
Concept explainers
(a)
The table showing various value of width
(a)
Answer to Problem 46PPS
| Width (x) | Length (2x) | Perimeter2(l+w) |
| 1 | 2 | 6 |
| 2 | 4 | 12 |
| 3 | 6 | 18 |
| 4 | 8 | 24 |
| 5 | 10 | 30 |
| 6 | 12 | 36 |
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given rectangle is
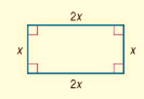
Calculation:
For various values of width:
| Width (x) | Length (2x) | Perimeter2(l+w) |
| 1 | 2 | 6 |
| 2 | 4 | 12 |
| 3 | 6 | 18 |
| 4 | 8 | 24 |
| 5 | 10 | 30 |
| 6 | 12 | 36 |
(b)
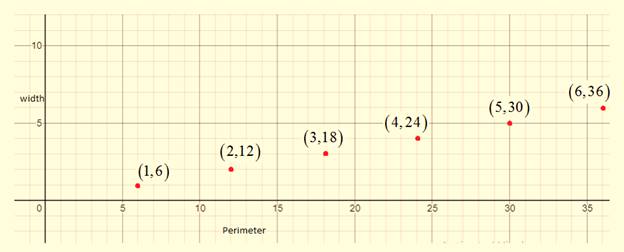
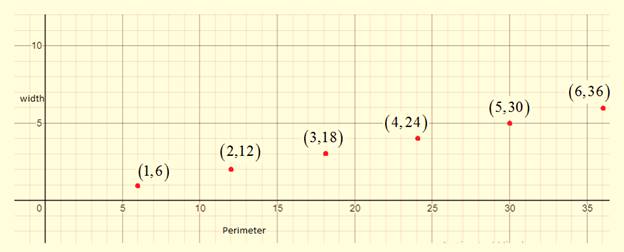
The graph of the ordered pairs
(b)
Answer to Problem 46PPS
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given rectangle is
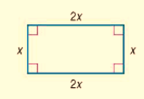
Calculation:
The ordered pairs (width, perimeter) are
The graph can be drawn as
(c)
The expression for the perimeter
(c)
Answer to Problem 46PPS
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given rectangle is
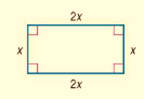
Calculation:
Let the width = w
The length = 2w
The perimeter will be
(d)
The effect on perimeter when the width is doubled
(d)
Answer to Problem 46PPS
The perimeter gets doubled
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given rectangle is
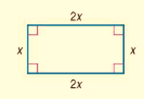
Calculation:
Let the width =2w
The length = 4w
The perimeter will be
Chapter 4 Solutions
EP PRE-ALGEBRA-STUDENTWORKS PLUS(1 YR.)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- The X is a variable in the picture, not a multiplication sign. After the variables the number is a power like X to the power of 9 Could I get assistance on how to solve this problem?arrow_forwardhow to do question 10 where u have to graph and then find domain and range. 10. y= 4x^2+24x+13arrow_forwardUse a . Venn Diagram (Euler Diagram) or truth table to decide whether each argument is valid or invalid Some of these kids are rude. Jimmy is one of these kids. Therefore, Jimmy is rude! Premise: Some of the kids are rude. Premise: Jimmy is one of these kids. Conclusion: Jimmy is rude! I dont have an image. Do you reallly need one?arrow_forward
- The functions f(x) = x² - 3 and g(x) = x² + 2 are shown on the graph. + N y 10 LO 5 f(x) = x² - 3 4 ♡ -3 -2 -10 -1 -2 -4- -5 x 2 3 4 56 7 8 9 g(x) = x² + 2 If the equations were changed to the inequalities shown, explain how the graph would change. y≤ x² - 3 y>-x²+2arrow_forwarda) find two linear map f. 9: R² →R³ s-t (1-5)=(1,-5)=(2, 2,0) b) let f: RR linear map set (3)=-\ find (√5) and (√7) f (-1) c) let X be Vector space over R and let sig ex difcid h: X-R³ s.t h(x)=(f(x),0,9(x)) xex Prove that his linear map- d) let f = L(x) S-t f²+2f+1=0 find §. e) find ker(s) s-t SiR³ R² = f(x, y, z)=(2x+1). ******arrow_forwardA craftsman of string instruments has received a new order to craft violins and guitars. The craftsman haslimited resources (wood, string, varnish) and time available to create the instruments. Each type of instrument(violin and guitar) requires specific amounts of these resources as well as a certain amount of time to complete.The craftsman wants to find the optimal number of violins and guitars to create in order to maximize the profitfrom selling them, while respecting the resource and time constraints (all instruments will be sold).The profit from selling each violin is 6,000 NOK, and the profit from selling each guitar is 3,000 NOK.Each violin requires 4 kg of wood, 0.3 l of varnish, and 2 m of string, and takes 3 days to craft. For eachguitar, the craftsman needs 5 kg of wood, 0.1 l of varnish, and 6 m of string, and it takes 2 days to make it.The craftsman’s workshop is stocked with 60 kg of wood, 2.5 l of varnish, and 65 m of string. The order needsto be completed in 30…arrow_forward
- C Clever | Portal x ALEKS - Marisa Haskins - Le Marisa Haskins - Essay Temp x Earth and Space 2 Desmos | Graphing Calculator x cwww-awy.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/10_u-IgNslkr7j8P3JH-IQ2_KWXW3dyps2nJxZ_kvzXfsB26H8ZG13mFzq9lmGAYN JJOEyt0CsUr4AMXmcIVNqw-dNsEi_PzyC7v ◇ Exponents and Exponential Functions Finding the final amount in a word problem on compound interest 0/5 Ma John deposited $4000 into an account with 4.6% interest, compounded annually. Assuming that no withdrawals are made, how much will he have in the account after 7 years? Do not round any intermediate computations, and round your answer to the nearest cent. $0 Explanation Check 1 ! 12 Q W # 3 品: S חח E $ SA 4 4 a R 5775 % e MacBook Air ৫ Di F6 DD ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessi 8 * ∞ & 27 Λ <6 T Y U DII DD FB 8° - A 1 2 小 F10 F11 ) ) 9 0 יו 0 P {arrow_forwardfor B in question 2, the inner product Is the picture given alonearrow_forward2. Assume that ƒ: R100 R² is linear and that for certain u, ER100 f(u) = - (4) and ƒ(v) = (2). Explicitly compute with work the following: (a). (b) (c) f(u+v) f(100) Assume that W is a vector space and g,h: W → R are both linear maps. Show that the function k : W→ R², k(w) = (()) is linear.arrow_forward
- 6 5 4 3 T 2 له 1- 1 -10-9 -8 -7 -6 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 2 3 4 5 -1- -2 -3 -4 -5. -8 -9. Which system is represented in the graph? Oy > x²+4x-5 y>x+5 Oy x²+4x-5 yarrow_forwardThe functions f(x) = x² - 3 and g(x) = x² + 2 are shown on the graph. + N y 10 LO 5 f(x) = x² - 3 4 ♡ -3 -2 -10 -1 -2 -4- -5 x 2 3 4 56 7 8 9 g(x) = x² + 2 If the equations were changed to the inequalities shown, explain how the graph would change. y≤ x² - 3 y>-x²+2arrow_forwardThe function f(x) is shown in the graph. 2 1 y -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 -1- -3. f(x) -4 -5 -6. Which type of function describes f(x)? ○ Exponential O Logarithmic ○ Rational O Polynomial .co. 6 7arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





