
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134110684
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 32EAP
A single force with x-component Fxacts on a 500 g object as it moves along the x-axis. A graph of Fxversus t is shown in FIGURE PS.32. Draw an acceleration graph (axversus t) for this object.
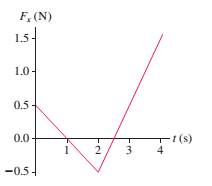
FIGURE PS.32
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Ch. 5 - An elevator suspended by a cable is descending at...Ch. 5 - A compressed spring is pushing a block across a...Ch. 5 - A brick is falling from the roof of a three-story...Ch. 5 - In FIGURE Q5.4 block B is falling and dragging...Ch. 5 - You toss a ball straight up in the air....Ch. 5 - A constant force applied to A causes A to...Ch. 5 - An object experiencing a constant force...Ch. 5 - An object experiencing a constant force...Ch. 5 - If an object is at rest, can you conclude that...Ch. 5 - If a force is exerted on an object, is it possible...
Ch. 5 - Is the statement “An object always moves in the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 12CQCh. 5 -
13. Is it possible for the friction force on an...Ch. 5 -
14. Suppose you press your physics book against...Ch. 5 - FIGURE Q5.15 shows a hollow tube forming...Ch. 5 - Prob. 16CQCh. 5 - Which of the following are inertial reference...Ch. 5 - Prob. 1EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 2EAPCh. 5 - A baseball player is sliding into second base....Ch. 5 - Prob. 4EAPCh. 5 -
5. An arrow has just been shot from a bow and is...Ch. 5 - Two rubber bands cause an object to accelerate...Ch. 5 - Two rubber bands pulling on an object cause it to...Ch. 5 - FIGURE EX5.8 shows acceleration-versus-force graph...Ch. 5 - Prob. 9EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 10EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 11EAPCh. 5 - FIGURE EX5.12 shows an acceleration-versus-force...Ch. 5 - Prob. 13EAPCh. 5 -
14. FIGURE EX5.14 shows the acceleration of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 15EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 16EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 17EAPCh. 5 - Exercise 17 trough 19 show two of the three forces...Ch. 5 - Exercise 17 trough 19 show two of the three forces...Ch. 5 - Prob. 20EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 5 - Exercise 23 through 27 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Exercise 23 through 27 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 -
Exercise 23 through 27 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 -
Exercise 23 through 27 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Exercise 23 through 27 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 31EAPCh. 5 - A single force with x-component Fxacts on a 500 g...Ch. 5 - A constant force is applied to an object, causing...Ch. 5 - A constant force is applied to an object, causing...Ch. 5 - Problem 35 through 40 show a free-body diagram....Ch. 5 - through 40 show a free-body diagram. For each:...Ch. 5 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 5 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 5 - Problem 35 through 40 show a free-body diagram....Ch. 5 - Problem 35 through 40 show a free-body diagram....Ch. 5 - In lab, you propel a cart with four known forces...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - Problems 42 through 52 describe a situation. For...Ch. 5 - The leaf hopper, champion jumper of the insect...Ch. 5 - Prob. 54EAPCh. 5 -
55. A heavy boxy is in the back of a truck. The...Ch. 5 - If a car stops suddenly, you feel “thrown...Ch. 5 - Prob. 57EAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardhelp me with the experimental set up for the excel i did. the grapharrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes how to calculate the average acceleration of any object? Average acceleration is always halfway between the initial acceleration of an object and its final acceleration. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in velocity of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the displacement of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in speed of an object divided by the time interval.arrow_forward
- The figure shows the velocity versus time graph for a car driving on a straight road. Which of the following best describes the acceleration of the car? v (m/s) t(s) The acceleration of the car is negative and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is constant. The acceleration of the car is positive and increasing. The acceleration of the car is positive and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is negative and increasing.arrow_forwardWhich figure could represent the velocity versus time graph of a motorcycle whose speed is increasing? v (m/s) v (m/s) t(s) t(s)arrow_forwardUnlike speed, velocity is a the statement? Poisition. Direction. Vector. Scalar. quantity. Which one of the following completesarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forward3.63 • Leaping the River II. A physics professor did daredevil stunts in his spare time. His last stunt was an attempt to jump across a river on a motorcycle (Fig. P3.63). The takeoff ramp was inclined at 53.0°, the river was 40.0 m wide, and the far bank was 15.0 m lower than the top of the ramp. The river itself was 100 m below the ramp. Ignore air resistance. (a) What should his speed have been at the top of the ramp to have just made it to the edge of the far bank? (b) If his speed was only half the value found in part (a), where did he land? Figure P3.63 53.0° 100 m 40.0 m→ 15.0 marrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams With Examples; Author: The Physics Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3rZR7FSSidc;License: Standard Youtube License