
Use the following information from Marvel Company for the month of July to answer questions 1 through 4.
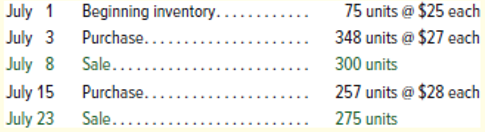
1. Perpetual: Assume that Marvel uses a perpetual FIFO inventory system. What is the dollar value of its ending inventory?
- $2,940
- $2,685
- $2,625
- $2,852
- $2,705
Perpetual Inventory System:
The perpetual inventory system is that system of accounting the inventory in which the inventory is verified physically. This is done so that the lost and misplaced items are also recorded. The entries are made through merchandise accounts.
The dollar value of the ending inventory using FIFO.
Explanation of Solution
Option a, $2,940 is correct.
Given,
The company uses perpetual FIFO inventory system.
Calculation of the value of ending inventory:
| Date | Goods purchased | Cost of goods sold | Inventory balance |
| July 1 | |||
| July 3 | 348 units | ||
| July 8 | |||
| July 15 | 257 units | ||
| July 23 | |||
| $15,527 | $2,940 |
The value of the ending inventory is $2,940.
Thus, option a is correct.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCT.FUND.(LOOSELEAF)
- Starbucks Corporation wants to make a profit of $32,000. It has variable costs of $65 per unit and fixed costs of $18,000. How much must it charge per unit if 5,000 units are sold?arrow_forwardSolution accountingarrow_forwardI am searching for the most suitable approach to this financial accounting problem with valid standards.arrow_forward
- incorrect solution will get unhelpful ratearrow_forwardYou are given the following information about Zephyr Company in 2021: The Company’s fixed costs are expected to be $195,000, the selling price per unit is $17, and the variable cost per unit is $5. The company wants to earn a net income of $84,000 during 2021. The required sales units to meet the target net income during 2021 is _.arrow_forwardI want the correct answer with accounting questionarrow_forward
- Custom Pools currently sells 420 Economy pools, 580 Standard pools, and 190 Premium pools each year. The firm is considering adding a Luxury pool and expects that, if it does, it can sell 310 of them. However, if the new pool is added, Economy pool sales are expected to decline to 290 units while Standard pool sales are expected to decline to 350. The sales of the Premium model will not be affected. Economy pools sell for an average of $16,200 each. Standard pools are priced at $24,500 and the Premium model sells for $42,000 each. The new Luxury pool will sell for $35,000. What is the value of erosion?arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forward6 MARKSarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





