
Concept explainers
The account balances for the Patterson International Company on January 31. 2019, follow. The balances shown are after the first month of operations.
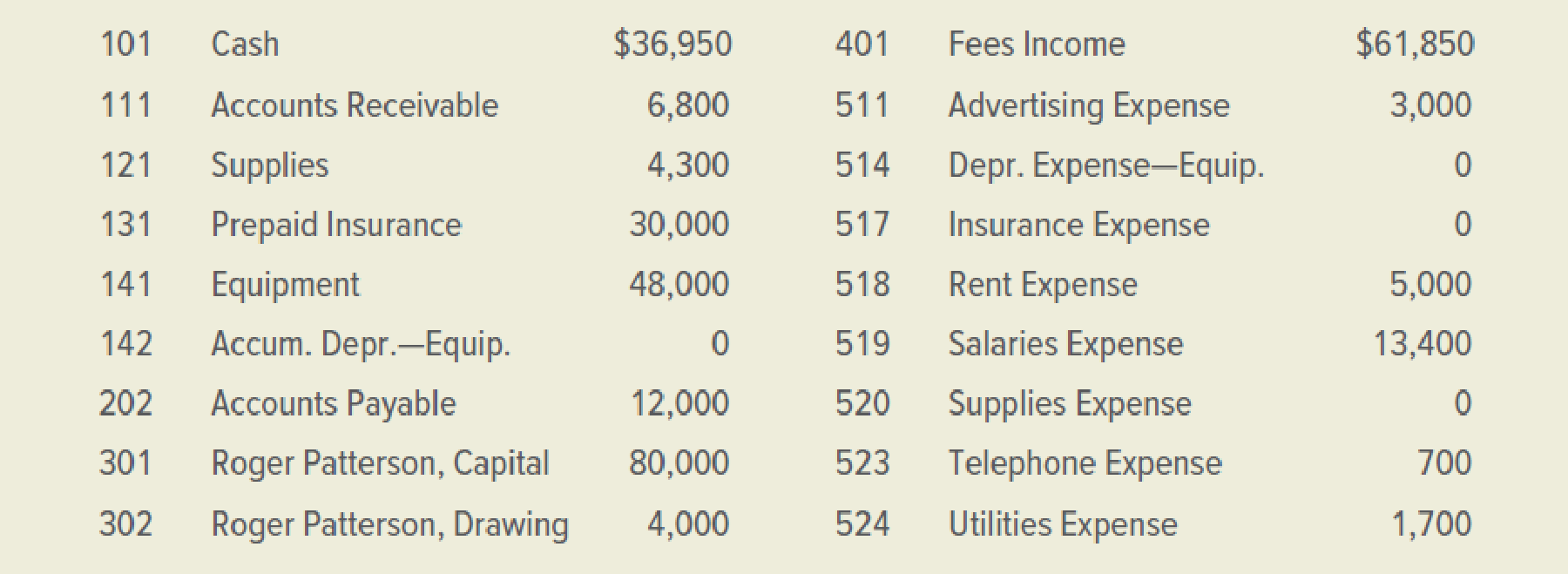
INSTRUCTIONS
- 1. Prepare the
Trial Balance section of the worksheet. - 2. Record the following adjustments in the Adjustments section of the worksheet:
- a. Supplies used during the month amounted to $2,100.
- b. The amount in the Prepaid Insurance account represents a payment made on January 1. 2019, for six months of insurance coverage.
- c. The equipment, purchased on January 1.2019, has an estimated useful life of 10 years with no salvage value. The firm uses the straight-line method of
depreciation.
- 3. Complete the worksheet.
- 4. Prepare an income statement, statement of owner’s equity, and
balance sheet (use the report form). - 5. Record the balances in the general ledger accounts, then journalize and
post the adjusting entries. Use 3 for the journal page number.
Analyze: If the useful life of the equipment had been 12 years instead of 10 years, how would net income have been affected?
1, 2 and 3.
Prepare trial balance section, indicate the given adjustments, and complete the worksheet for Company PI for the month ended January 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: Worksheet is an accounting tool that helps accountants to record adjustments and up-date balances required to prepare financial statements. Worksheet is a central place where trial balance, adjustments, adjusted trial balance, income statement, and balance sheet are presented.
Prepare trial balance section, indicate the given adjustments, and complete the worksheet for Company PI for the month ended January 31, 2019.
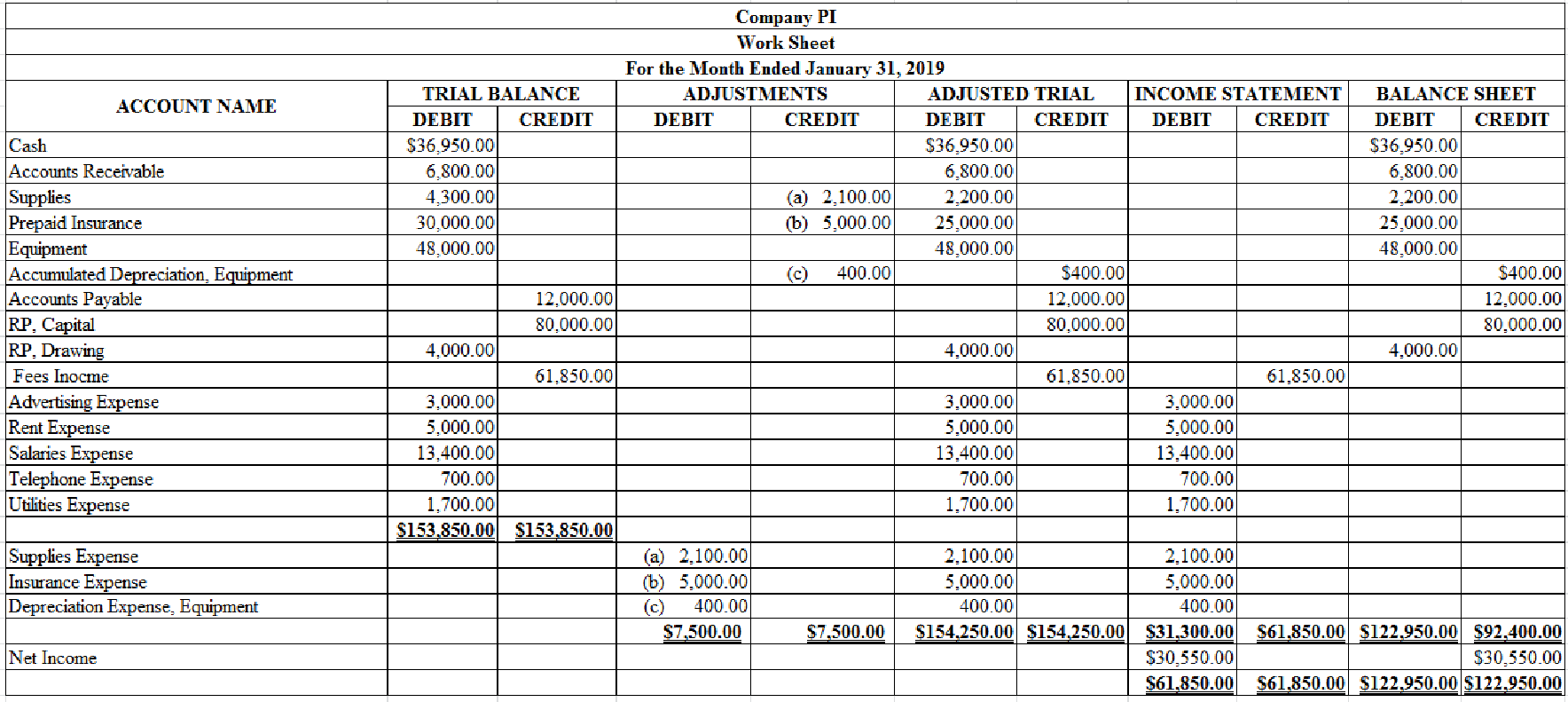
Table (1)
4.
Prepare income statement, statement of owners’ equity, and balance sheet for Company PI for the month of January, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operation and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare an income statement for Company PI for the month ended January 31, 2019.
| Company PI | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Month Ended January 31, 2019 | ||
| Revenues: | ||
| Fees Income | 61,850 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Advertising Expense | $3,000 | |
| Depreciation Expense, Equipment | 400 | |
| Rent Expense | 5,000 | |
| Salaries Expense | 13,400 | |
| Supplies Expense | 2,100 | |
| Insurance Expense | 5,000 | |
| Utilities Expense | 1,700 | |
| Telephone Expense | 700 | |
| Total expenses | 31,300 | |
| Net income | $30,550 | |
Table (2)
Statement of owners’ equity: This statement reports the beginning owner’s equity and all the changes which led to ending owners’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to, and drawings are deducted from beginning owner’s equity to arrive at the end result, ending owner’s equity.
Prepare a statement for Company PI for the month ended January 31, 2019.
| Company PI | ||
| Statement of Owners’ Equity | ||
| For the Month Ended January 31, 2019 | ||
| RP, Capital, January 1, 2019 | $80,000 | |
| Net income for January | 30,550 | |
| Less: Withdrawals for January | 4,000 | |
| Increase in capital | 26,550 | |
| RP, Capital, January 31, 2019 | $106,550 | |
Table (3)
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and owners (owners’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by owners and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity.
Prepare the balance sheet Company PI as at January 31, 2019.
| Company PI | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| January 31, 2019 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $36,950 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 6,800 | |
| Supplies | 2,200 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 25,000 | |
| Equipment | $48,000 | |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation | 400 | 47,600 |
| Total Assets | $118,550 | |
| Liabilities and owner’s equity | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | 12,000 | |
| Owners’ Equity | ||
| RP, Capital | 106,550 | |
| Total Liabilities and Owners’ Equity | $118,550 | |
Table (4)
5.
Prepare adjusting entry and post the transactions in general ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and owners’ or stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle and matching concept.
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare adjusting entry for supplies.
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 3 | |||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2019 | Supplies expense | 520 | 2,100 | |
| Supplies | 121 | 2,100 | ||
| (to record supplies used) | ||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Supplies Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Supplies is an asset account. Since amount of supplies is used, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Prepare adjusting entry for insurance expense:
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 3 | |||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2019 | Insurance expense | 517 | 5,000 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 131 | 5,000 | ||
| (to record part of prepaid insurance expired) | ||||
Table (6)
Description:
- Insurance Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Prepaid Insurance is an asset account. Since amount of insurance is expired, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Prepare adjusting entry for depreciation expense-equipment:
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 3 | |||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2019 | Depreciation expense-Equipment | 514 | 400 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Equipment | 142 | 400 | ||
| (to record depreciation expense) | ||||
Table (7)
Description:
- Depreciation Expense, Equipment is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation, Equipment is a contra-asset account, and contra-asset accounts would have a normal credit balance, hence, the account is credited.
Post the above transactions in the general ledger.
| ACCOUNT Supplies ACCOUNT NO. 121 | |||||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| January | 1 | Balance | 4,300 | 4,300 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 2,100 | 2,200 | |||
Table (8)
| ACCOUNT Prepaid Insurance ACCOUNT NO. 131 | |||||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| January | 1 | Balance | 30,000 | 30,000 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 5,000 | 25,000 | |||
Table (9)
| ACCOUNT Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment ACCOUNT NO. 142 | |||||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| January | 1 | Balance | 0 | 0 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 400 | 400 | |||
Table (10)
| ACCOUNT Depreciation Expense - Equipment ACCOUNT NO. 514 | |||||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| January | 1 | Balance | 0 | 0 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 400 | 400 | |||
Table (11)
| ACCOUNT Insurance Expense ACCOUNT NO. 517 | |||||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| January | 1 | Balance | 0 | 0 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 5,000 | 5,000 | |||
Table (12)
| ACCOUNT Supplies Expense ACCOUNT NO. 520 | |||||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| January | 1 | Balance | 0 | 0 | |||
| 31 | Adjusting | 3 | 2,100 | 2,100 | |||
Table (13)
Analyze: If the useful life of the equipment is 12 years instead of 10 years, then the depreciation expense for the month would be $334 rather than $400. As a result, the net income would increase by $66.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE ACCOUNTING ETEXT+CONNECT ACCESS
- Please explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardKindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this Financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
- I am looking for the correct answer to this Financial accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardEcho Tone Technologies reports annual sales of $90,000, and it expects sales to increase to $135,000 next year. The company has a degree of operating leverage (DOL) of 4.2. By what percentage should net income increase? A. 70% B. 189% C. 150% D. 210%arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt Which account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalarrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardI need help Which account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning - Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage



