
Imports and exports: The following table presents the U.S. imports and exports (in billions of dollars) for each of 29 months.
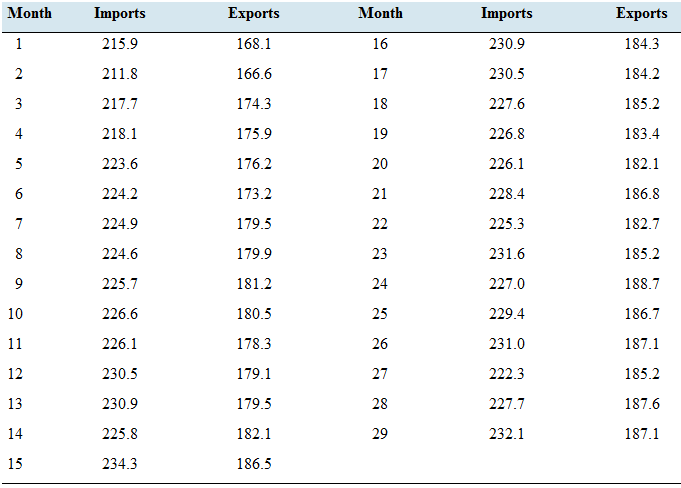
- Compute the least-squares regression line for predicting exports (y) from imports (x).
- Compute the coefficient of determination.
- The months two lowest exports are months 1 and 2. when the exports were 168.1 and 166.6, respectively. Remove these points and compute the least-squares regression line. Is die result noticeably different?
- Compute the coefficient of determination for the data set months 1 and 2 removed.
- Two economists decide to study the relationship between imports and exports. One uses data from months 1 through 29 and the other uses data from months 3 through 29. For which data set will the proportion of variance explained by the least-squares regression line be greater?
a.
To find: The least-square regression line for the given data set.
Answer to Problem 26E
The least square regression line of the given data set is,
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The import and exports of United States within
Calculation:
The least-square regression is given by the formula,
Where
The correlation coefficient is given by the formula,
Considering the exports as

The correlation coefficient can be obtained by the following table.
| x | y | Zx | Zy | ZxZy |
| 215.9 | 168.1 | -1.99175 | -2.32277 | 4.626396 |
| 211.8 | 166.6 | -2.79101 | -2.58707 | 7.220549 |
| 217.7 | 174.3 | -1.64086 | -1.23035 | 2.018834 |
| 218.1 | 175.9 | -1.56288 | -0.94844 | 1.482294 |
| 223.6 | 176.2 | -0.49071 | -0.89558 | 0.439465 |
| 224.2 | 173.2 | -0.37374 | -1.42417 | 0.532271 |
| 224.9 | 179.5 | -0.23728 | -0.31412 | 0.074536 |
| 224.6 | 179.9 | -0.29576 | -0.24365 | 0.072062 |
| 225.7 | 181.2 | -0.08133 | -0.01459 | 0.001187 |
| 226.6 | 180.5 | 0.094118 | -0.13793 | -0.01298 |
| 226.1 | 178.3 | -0.00335 | -0.52556 | 0.001762 |
| 230.5 | 179.1 | 0.854389 | -0.3846 | -0.3286 |
| 230.9 | 179.5 | 0.932365 | -0.31412 | -0.29288 |
| 225.8 | 182.1 | -0.06184 | 0.143989 | -0.0089 |
| 234.3 | 186.5 | 1.595165 | 0.919257 | 1.466367 |
| 230.9 | 184.3 | 0.932365 | 0.531623 | 0.495667 |
| 230.5 | 184.2 | 0.854389 | 0.514003 | 0.439158 |
| 227.6 | 185.2 | 0.289059 | 0.6902 | 0.199509 |
| 226.8 | 183.4 | 0.133106 | 0.373045 | 0.049655 |
| 226.1 | 182.1 | -0.00335 | 0.143989 | -0.00048 |
| 228.4 | 186.8 | 0.445012 | 0.972116 | 0.432603 |
| 225.3 | 182.7 | -0.15931 | 0.249707 | -0.03978 |
| 231.6 | 185.2 | 1.068824 | 0.6902 | 0.737703 |
| 227 | 188.7 | 0.172094 | 1.306891 | 0.224908 |
| 229.4 | 186.7 | 0.639953 | 0.954496 | 0.610833 |
| 231 | 187.1 | 0.951859 | 1.024975 | 0.975632 |
| 222.3 | 185.2 | -0.74413 | 0.6902 | -0.5136 |
| 227.7 | 187.6 | 0.308553 | 1.113074 | 0.343442 |
| 232.1 | 187.1 | 1.166295 | 1.024975 | 1.195423 |
The sum of
Hence, the correlation coefficient is,
Then, the coefficient
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The least square regression line is found to be,
b.
To calculate: The coefficient of determination.
Answer to Problem 26E
The coefficient of determination is found to be,
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The correlation coefficient
The coefficient of determination is calculated by taking the square of the correlation coefficient.
Therefore, the coefficient of determination should be,
Simplifying the square,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the coefficient of determination is found to be
c.
To find:The least-square regression line without considering the lowest two exports.
Answer to Problem 26E
The least square regression line of the given data set is,
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From the all
The statistics should be calculated again for the current data set, imports and exports of last

The calculations can be completed using a table.
| x | y | Zx | Zy | ZxZy |
| 217.7 | 174.3 | -2.36254 | -1.85805 | 4.389725 |
| 218.1 | 175.9 | -2.26121 | -1.48713 | 3.362707 |
| 223.6 | 176.2 | -0.86789 | -1.41758 | 1.230299 |
| 224.2 | 173.2 | -0.71589 | -2.11306 | 1.512718 |
| 224.9 | 179.5 | -0.53856 | -0.65255 | 0.351434 |
| 224.6 | 179.9 | -0.61456 | -0.55982 | 0.344039 |
| 225.7 | 181.2 | -0.33589 | -0.25844 | 0.086808 |
| 226.6 | 180.5 | -0.10789 | -0.42072 | 0.045393 |
| 226.1 | 178.3 | -0.23456 | -0.93074 | 0.218314 |
| 230.5 | 179.1 | 0.880098 | -0.74528 | -0.65592 |
| 230.9 | 179.5 | 0.98143 | -0.65255 | -0.64043 |
| 225.8 | 182.1 | -0.31056 | -0.0498 | 0.015465 |
| 234.3 | 186.5 | 1.842756 | 0.970245 | 1.787925 |
| 230.9 | 184.3 | 0.98143 | 0.460224 | 0.451678 |
| 230.5 | 184.2 | 0.880098 | 0.437042 | 0.384639 |
| 227.6 | 185.2 | 0.145437 | 0.668869 | 0.097279 |
| 226.8 | 183.4 | -0.05723 | 0.251579 | -0.0144 |
| 226.1 | 182.1 | -0.23456 | -0.0498 | 0.01168 |
| 228.4 | 186.8 | 0.348102 | 1.039794 | 0.361955 |
| 225.3 | 182.7 | -0.43722 | 0.0893 | -0.03904 |
| 231.6 | 185.2 | 1.158762 | 0.668869 | 0.77506 |
| 227 | 188.7 | -0.00656 | 1.480266 | -0.00971 |
| 229.4 | 186.7 | 0.601433 | 1.016611 | 0.611424 |
| 231 | 187.1 | 1.006763 | 1.109342 | 1.116845 |
| 222.3 | 185.2 | -1.19722 | 0.668869 | -0.80078 |
| 227.7 | 187.6 | 0.170771 | 1.225256 | 0.209238 |
| 232.1 | 187.1 | 1.285427 | 1.109342 | 1.425979 |
The sum the values in the right most column is found to be,
Hence, the correlation coefficient is,
Then, the coefficient
Therefore,
Conclusion:
The least square regression line is found to be,
d.
To calculate: The coefficient of determination for the last
Answer to Problem 26E
The coefficient of determination is found to be,
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The correlation coefficient
The coefficient of determination is calculated by taking the square of the correlation coefficient.
Simplifying the square,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the coefficient of determination is found to be
e.
To find: The data set which
Answer to Problem 26E
The data set with all
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The coefficient of determination for the all
Then, the coefficient of determination for the
The coefficient of determination denotes the proportion of variance that is explained by the least-square regression line.
For the all
Conclusion:
Since
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
ELEMENTARY STATISTICS-ALEKS ACCESS CODE
- The acidity or alkalinity of a solution is measured using pH. A pH less than 7 is acidic; a pH greater than 7 is alkaline. The accompanying data represent the pH in samples of bottled water and tap water. Complete parts (a) and (b). Click the icon to view the data table. (a) Determine the mean, median, and mode pH for each type of water. Comment on the differences between the two water types. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice. A. For tap water, the mean pH is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) B. The mean does not exist. Data table Тар 7.64 7.45 7.45 7.10 7.46 7.50 7.68 7.69 7.56 7.46 7.52 7.46 5.15 5.09 5.31 5.20 4.78 5.23 Bottled 5.52 5.31 5.13 5.31 5.21 5.24 - ☑arrow_forwardく Chapter 5-Section 1 Homework X MindTap - Cengage Learning x + C webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/submit?pos=3&dep=36701632&tags=autosave #question3874894_3 M Gmail 品 YouTube Maps 5. [-/20 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES BBUNDERSTAT12 5.1.020. ☆ B Verify it's you Finish update: All Bookmarks PRACTICE ANOTHER A computer repair shop has two work centers. The first center examines the computer to see what is wrong, and the second center repairs the computer. Let x₁ and x2 be random variables representing the lengths of time in minutes to examine a computer (✗₁) and to repair a computer (x2). Assume x and x, are independent random variables. Long-term history has shown the following times. 01 Examine computer, x₁₁ = 29.6 minutes; σ₁ = 8.1 minutes Repair computer, X2: μ₂ = 92.5 minutes; σ2 = 14.5 minutes (a) Let W = x₁ + x2 be a random variable representing the total time to examine and repair the computer. Compute the mean, variance, and standard deviation of W. (Round your answers…arrow_forwardThe acidity or alkalinity of a solution is measured using pH. A pH less than 7 is acidic; a pH greater than 7 is alkaline. The accompanying data represent the pH in samples of bottled water and tap water. Complete parts (a) and (b). Click the icon to view the data table. (a) Determine the mean, median, and mode pH for each type of water. Comment on the differences between the two water types. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice. A. For tap water, the mean pH is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) B. The mean does not exist. Data table Тар Bottled 7.64 7.45 7.46 7.50 7.68 7.45 7.10 7.56 7.46 7.52 5.15 5.09 5.31 5.20 4.78 5.52 5.31 5.13 5.31 5.21 7.69 7.46 5.23 5.24 Print Done - ☑arrow_forward
- The median for the given set of six ordered data values is 29.5. 9 12 23 41 49 What is the missing value? The missing value is ☐.arrow_forwardFind the population mean or sample mean as indicated. Sample: 22, 18, 9, 6, 15 □ Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. O A. x= B. μεarrow_forwardWhy the correct answer is letter A? Students in an online course are each randomly assigned to receive either standard practice exercises or adaptivepractice exercises. For the adaptive practice exercises, the next question asked is determined by whether the studentgot the previous question correct. The teacher of the course wants to determine whether there is a differencebetween the two practice exercise types by comparing the proportion of students who pass the course from eachgroup. The teacher plans to test the null hypothesis that versus the alternative hypothesis , whererepresents the proportion of students who would pass the course using standard practice exercises andrepresents the proportion of students who would pass the course using adaptive practice exercises.The teacher knows that the percent confidence interval for the difference in proportion of students passing thecourse for the two practice exercise types (standard minus adaptive) is and the percent…arrow_forward
- Carpetland salespersons average $8,000 per week in sales. Steve Contois, the firm's vice president, proposes a compensation plan with new selling incentives. Steve hopes that the results of a trial selling period will enable him to conclude that the compensation plan increases the average sales per salesperson. a. Develop the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses.H 0: H a:arrow_forwardتوليد تمرين شامل حول الانحدار الخطي المتعدد بطريقة المربعات الصغرىarrow_forwardThe U.S. Postal Service will ship a Priority Mail® Large Flat Rate Box (12" 3 12" 3 5½") any where in the United States for a fixed price, regardless of weight. The weights (ounces) of 20 ran domly chosen boxes are shown below. (a) Make a stem-and-leaf diagram. (b) Make a histogram. (c) Describe the shape of the distribution. Weights 72 86 28 67 64 65 45 86 31 32 39 92 90 91 84 62 80 74 63 86arrow_forward
- (a) What is a bimodal histogram? (b) Explain the difference between left-skewed, symmetric, and right-skewed histograms. (c) What is an outlierarrow_forward(a) Test the hypothesis. Consider the hypothesis test Ho = : against H₁o < 02. Suppose that the sample sizes aren₁ = 7 and n₂ = 13 and that $² = 22.4 and $22 = 28.2. Use α = 0.05. Ho is not ✓ rejected. 9-9 IV (b) Find a 95% confidence interval on of 102. Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).arrow_forwardLet us suppose we have some article reported on a study of potential sources of injury to equine veterinarians conducted at a university veterinary hospital. Forces on the hand were measured for several common activities that veterinarians engage in when examining or treating horses. We will consider the forces on the hands for two tasks, lifting and using ultrasound. Assume that both sample sizes are 6, the sample mean force for lifting was 6.2 pounds with standard deviation 1.5 pounds, and the sample mean force for using ultrasound was 6.4 pounds with standard deviation 0.3 pounds. Assume that the standard deviations are known. Suppose that you wanted to detect a true difference in mean force of 0.25 pounds on the hands for these two activities. Under the null hypothesis, 40 = 0. What level of type II error would you recommend here? Round your answer to four decimal places (e.g. 98.7654). Use a = 0.05. β = i What sample size would be required? Assume the sample sizes are to be equal.…arrow_forward
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt





