
Concept explainers
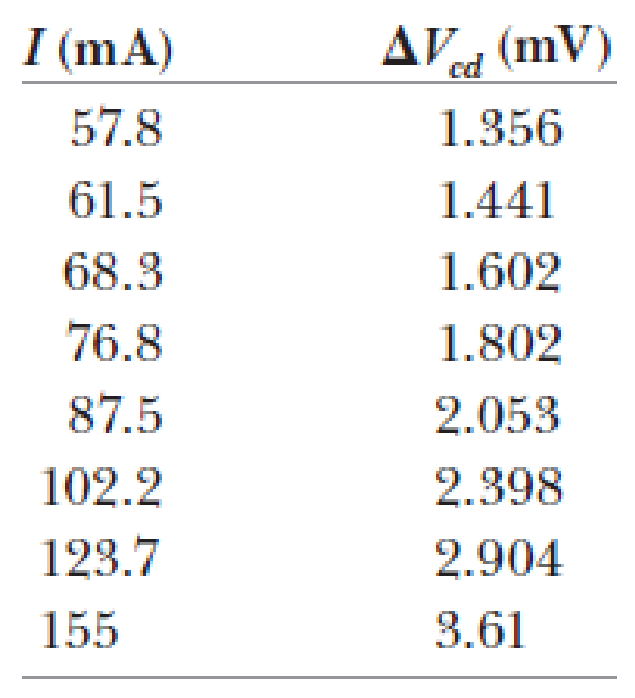
A direct and relatively simple demonstration of zero DC resistance can be carried out using the four-point probe method. The probe shown in Figure P43.52 consists of a disk of YBa2Cu3O7 (a high-Tc superconductor) to which four wires are attached. Current is maintained through the sample by applying a DC voltage between points a and b, and it is measured with a DC ammeter. The current can be varied with the variable resistance R. The potential difference ΔVcd between c and d is measured with a digital voltmeter. When the probe is immersed in liquid nitrogen, the sample quickly cools to 77 K, below the critical temperature of the material, 92 K. The current remains approximately constant, but ΔVcd drops abruptly to zero, (a) Explain this observation on the basis of what you know about superconductors. (b) The data in the accompanying table represent actual values of ΔVcd for different values of I taken on the sample at room temperature in the senior author’s laboratory. A 6-V battery in series with a variable resistor R supplied the current. The values of R ranged from 10 Ω to 100 Ω. Make an I-ΔV plot of the data and determine whether the sample behaves in a linear manner, (c) From the data, obtain a value for the DC resistance of the sample at room temperature. (d) At room temperature, it was found that ΔVcd = 2.234 mV for I = 100.3 mA, but after the sample was cooled to 77 K, ΔVcd = 0 and I = 98.1 mA. What do you think might have caused the slight decrease in current?
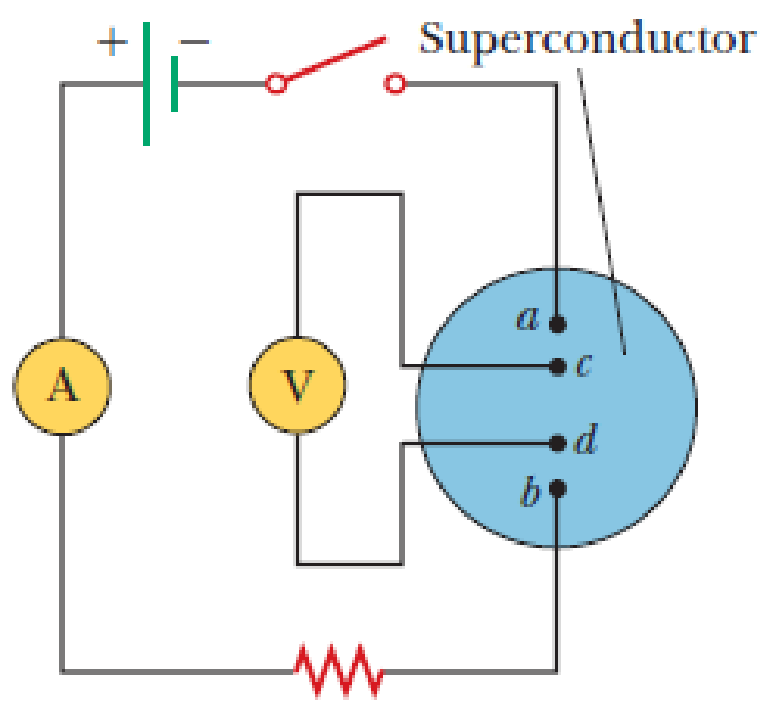
Figure P43.52
Current Versus Potential Difference ΔVcd Measured in a Bulk Ceramic Sample of YBa2Cu3O7−δ at Room Temperature
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 43 Solutions
Physics For Scientists And Engineers With Modern Physics, 9th Edition, The Ohio State University
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer .arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forward
- Good explanation it sure experts solve it.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Asaparrow_forwardA satellite has a mass of 100kg and is located at 2.00 x 10^6 m above the surface of the earth. a) What is the potential energy associated with the satellite at this loction? b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on the satellite?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardCorrect answer No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardStatistical thermodynamics. The number of imaginary replicas of a system of N particlesa) cannot be greater than Avogadro's numberb) must always be greater than Avogadro's number.c) has no relation to Avogadro's number.arrow_forward
- Lab-Based Section Use the following information to answer the lab based scenario. A student performed an experiment in an attempt to determine the index of refraction of glass. The student used a laser and a protractor to measure a variety of angles of incidence and refraction through a semi-circular glass prism. The design of the experiment and the student's results are shown below. Angle of Incidence (°) Angle of Refraction (º) 20 11 30 19 40 26 50 31 60 36 70 38 2a) By hand (i.e., without using computer software), create a linear graph on graph paper using the student's data. Note: You will have to manipulate the data in order to achieve a linear function. 2b) Graphically determine the index of refraction of the semi-circular glass prism, rounding your answer to the nearest hundredth.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





