
Concept explainers
Three objects are connected on a table as shown in Figure P5.14. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block of mass m2 and the table is 0.350. The objects have masses of m1 = 4.00 kg, m2 = 1.00 kg, and m3 = 2.00 kg, and the pulleys are frictionless. (a) Draw a free-body diagram of each object. (b) Determine the acceleration of each object, including its direction. (c) Determine the tensions in the two cords. What If? (d) If the tabletop were smooth, would the tensions increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain.

Figure P5.14
(a)
Draw free body diagram of the each object.
Answer to Problem 14P
The free body diagram of the mass of block
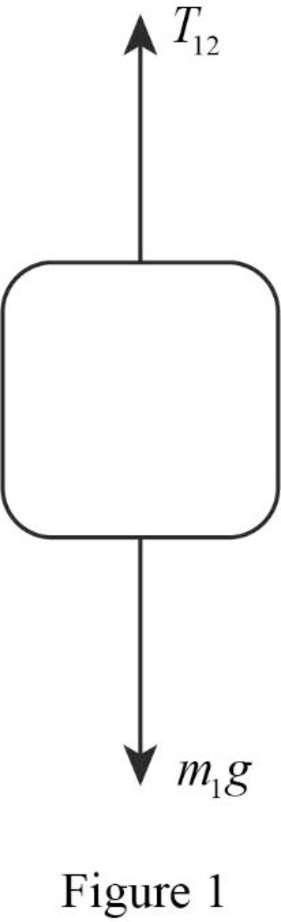
The free body diagram of the mass of block
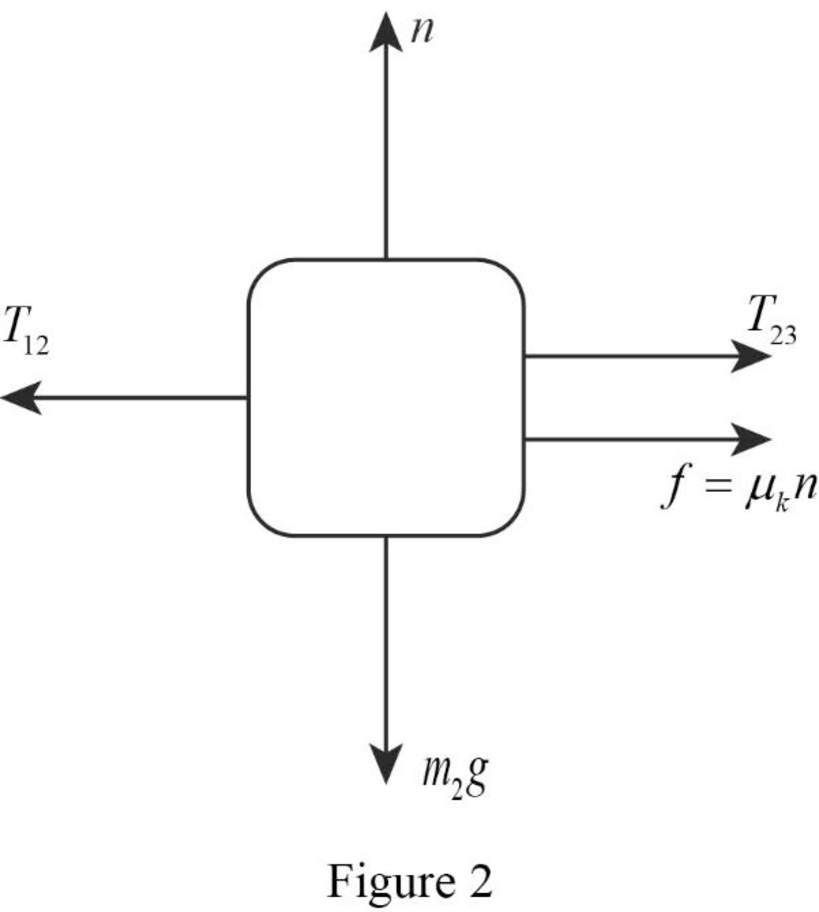
The free body diagram of the mass of block
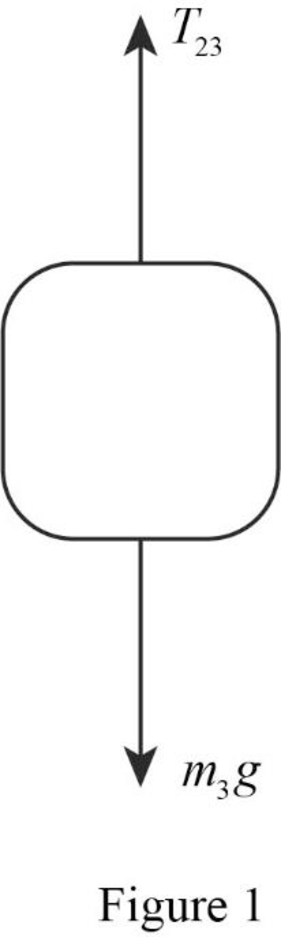
Explanation of Solution
The free body diagram is the graphical illustration used to visualize the movements and forces applied on a body.
Let
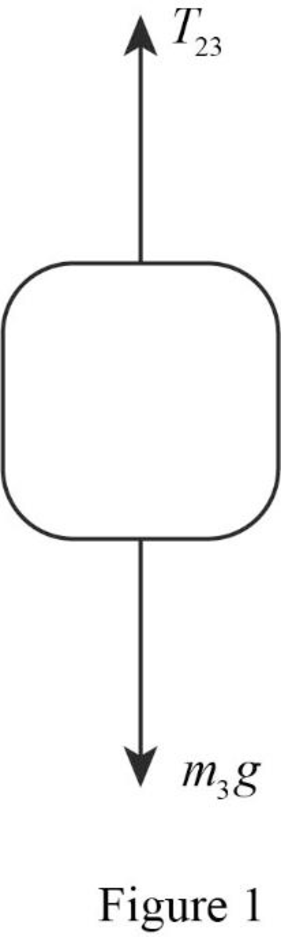
The free body diagram of the mass of block
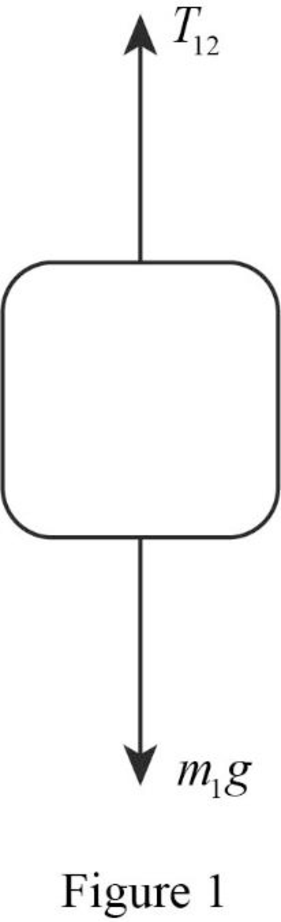
The free body diagram of the mass of block
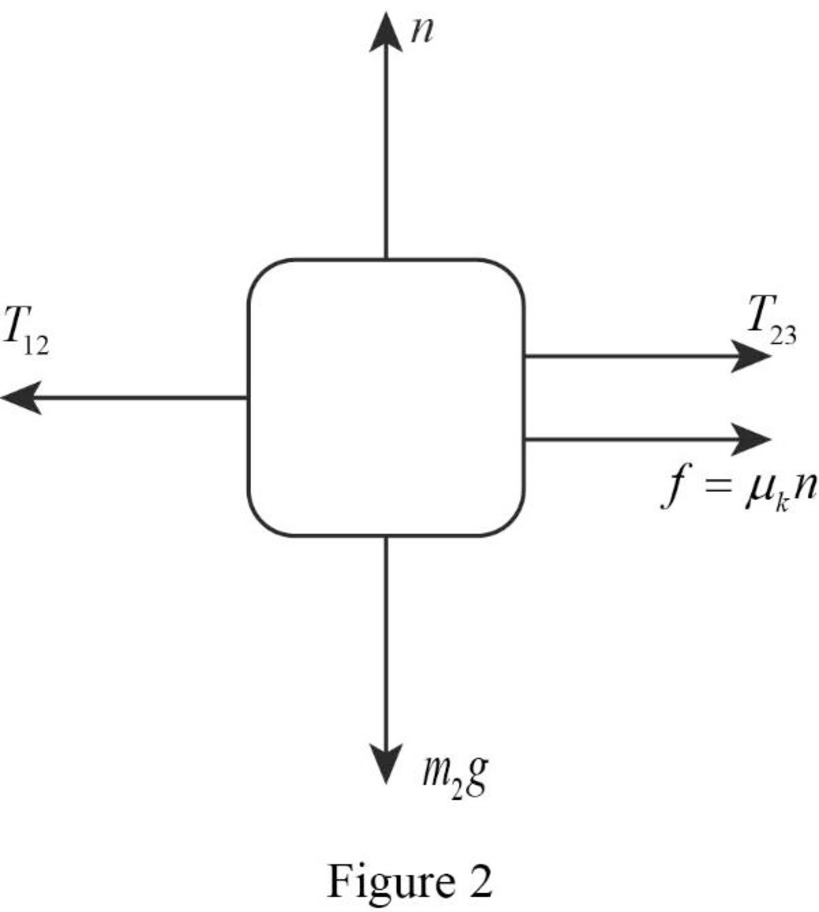
The free body diagram of the mass of block
Conclusion:
Therefore, the free body diagram of the mass of block
(b)
The magnitude and direction of acceleration of each object.
Answer to Problem 14P
The magnitude of acceleration of each object is
Explanation of Solution
Apply Newton’s second law for in the
Here,
From the Figure 1, write the expression for net force in the
Here,
Substitute,
From the Figure 2, write the expression for net force in the
Since,
Here,
From the Figure 2, write the expression for net force in the
From the Figure 3, write the expression for net force in the
Add equation (III), (IV), and (VI).
Write the expression for normal force for mass
Use,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the magnitude of acceleration of each object is
(c)
The tension in the two cords.
Answer to Problem 14P
Tension in the first code is
Explanation of Solution
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Therefore, tension in the first code is
(d)
Whether the tension increase, decrease, or remain the same if the tabletop were smooth.
Answer to Problem 14P
The tension in the left rope will decreases, and the tension in the right rope will increases.
Explanation of Solution
If the table top is smooth, the friction on the top will disappear. So the acceleration become larger.
From the equation (III),
Conclusion:
Therefore, the tension in the left rope will decreases, and the tension in the right rope will increases.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
- Hi! I need help with these calculations for part i and part k for a physics Diffraction Lab. We used a slit width 0.4 mm to measure our pattern.arrow_forwardExamine the data and % error values in Data Table 3 where the angular displacement of the simple pendulum decreased but the mass of the pendulum bob and the length of the pendulum remained constant. Describe whether or not your data shows that the period of the pendulum depends on the angular displacement of the pendulum bob, to within a reasonable percent error.arrow_forwardIn addition to the anyalysis of the graph, show mathematically that the slope of that line is 2π/√g . Using the slope of your line calculate the value of g and compare it to 9.8.arrow_forward
- An object is placed 24.1 cm to the left of a diverging lens (f = -6.51 cm). A concave mirror (f= 14.8 cm) is placed 30.2 cm to the right of the lens to form an image of the first image formed by the lens. Find the final image distance, measured relative to the mirror. (b) Is the final image real or virtual? (c) Is the final image upright or inverted with respect to the original object?arrow_forwardConcept Simulation 26.4 provides the option of exploring the ray diagram that applies to this problem. The distance between an object and its image formed by a diverging lens is 5.90 cm. The focal length of the lens is -2.60 cm. Find (a) the image distance and (b) the object distance.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





