
Concept explainers
Estimating Cost Behavior Using Scattergraph and High-Low Methods
Camp Rainbow offers overnight summer camp programs for children ages 10 to 14 every summer during June and July. Each camp session is one week and can accommodate up to 200 children. The camp is not coed, so boys attend during the odd-numbered weeks and girls attend during the even-numbered weeks. While at the camp, participants make crafts, participate in various sports, help care for the Camp’s resident animals, have cookouts and hayrides, and help assemble toys for local underprivileged children.
The camp provides all food as well as materials for all craft classes and the toys to be assembled. One cabin can accommodate up to 10 children, and one camp counselor is assigned to each cabin. Three camp managers are on-site regardless of the number of campers enrolled.
Following is the cost information for Camp Rainbow s operations last summer
1. For each of the following items. Identify, whether the cost is variable, fixed, mixed, step-variable, or step-fixed. State any assumptions you make.
a. Cost of meals for campers.
b. Cost of camp counselor wanes.
c. Cost of crafting materials.
d.
e. Feed for the camp animals.
f. Electricity for the camp.
g. Camp managers’ salaries.
h. Cost of toys to be assembled by campers.
I. Housekeeping (e.g. cleaning cabins between sessions, laundering bed linens).
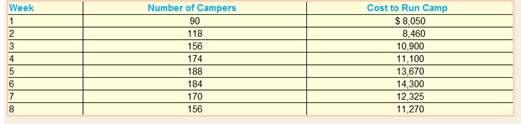
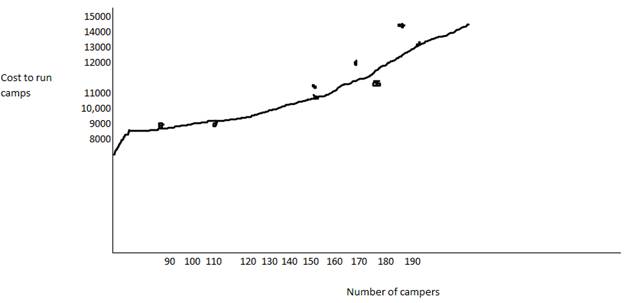
2. Prepare a scattergraph of Camp Rainbows operating cost and draw the line you believe best fits the data.
3. Based on this graph, estimate Camp Rainbow s total fixed costs per month.
4. Using the high-low method, calculate Camp Rainbow s total fixed operating costs and variable operating cost per child.
5. Using the high-low method results, calculate the camps expected operating cost if 170 children attend a session.
(a)
Concept introduction:
Variable cost:
Variable costs are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Example: Cloth (i.e., the raw material) used for producing shirt is a variable costs.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost is the cost which remains fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost is the cost which has some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example includes some production cost which remains fixed at $800 and also increases by $2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increases in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
The nature of given expenses.
Answer to Problem 10E
| a. | variable |
| b | step-fixed |
| c | step-variable |
| d | fixed |
| e | fixed |
| f | step-fixed |
| g | fixed |
| h | variable |
Explanation of Solution
| a. | Cost of meal will vary on the number of participants. |
| b | Camp counselor wages vary slightly depending on the number of participants. |
| c | Camp counselor wages will vary highly on the number of participants |
| d | Depreciation will remain fixed |
| e | feed of the camp animals will remain fixed |
| f | Electricity expenses remain fixed upto a certain limit |
| g | Camp manager's salary will remain fixed |
| h | Variable based on the number of participants |
Thus, thenature of expenses has been determined.
(b)
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
To prepare:
The scatter-graph and estimate the fixed costs.
Answer to Problem 10E
Explanation of Solution
The points have been plotted and a straight line has been drawn near the points.
Thus, the scatter-graph has been prepared
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
Variable cost:
Variable cost are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Examples include clothes in production of shirts is a variable costs the clothes and other accessories utilized can be directly traced to units of shirts produced.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost are the cost which remain fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost are the cost which have some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example include some production cost which remain fixed at $800 and also increases by R$2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increase in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
Requirement 3
To provide
The estimated fixed costs
Answer to Problem 10E
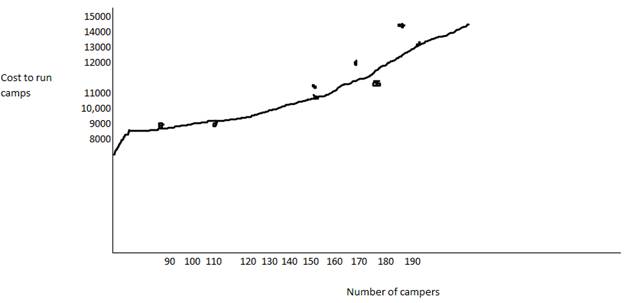
The estimated fixed cost is $7,000.
Explanation of Solution
The intercept is at hence the fixed cost is estimated
Thus, the estimated fixed cost has been provided.
(d)
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
Variable cost:
Variable cost are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Examples include clothes in production of shirts is a variable costs the clothes and other accessories utilized can be directly traced to units of shirts produced.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost are the cost which remain fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost are the cost which have some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example include some production cost which remain fixed at $800 and also increases by R$2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increase in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
To compute:
The fixed and variable cost using high low method.
Answer to Problem 10E
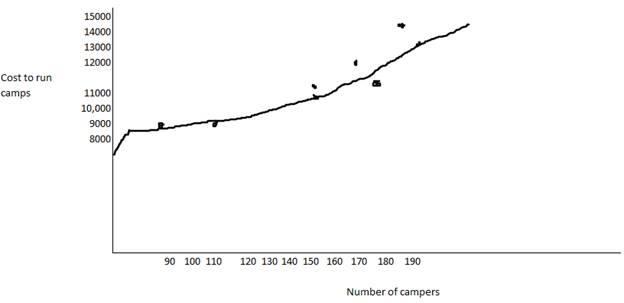
The fixed operating cost is $2839
The variable operating cost is $57.35/camper
Explanation of Solution
The highest point is 188campers with total cost $13,670
The lowest point is 90 campers with total cost $8050
So, variable cost per camper =
So, fixed cost for 90 camper=8050-(90*57.37) = 8050-5161.22=$2839
Hence, the fixed cost and variable cost has been determined.
(e)
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
Variable cost:
Variable cost are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Examples include clothes in production of shirts is a variable costs the clothes and other accessories utilized can be directly traced to units of shirts produced.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost are the cost which remain fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost are the cost which have some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example include some production cost which remain fixed at $800 and also increases by R$2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increase in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
To compute:
The estimated cost at given number of units.
Answer to Problem 10E
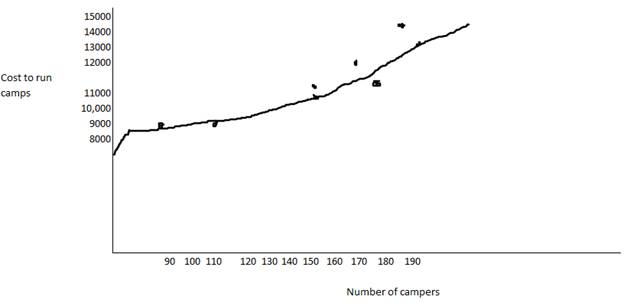
The expected operating cost of 170 children using high-low method is $12,587
Explanation of Solution
The cost of 170 campers = 2839+(170*57.35) = $12,588
Hence, the estimated costs has been determined
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub



