
An elevator suspended by a cable is descending at constant velocity. How many forcevector would be shown on a free-body diagram? Name them.
The force vectors acting on the elevator under given conditions
Explanation of Solution
The elevator is descending at a constant velocity.
Since the elevator is descending at a constant velocity, it experiences no acceleration. Therefore, the net force acting on the elevator is zero. The elevator is supported by the cable. Therefore, the tension of the cable acts upward. The other force on the elevator is its weight. The situation is explained by the free-body diagram given below.
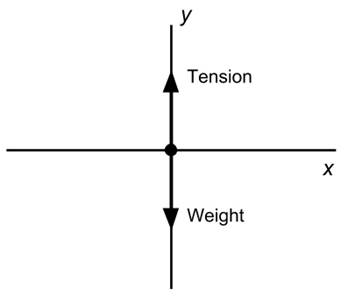
When the net force acting on the elevator is zero and two forces act on it, both forces will be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
Conclusion:
There are two forces acting on the elevator when it is descending with a constant velocity. The forces are the tension of the cable and the weight of the elevator.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- (a) For a spherical capacitor with inner radius a and outer radius b, we have the following for the capacitance. ab C = k₂(b- a) 0.0695 m 0.145 m (8.99 × 10º N · m²/c²)( [0.145 m- 0.0695 m × 10-11 F = PF IIarrow_forwardA pendulum bob A (0.5 kg) is given an initialspeed of vA = 4 m/s when the chord ishorizontal. It then hits a stationary block B (1kg) which then slides to a maximum distanced before it stops. Determine the value of d.The coefficient of static friction between theblock and the plane is μk = 0.2. The coefficientof restitution between A and B is e = 0.8.Ans: d=1.0034 marrow_forwardFigure 29-43 Problem 12. ••13 In Fig. 29-44, point P₁ is at distance R = 13.1 cm on the perpendicular bisector of a straight wire of length L = 18.0 cm carrying current i = 58.2 mA. (Note that the wire is not long.) What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at P₁ due to i? P2° R R Larrow_forward
- Checkpoint 1 The figure shows the current i in a single-loop circuit with a battery B and a resistance R (and wires of neg- ligible resistance). (a) Should the emf arrow at B be drawn pointing leftward or rightward? At points a, B C R b, and c, rank (b) the magnitude of the current, (c) the electric potential, and (d) the electric potential energy of the charge carriers, greatest first.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help asaparrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
 An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





