
Concept explainers
A truss can be supported in the eight different ways shown A connections consist of smooth pins, rollers, or short links. For case, answer the questions listed in Prob. 4.59, and, wherever possible, compute the reactions, assuming that the magnitude force P is 12 kips.
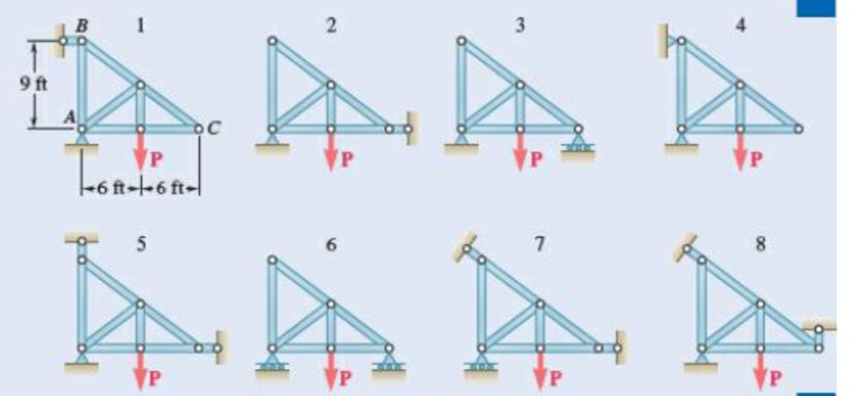
Fig. P4.60
(a)
Find whether the plate is completely, partially, or improperly constrained.
Answer to Problem 4.60P
The plate in figure 1 is
The plate figure 2 is
The plate figure 3 is
The plate figure 4 is
The plate figure 5 is
The plate figure 6 is
The plate figure 7 is
The plate figure 8 is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The magnitude of the force P is 12 kips.
Calculation:
Figure 1:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 1.
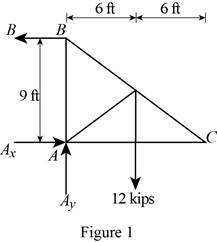
The three reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate in figure 1 is
Figure 2:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 2.
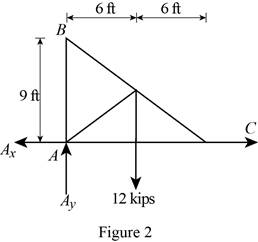
The three reactions in the plate behave like concurrent force system.
The plate figure 2 is
Figure 3:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 3.
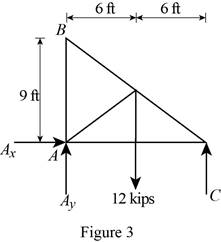
The three reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate figure 3 is
Figure 4:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 4.
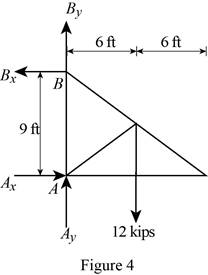
The four reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate figure 4 is
Figure 5:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 5.
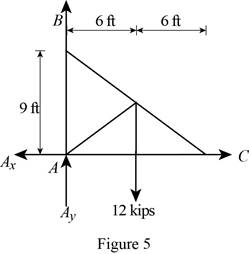
The four reactions in the plate behave like concurrent force system.
The plate figure 5 is
Figure 6:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 6.
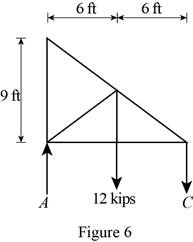
The two reactions in the plate behave like concurrent force system.
The plate figure 6 is
Figure 7:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 7.
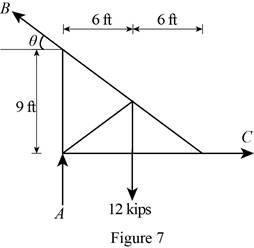
The three reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate figure 7 is
Figure 8:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 8.
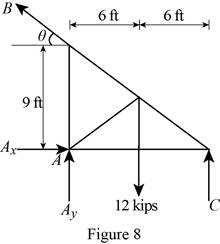
The four reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate figure 8 is
(b)
Find whether the reactions are statically determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 4.60P
The reactions in figure 1 is
The reactions in figure 2 is
The reactions in figure 3 is
The reactions in figure 4 is
The reactions in figure 5 is
The reactions in figure 6 is
The reactions in figure 7 is
The reactions in figure 8 is
Explanation of Solution
Refer Figure 1:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 1 is
Refer Figure 2:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
But the plate is improperly constrained and the plate is not in equilibrium.
The reactions in figure 2 is
Refer Figure 3:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 3 is
Refer Figure 4:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are not enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 4 is
Refer Figure 5:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
But the plate is improperly constrained and the plate is not in equilibrium.
The reactions in figure 5 is
Refer Figure 6:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 6 is
Refer Figure 7:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 7 is
Refer Figure 8:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are not enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 8 is
(c)
Find whether the equilibrium of the plate is maintained.
Answer to Problem 4.60P
The reactions in the plate 1 are
The plate 1 is in
The plate 2 is in
The reactions in the plate 3 are
The plate 3 is in
The reactions in the plate 4 are
The plate 4 is in
The plate 5 is in
The reactions in the plate 6 are
The plate 6 is in
The reactions in the plate 7 are
The plate 7 is in
The reactions in the plate 8 are
The plate 8 is in
Explanation of Solution
Refer Figure 1:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Find the resultant force at A;
Find the angle
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 1 are
The plate 1 is in
Refer Figure 2:
The equilibrium equations are;
The moment about point A is not equal to zero.
The plate 2 is in
Refer Figure 3:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 3 are
The plate 3 is in
Refer Figure 4:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 4 are
The plate 4 is in
Refer Figure 5:
The equilibrium equations are;
The moment about point A is not equal to zero.
The plate 5 is in
Refer Figure 6:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 6 are
The plate 6 is in
Refer Figure 7:
The equilibrium equations are;
Find the angle
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 7 are
The plate 7 is in
Refer Figure 8:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point C.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 8 are
The plate 8 is in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Research and select any different values for the Ratio of connecting rod length to crank radius from various engine models, then analyze how these changes affect instantaneous velocity and acceleration, presenting your findings visually using graphs.arrow_forwardPb 9) 4.44 bas gnibus& WX 002 grillimatul fred bail (e) For the simply supported I-beam, a load of 1000 lb in center. Find the maximum transverse shear stress. Compare your answer with the approximation obtained by dividing the shear load by the area of the web only with the web considered to extend for the full 8-in depth. - 3½ in. 12 bas in 0% to tolerabib tormi no grived in. 8 in. 38 in. 12 ½ in.arrow_forwardPb 12) 4.61 Draw the Mohr circle for the stresses experienced by the surface of an internally pressurized steel tube that is subject to the tangential and axial stresses in the outer surface of 45 ksi and 30 ksi, respectively, and a torsional stress of 18 ksi. yx 18 45 30arrow_forward
- Pb 8) 4.39 For the C-clamp shown, what force F can be exerted by the screw if the maximum tensile stress in the clamp is to be limited to 30 ksi? F 2 in. სის 3436 16 13 blos 0101 alos12 nodus 121A (s 3 in. in. 16 in. 16 web leonas OFF elson yollA (d 016 (& d of bolow-bloo ai 15912 020112LA sue) vilisub 22 bal.90 Swman a bris ctxibasqqA) laste is tools?arrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 6mm, for w2 h2 = 5mm, and for w3 is h3 =5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx). 140 S Find the centroid I want university professor solutions O REDMI NOTE 8 PRO CAI QUAD CAMERA 101.15 Farrow_forwardPb 6) 4.31 do = 25 mm 4.31 What bending moment is required to produce a maximum normal stress of 400 MPa: (a) In a straight round rod of 40-mm diameter? (b) In a straight square rod, 40 mm on a side (with bending about the X axis as shown for a rectangular section in Appendix B-2)?arrow_forward
- Pb 13) 4.73 Find the maximum value of stress at the hole and semicircular notch. 45000 N 50 mm 100 mm 15 mm 25 mm 45000 Narrow_forwardPb 11) 4.53 Consider the 1-in solid round shaft supported by self-aligning bearings at A and B. Attached to the shaft are two chain sprockets that are loaded as shown. Treat this as a static loading problem and identify the specific shat location subjected to the most severe state of stress and make a Mohr circle representation of this stress state. 1-in.-dia. shaft 500 lb 2 in. 1000 lb 3 in. 3 in.arrow_forwardPb 5) 4.19 Estimate the torque required to produce a maximum shear stress of 570 MPa in a hollow shaft having an inner diameter of 20 mm and an outer diameter of 25 mm. d; = 20 mm T d = 25 mm Tmax = 570 MPaarrow_forward
- Quiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 6mm, for w2 h2 = 5mm, and for w3 is h3 =5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx). I want university professor solutions O REDMI NOTE 8 PRO CAI QUAD CAMERA 140 S 101.15 Farrow_forwardResearch and select different values for the R ratio from various engine models, then analyze how these changes affect instantaneous velocity and acceleration, presenting your findings visually using graphsarrow_forwardMeh Battery operated train Coll CD Af Pair 160,000kg 0.0005 0.15 5m² 1.2kg/m³ 19 7et nong 0.98 0.9 0.88 Tesla Prated Tesla Trated Ywheel ng Jaxle. 270kW 440NM 0.45m 20 2 8.5kgm² Consider a drive cycle of a 500km trip with 3 stops in the middle. Other than the acceleration and deceleration associated with the three stops, the tran maintains. constant cruise speed velocity of 324 km/hr. The tran will fast charge at each stop for 15 min at a rate Peharge = 350 kW (ผม τ (MN 15MIN Stop w charging (350kW GMIJ restored during 15 minutes of fast charging at Calculate the battery energy Pcharge = 350kW Calculate the net energy gain per stop t 64 Determice the total battery energy required Ebat to complete the 500km trip with 3 stops. etcarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





