch. 5 - An airplane moves through the air at a constant...Ch. 5 - Is it possible for an object to travel in air...Ch. 5 - For Questions 17 through 20, determine the tension...Ch. 5 - For Questions 17 through 20, determine the tension...Ch. 5 - For Questions 17 through 20, determine the tension...Ch. 5 - For Questions 17 through 20, determine the tension...Ch. 5 - In Figure Q5.21, block 2 is moving to the right....Ch. 5 - The wood block in Figure Q5.22 is at rest on a...Ch. 5 - A 2.0 kg ball is suspended by two light strings as...Ch. 5 - While standing in a low tunnel, you raise your...Ch. 5 - A 5.0 kg dog sits on the floor of an elevator that...Ch. 5 - A 3.0 kg puck slides due east on a horizontal...Ch. 5 - Eric has a mass of 60 kg. He is standing on a...Ch. 5 - The two blocks in Figure Q5.28 are at rest on...Ch. 5 - A football player at practice pushes a 60 kg...Ch. 5 - Two football players are pushing a 60 kg blocking...Ch. 5 - Land Rover ads used to claim that their vehicles...Ch. 5 - A truck is traveling at 30 m/s on a slippery road....Ch. 5 - The three ropes in Figure P5.1 are tied to a...Ch. 5 - The three ropes in Figure P5.2 are tied to a...Ch. 5 - A 20 kg loudspeaker is suspended 2.0 m below the...Ch. 5 - A construction crew would like to support a 1000...Ch. 5 - When you bend your knee, the quadriceps muscle is...Ch. 5 - An early submersible craft for deep-sea...Ch. 5 - The two angled ropes are used to support the crate...Ch. 5 - A 65 kg student is walking on a slackline, a...Ch. 5 - Section 5.2 Dynamics and Newtons Second Law 9. A...Ch. 5 - The forces in Figure P5.10 are acting on a 2.0 kg...Ch. 5 - The forces in Figure P5.11 are acting on a 2.0 kg...Ch. 5 - A horizontal rope is tied to a 50 kg box on...Ch. 5 - A crate pushed along the floor with velocity vi...Ch. 5 - In a head-on collision, a car stops in 0.10 s from...Ch. 5 - An astronauts weight on earth is 800 N. What is...Ch. 5 - A woman has a mass of 55.0 kg. a. What is her...Ch. 5 - A 75 kg passenger is seated in a cage in the Sling...Ch. 5 - a. How much force does an 80 kg astronaut exert on...Ch. 5 - It takes the elevator in a skyscraper 4.0 s to...Ch. 5 - Riders on the Power Tower are launched skyward...Ch. 5 - Zach, whose mass is 80 kg, is in an elevator...Ch. 5 - A kangaroo carries her 0.51 kg baby in her pouch...Ch. 5 - Figure P5.23 shows the velocity graph of a 75 kg...Ch. 5 - a. A 0.60 kg bullfrog is sitting at rest on a...Ch. 5 - A 23 kg child goes down a straight slide inclined...Ch. 5 - Two workers are sliding a 300 kg crate across the...Ch. 5 - A 4000 kg truck is parked on a 7.0 slope. How big...Ch. 5 - A 1000 kg car traveling at a speed of 40 m/s skids...Ch. 5 - A stubborn 120 kg pig sits down and refuses to...Ch. 5 - It is friction that provides the force for a car...Ch. 5 - The rolling resistance for steel on steel is quite...Ch. 5 - What is the minimum downward force on the box in...Ch. 5 - What is the drag force on a 1.6-m-wide, 1.4-m-high...Ch. 5 - A 22-cm-diameter bowling ball has a terminal speed...Ch. 5 - Running on a treadmill is slightly easier than...Ch. 5 - A 75 kg skydiver can be modeled as a rectangular...Ch. 5 - The air is less dense at higher elevations, so...Ch. 5 - A 1000 kg car pushes a 2000 kg truck that has a...Ch. 5 - A 2200 kg truck has put its front bumper against...Ch. 5 - Blocks with masses of 1.0 kg, 2.0 kg, and 3.0 kg...Ch. 5 - What is the tension in the rope of Figure P5.42...Ch. 5 - A 2.0-m-long, 500 grope pulls a 10 kg block of ice...Ch. 5 - Each of 100 identical blocks sitting on a...Ch. 5 - Two blocks on a frictionless table, A and B, are...Ch. 5 - A 500 kg piano is being lowered into position by a...Ch. 5 - Dana has a sports medal suspended by a long ribbon...Ch. 5 - Figure P5.49 shows the velocity graph of a 2.0 kg...Ch. 5 - Your forehead can withstand a force of about 6.0...Ch. 5 - A 50 kg box hangs from a rope. What is the tension...Ch. 5 - A fisherman has caught a very large, 5.0 kg fish...Ch. 5 - A 50 kg box hangs from a rope. What is the tension...Ch. 5 - Riders on the Tower of Doom, an amusement park...Ch. 5 - Seat belts and air bags save lives by reducing the...Ch. 5 - Elite quarterbacks can throw a football 70 m. To...Ch. 5 - A 20,000 kg rocket has a rocket motor that...Ch. 5 - Youve always wondered about the acceleration of...Ch. 5 - A 23 kg child goes down a straight slide inclined...Ch. 5 - An impala is an African antelope capable of a...Ch. 5 - Josh starts his sled at the top of a 3.0-m-high...Ch. 5 - The drag force is an important fact of life for...Ch. 5 - A wood block, after being given a starting push,...Ch. 5 - Researchers often use force plates to measure the...Ch. 5 - A person with compromised pinch strength in his...Ch. 5 - Its possible for a determined group of people to...Ch. 5 - A 1.0 kg wood block is pressed against a vertical...Ch. 5 - Two blocks are at rest on a frictionless incline,...Ch. 5 - Running indoors on a treadmill is slightly easier...Ch. 5 - Two identical 2.0 kg blocks are stacked as shown...Ch. 5 - A wood block is sliding up a wood ramp. If the...Ch. 5 - A 2.7 g Ping-Pong ball has a diameter of 4.0 cm....Ch. 5 - Two blocks are connected by a string as in Figure...Ch. 5 - The ramp in Figure P5.75 is frictionless. If the...Ch. 5 - The 100 kg block in Figure P5.76 takes 6.0 s to...Ch. 5 - MCAT-Style Passage Problems Sliding on the Ice In...Ch. 5 - MCAT-Style Passage Problems Sliding on the Ice In...Ch. 5 - MCAT-Style Passage Problems Sliding on the Ice In...Ch. 5 - MCAT-Style Passage Problems Sliding on the Ice In...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
25. The 100 kg block in FIGURE EX7.25 takes 6.0 s to reach the floor after being released from rest. What is th...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
95. What is the minimum amount of necessary to produce 15.0 g of according to the reaction:
...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Which one of the following is not a fuel produced by microorganisms? a. algal oil b. ethanol c. hydrogen d. met...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Acetobacter is necessary for only one of the steps of vitamin C manufacture. The easiest way to accomplish this...
Microbiology: An Introduction
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Why is petroleum jelly used in the hanging-drop procedure?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The faster a molecule is moving in the upper atmosphere, the more likely it is to escape Earth's gravity. Given this fact, and your knowledge of rms speed, which of the following molecules can escape most easily from Earth's atmosphere if they are all at the same temperature?arrow_forwardThe temperature in one part of a flame is 2,100 K. What is the rms velocity of the carbon dioxide molecules at this temperature? Give your answer as the number of meters per second. mass of 1 mole of CO2 = 44.0 grams 1 mole contains 6.02 x 1023 molecules the Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/Karrow_forwardThe specific heat of a certain substance is 375 J/(kg°C). How much heat energy would you have to add to increase the temperature of 22 kg of this substance from 33°C up to 44°C in a number of Joules?arrow_forward
- 3.9 moles of an ideal gas are sealed in a container with volume 0.22 m3, at a pressure of 146,000 N/m2. What is the temperature of the gas in degrees Celsius?arrow_forwardwhen a cannon is launched at a 65 degree angle, will it have the same horizontal velocity as when it is launched from a 25 degree angle as long as the initial speed is the same?arrow_forwardPlease solve the problem step by step and provide explanations along each step stating what's being done. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Figure 8.14 shows a cube at rest and a small object heading toward it. (a) Describe the directions (angle 1) at which the small object can emerge after colliding elastically with the cube. How does 1 depend on b, the so-called impact parameter? Ignore any effects that might be due to rotation after the collision, and assume that the cube is much more massive than the small object. (b) Answer the same questions if the small object instead collides with a massive sphere.arrow_forward2. A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle 0,, with an initial velocity magnitude vo, from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile hits an apple atop a child's noggin (see Figure 1). The apple is a height y above the tabletop, and a horizontal distance x from the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for x. That is, determine an expression for x in terms of only v₁, 0, y and g. Actually, this is quite a long expression. So, if you want, you can determine an expression for x in terms of v., 0., and time t, and determine another expression for timet (in terms of v., 0.,y and g) that you will solve and then substitute the value of t into the expression for x. Your final equation(s) will be called Equation 3 (and Equation 4).arrow_forwardDraw a phase portrait for an oscillating, damped spring.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's First Law of Motion: Mass and Inertia; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XSyyjcEHo0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY