
a.
The period of each function.
a.
Answer to Problem 83E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The normal monthly high temperatures
and the normal monthly low temperatures
where is
(a) What is the period of each function?
Calculation: The normal monthly high temperatures
where is
Let us consider the following figure,
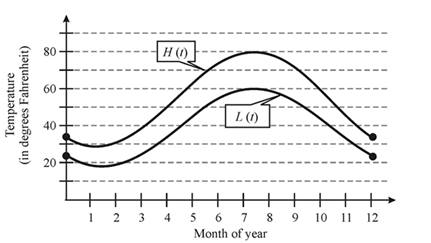
From the above figure, we can see that the curve for normal monthly high temperatures
Hence, the period of
b.
Greatest and smallest difference between the normal high and normal low temperatures.
b.
Answer to Problem 83E
Greatest in summer months and smallest in winter months.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The normal monthly high temperatures
and the normal monthly low temperatures
Where is
During what part of the year is the difference between the normal high and normal low temperatures greatest? When is it smallest?
Calculation:
The normal monthly high temperatures
where is
Let us consider the following figure,
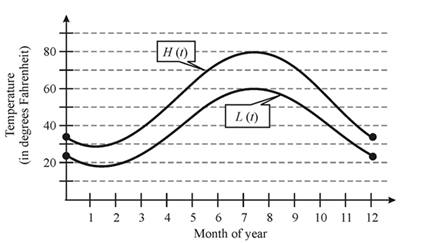
From the above figure, we can see that, the difference between the normal high
Also, the difference between the normal high
Hence, the difference between the temperatures is greatest in summer months and smallest in winter months.
c.
Approximate the lag time.
c.
Answer to Problem 83E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The normal monthly high temperatures
and the normal monthly low temperatures
where is
The sun is northernmost in the sky around June 21, but the graph shows the warmest temperatures at a later date. Approximate the lag time of the temperatures relative to the position of the sun.
Calculation: The normal monthly high temperatures
where is
Let us consider the following figure,
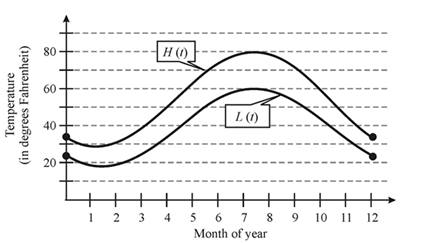
From the above graph, it can be seen thst the curves attains its peak in the
So, the warmest of the temperature will be in the month of July, instead of being on 21 of June., which means approximately
Hence, the lag time of the temperatures relative to the position of sun will be
Chapter 4 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits
- A Content X MindTap - Cengage Learning x Function Evaluations x + /ui/evo/index.html?elSBN=9780357038406&id=339416021&snapshotld=877369& GE MINDTAP , Limits, and the Derivative ⭑ វា a ANSWEI 16. Refer to the graph of the function f in the following figure. कर्ट AA C 54 -3-2 7 7 Ay 6. S 5. y=f(x) 4 3. 2. 1 -3- 34567 8 00 9 10 a. Find the value of ƒ (7). b. Find the values of x corresponding to the point(s) on the graph of ƒ located at a height of 5 units from the x-axis. c. Find the point on the x-axis at which the graph of ƒ crosses it. What is the value of f (x) at this point? d. Find the domain and range of f. MacBook Pro G Search or type URL + > % Λ & 5 6 7 29 ( 8 9 0arrow_forwardMorgan F. - C X A Courses MindTap - Cengage Learning Х Domain of Square Roots X + gage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?elSBN 9780357038406&id=339416021&snapshotld=877369& CENGAGE MINDTAP 2: Functions, Limits, and the Derivative 47. x if x < 0 f(x) = 2x+1 if x 0 Answerarrow_forwardA Content MindTap - Cengage Learning × Function Evaluations * + c/nb/ui/evo/index.html?elSBN 9780357038406&id=339416021&snapshotld=877369& GAGE MINDTAP ions, Limits, and the Derivative 15. Refer to the graph of the function f in the following figure. 6 y = f(x) 5 4+ 3- 2- 1 + 2 -1 3 4 5 6 a. Find the value of ƒ (0). Answer-> b. Find the value of x for which (i) f (x) = 3 and (ii) f (x) = 0. Answer ▾ c. Find the domain of f. Answer + d. Find the range of f. Answer+ MacBook Proarrow_forward
- Answer-> 12. Let g be the function defined by Find g(-2), g(0), g (2), and g (4). - +1 if x <2 g(x) = √√√x-2 if x 2arrow_forward13. Let f be the function defined by Find f (-1), f (0), ƒ (1) and ƒ (2). Answer f(x) = .2 J-x² +3 if x <1 2x²+1 2x²+1 if x ≥ 1arrow_forwardΛ Content Mind Tap - Cengage Learning × Function Evaluations x + c/nb/ui/evo/index.html?elSBN 9780357038406&id=339416021&snapshotld=877369& GAGE MINDTAP ons, Limits, and the Derivative 14. Let f be the function defined by Find f (0), f (1), and f (2). 2+1 x if x 1 if x 1 f(x) = 1 1-xarrow_forward
- A Content c/nb/ui/evo/index.html?elSBN 9780357038406&id=339416021&snapshotld=877369& GAGE MINDTAP ons, Limits, and the Derivative 11. Let f be the function defined by Find f (-2), f (0), and f (1). Answer f(x) = [ x² + 1 if x ≤ 0 if x > 0arrow_forwardGiven that 4−4i is a zero, factor the following polynomial function completely. Use the Conjugate Roots Theorem, if applicable. f(x)=x4−5x3−2x2+176x−320arrow_forwardeliminate the parameter to find the cartesian equation of the curve and sketch the graph. On the graph show the direction it takes and the initial and terminal point. Please draw by hand and show how you got to each steparrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





