
For Exercises 32 to 35, consider kite
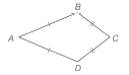
For kite
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Elementary Geometry for College Students
- 16:39 < 文字 15:28 |美图秀秀 保存 59% 5G 46 照片 完成 Bonvicino - Period Name: 6. A right regular hexagonal pyramid with the top removed (as shown in Diagram 1) in such a manner that the top base is parallel to the base of the pyramid resulting in what is shown in Diagram 2. A wedge (from the center) is then removed from this solid as shown in Diagram 3. 30 Diogram 1 Diegrom 2. Diagram 3. If the height of the solid in Diagrams 2 and 3 is the height of the original pyramid, the radius of the base of the pyramid is 10 cm and each lateral edge of the solid in Diagram 3 is 12 cm, find the exact volume of the solid in Diagram 3, measured in cubic meters. Show all work. (T 文字 贴纸 消除笔 涂鸦笔 边框 马赛克 去美容arrow_forwardAnswer question 4 pleasearrow_forward16:39 < 文字 15:28 |美图秀秀 保存 59% 5G 46 照片 完成 Bonvicino - Period Name: 6. A right regular hexagonal pyramid with the top removed (as shown in Diagram 1) in such a manner that the top base is parallel to the base of the pyramid resulting in what is shown in Diagram 2. A wedge (from the center) is then removed from this solid as shown in Diagram 3. 30 Diogram 1 Diegrom 2. Diagram 3. If the height of the solid in Diagrams 2 and 3 is the height of the original pyramid, the radius of the base of the pyramid is 10 cm and each lateral edge of the solid in Diagram 3 is 12 cm, find the exact volume of the solid in Diagram 3, measured in cubic meters. Show all work. (T 文字 贴纸 消除笔 涂鸦笔 边框 马赛克 去美容arrow_forward
- To approximate the length of a marsh, a surveyor walks x = 400 meters from point A to point B. Then, the surveyor turns 75° and walks 220 meters to point C (see figure). Approximate the length AC of the marsh. (Round your answer to one decimal place.) m C B 75° 220 m x marrow_forward. The students who attend Memorial High School have a wide variety of extra-curricular activities to choose from in the after-school program. Students are 38% likely to join the dance team; 18% likely to participate in the school play; 42% likely to join the yearbook club; and 64% likely to join the marching band. Many students choose to participate in multiple activities. Students have equal probabilities of being freshmen, sophomores, juniors, or seniors.What is the probability of the union of being either a freshman or senior? 0.07 0.44 0.50 0.25arrow_forwardWhich angles are complementary to each other? Select all that apply. 3 2 4 in 5 1 Z1 and 23 Z1 and 25 22 and 23 Z2 and 25 Submitarrow_forward
- Which angles are adjacent to each other? Select all that apply. 3 2 4 67 5 8 11 10 12 12 9 27 and 28 Z9 and 12 Z3 and 24 Z10 and Z11arrow_forwardIf the arc length of NMP is 11π, what is the length of MNP expressed in terms of πT? M N 5 44% ○ A. 54π OB. 108π P О с. 103 18 O D. 108arrow_forwardGiven: Circle J 2 What is the value of y? A. 38 C. 68 B. 50 D. 92arrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





