
Concept explainers
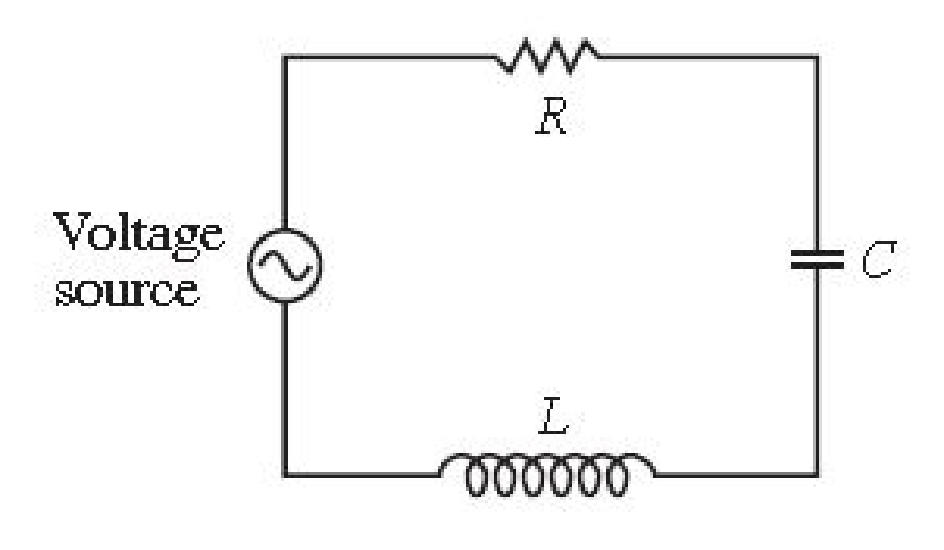
(RLC circuit) The circuit in the figure consists of a resistor (R ohms), an inductor (L henrys), a capacitor (C farads), and an initial voltage source. Let b = R/(2L), and suppose R, L, and C have been selected so that b also equals
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Thomas' Calculus and Linear Algebra and Its Applications Package for the Georgia Institute of Technology, 1/e
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
- Solve the equation. Write the smaller answer first. 2 (x-6)² = 36 x = Α x = Previous Page Next Pagearrow_forwardWrite a quadratic equation in factored form that has solutions of x = 2 and x = = -3/5 ○ a) (x-2)(5x + 3) = 0 ○ b) (x + 2)(3x-5) = 0 O c) (x + 2)(5x -3) = 0 ○ d) (x-2)(3x + 5) = 0arrow_forwardA vacant lot is being converted into a community garden. The garden and a walkway around its perimeter have an area of 690 square feet. Find the width of the walkway (x) if the garden measures 14 feet wide by 18 feet long. Write answer to 2 decimal places. (Write the number without units). Hint: add 2x to each of the garden dimensions of 14 x 18 feet to get the total area for the length multiplied by width.arrow_forward
- Solve the rational equation 14 1 + x-6 x x-7 x-7 ○ a) x = 1, x = 8 ○ b) x = 1 ○ c) x = 7 ○ d) x = 1, x = 7arrow_forwardSolve the absolute inequality | x + 5 > 3 ○ a) (-∞, -8] U[-2, ∞0) ☐ b) (-8, -2) c) (-2, ∞0) ○ d) (-∞, - 8) U(-2, ∞0)arrow_forward1) Listen Describe the error in the problem X 3 X x 3 - 2 = 25x = 0 25x 25 x = ±5arrow_forward
- A falling object travels a distance given by the formula d = 6t + 7t² where d is in feet and t is the time in seconds. How many seconds will it take for the object to travel 115 feet? Round answer to 2 decimal places. (Write the number, not the units). Your Answer:arrow_forwardListen Solve the quadratic equation. Write the smaller answer first. 2 Xx - 5x = 24 x = Α x =arrow_forwardSolve the absolute equation |2x = 4| = 10 ○ a) x = -7, x = 3 ○ b) x = -2, x = 6 ○ c) x = -3, x = 7 ○ d) x = 7arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


