
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398242
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.3, Problem 4.102P
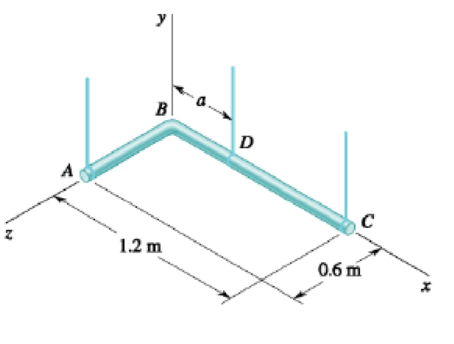
PROBLEM 4.102
For the pipe assembly of Problem 4.101, determine (a) the largest permissible value of a if the assembly is not to tip, (b) the corresponding tension in each wire.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(read image) (answer given)
A cylinder and a disk are used as pulleys, as shown in the figure. Using the data
given in the figure, if a body of mass m = 3 kg is released from rest after falling a
height h 1.5 m, find:
a) The velocity of the body.
b) The angular velocity of the disk.
c) The number of revolutions the cylinder has made.
T₁
F
Rd =
0.2 m
md =
2 kg
T
T₂1
Rc = 0.4 m
mc = 5 kg
☐ m = 3 kg
(read image) (answer given)
Chapter 4 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 4.1 - Two crates, each of mass 350 kg, are placed as...Ch. 4.1 - A lever AB is hinged at C and attached to a...Ch. 4.1 - A light rod AD is supported by frictionless pegs...Ch. 4.1 - A tension of 20 N is maintained in a tape as it...Ch. 4.1 - A gardener uses a 60 N wheelbarrow to transport a...Ch. 4.1 - The gardener of Prob. 4.1 wishes to transport a...Ch. 4.1 - A 2100-lb tractor is used to lift 900 lb of grave....Ch. 4.1 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 4.1 - A load of lumber of weight W = 25 kN is being...Ch. 4.1 - A load of lumber of weight W = 25 kN is being...
Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.7PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.8PCh. 4.1 - Three loads are applied as shown to a light beam...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.10PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.11PCh. 4.1 - For the beam of Sample Prob. 4.2, determine the...Ch. 4.1 - The maximum allowable value of each of the...Ch. 4.1 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 4.1 - 4.15 Two links AB and DE are connected by a bell...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.16PCh. 4.1 - 4.17 The required tension in cable AB is 200 lb....Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.18PCh. 4.1 - The bracket BCD is hinged at C and attached to a...Ch. 4.1 - The ladder AB, of length L and weight W, can be...Ch. 4.1 - 4.21 The 40-ft boom AB weighs 2 kips; the distance...Ch. 4.1 - A lever AB is hinged at C and attached to a...Ch. 4.1 - 4.23 and 4.24 For each of the plates and loadings...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.24PCh. 4.1 - A rod AB, hinged at A and attached at B to cable...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.26PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.27PCh. 4.1 - Determine the reactions at A and C when (a) = 0,...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.29PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.30PCh. 4.1 - Neglecting friction, determine the tension in...Ch. 4.1 - Fig. P4.31 and P4.32 4.32 Neglecting friction,...Ch. 4.1 - PROBLEM 4.33 A force P of magnitude 90 lb is...Ch. 4.1 - PROBLEM 4.34 Solve Problem 4,33 for a = 6 in,...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.35PCh. 4.1 - PROBLEM 4.36 A light bar AD is suspended from a...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.37PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.38PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.39PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.40PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.41PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.42PCh. 4.1 - The rig shown consists of a 1200-lb horizontal...Ch. 4.1 - Fig. P4.43 4.44 For the rig and crate of Prob....Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.45PCh. 4.1 - Knowing that the tension in wire BD is 1300 N,...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.47PCh. 4.1 - Beam AD carries the two 40-lb loads shown. The...Ch. 4.1 - Fig. P4.48 and P4.49 4.49 For the beam and loading...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.50PCh. 4.1 - A uniform rod AB with a length of l and weight of...Ch. 4.1 - Rod AD is acted upon by a vertical force P at end...Ch. 4.1 - A slender rod AB with a weigh of W is attached to...Ch. 4.1 - 4.54 and 4.55 A vertical load P is applied at end...Ch. 4.1 - 4.54 and 4.55 A vertical load P is applied at end...Ch. 4.1 - A collar B with a weight of W can move freely...Ch. 4.1 - A 400-lb weight is attached at A to the lever...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.58PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.59PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.60PCh. 4.2 - A 500-lb cylindrical tank, 8 ft in diameter, is to...Ch. 4.2 - 4.62 Determine the reactions at A and B when a =...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.63PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.64PCh. 4.2 - Determine the reactions at B and C when a = 30 mm.Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.66PCh. 4.2 - Determine the reactions at B and D when b = 60 mm....Ch. 4.2 - For the frame and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 4.2 - A 50-kg crate is attached to the trolley-beam...Ch. 4.2 - One end of rod AB rests in the corner A and the...Ch. 4.2 - For the boom and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.72PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.73PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.74PCh. 4.2 - Rod AB is supported by a pin and bracket at A and...Ch. 4.2 - Solve Prob. 4.75, assuming that the 170-N force...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.77PCh. 4.2 - Using the method of Sec. 4.2B, solve Prob. 4.22....Ch. 4.2 - Knowing that = 30, determine the reaction (a) at...Ch. 4.2 - Knowing that = 60, determine the reaction (a) at...Ch. 4.2 - Determine the reactions at A and B when = 50....Ch. 4.2 - Determine the reactions at A and B when = 80.Ch. 4.2 - Rod AB is bent into the shape of an arc of circle...Ch. 4.2 - A slender rod of length L is attached to collars...Ch. 4.2 - An 8-kg slender rod of length L is attached to...Ch. 4.2 - Prob. 4.86PCh. 4.2 - A slender rod BC with a length of L and weight W...Ch. 4.2 - A thin ring with a mass of 2 kg and radius r = 140...Ch. 4.2 - A slender rod with a length of L and weight W is...Ch. 4.2 - Fig. P4.89 4.90 Knowing that for the rod of Prob....Ch. 4.3 - Two tape spools are attached to an axle supported...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.6FBPCh. 4.3 - A 20-kg cover for a roof opening is hinged at...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.91PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.92PCh. 4.3 - A small winch is used to raise a 120-lb load. Find...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.94PCh. 4.3 - A 250 400-mm plate of mass 12 kg and a...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.96PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.97PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.98PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.99PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.100PCh. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.101 Two steel pipes AB and BC, each...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.102 For the pipe assembly of Problem...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.103 The 24-lb square plate shown is...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.104 The table shown weighs 30 lb and has...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.105 A 10-ft boom is acted upon by the...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.106 The 6-m pole ABC is acted upon by a...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.107 Solve Problem 4.106 for a = 1.5 m....Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.108PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.109PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.110PCh. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.111 A 48-in. boom is held by a...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.112 Solve Problem 4.111, assuming that...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.114 The bent rod ABEF is supported by...Ch. 4.3 - The bent rod ABEF is supported by bearings at C...Ch. 4.3 - The horizontal platform ABCD weighs 60 lb and...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.116PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.117PCh. 4.3 - Solve Prob. 4.117, assuming that cable DCE is...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.119 Solve Prob. 4.113, assuming that the...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.120 Solve Prob. 4.115, assuming that the...Ch. 4.3 - PROBLEM 4.121 The assembly shown is used to...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.122PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.123PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.124PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.125PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.126PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.127PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.128PCh. 4.3 - Frame ABCD is supported by a ball-and-socket joint...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.130PCh. 4.3 - The assembly shown consists of an 80-mm rod AF...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.132PCh. 4.3 - The frame ACD is supported by ball-and-socket...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.134PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.135PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.136PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.137PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.138PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.139PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.140PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.141PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.142RPCh. 4 - 4. 143 The lever BCD is hinged at C and attached...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.144RPCh. 4 - Neglecting friction and the radius of the pulley,...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.146RPCh. 4 - PROBLEM 4.147 A slender rod AB, of weight W, is...Ch. 4 - PROBLEM 4.148 Determine the reactions at A and B...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.149RPCh. 4 - PROBLEM 4.150 A 200-mm lever and a 240-mm-diameter...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.151RPCh. 4 - Prob. 4.152RPCh. 4 - A force P is applied to a bent rod ABC, which may...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 11-5. Compute all the dimensional changes for the steel bar when subjected to the loads shown. The proportional limit of the steel is 230 MPa. 265 kN 100 mm 600 kN 25 mm thickness X Z 600 kN 450 mm E=207×103 MPa; μ= 0.25 265 kNarrow_forwardT₁ F Rd = 0.2 m md = 2 kg T₂ Tz1 Rc = 0.4 m mc = 5 kg m = 3 kgarrow_forward2. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of known functions. (x + 2)²y" + (x + 2)y' - y = 0 ; Hint: Let: z = x+2arrow_forward
- 1. Find a power series solution in powers of x. y" - y' + x²y = 0arrow_forward3. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of known functions. 8x2y" +10xy' + (x 1)y = 0 -arrow_forwardHello I was going over the solution for this probem and I'm a bit confused on the last part. Can you please explain to me 1^4 was used for the Co of the tubular cross section? Thank you!arrow_forward
- Blood (HD = 0.45 in large diameter tubes) is forced through hollow fiber tubes that are 20 µm in diameter.Equating the volumetric flowrate expressions from (1) assuming marginal zone theory and (2) using an apparentviscosity for the blood, estimate the marginal zone thickness at this diameter. The viscosity of plasma is 1.2 cParrow_forwardQ2: Find the shear load on bolt A for the connection shown in Figure 2. Dimensions are in mm Fig. 2 24 0-0 0-0 A 180kN (10 Markarrow_forwarddetermine the direction and magnitude of angular velocity ω3 of link CD in the four-bar linkage using the relative velocity graphical methodarrow_forward
- Four-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forwardFour-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forwardThe evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle utilizing R-123 as the refrigerant isbeing used to chill water. The evaporator is a shell and tube heat exchanger with the water flowingthrough the tubes. The water enters the heat exchanger at a temperature of 54°F. The approachtemperature difference of the evaporator is 3°R. The evaporating pressure of the refrigeration cycleis 4.8 psia and the condensing pressure is 75 psia. The refrigerant is flowing through the cycle witha flow rate of 18,000 lbm/hr. The R-123 leaves the evaporator as a saturated vapor and leaves thecondenser as a saturated liquid. Determine the following:a. The outlet temperature of the chilled waterb. The volumetric flow rate of the chilled water (gpm)c. The UA product of the evaporator (Btu/h-°F)d. The heat transfer rate between the refrigerant and the water (tons)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY