
Represent the maps given in Exercises 37-40 by graphs as we did in Example 6. Recall that we join two vertices by an edge if and only if the states that they represent share a stretch of common border
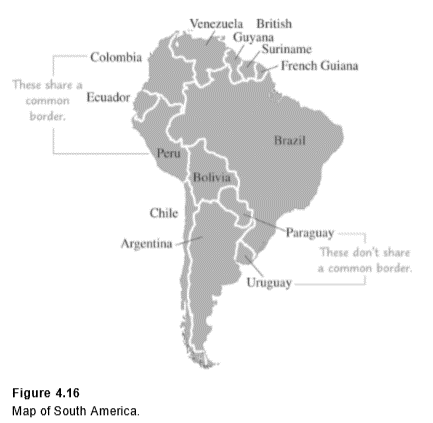
Example 6 Solving the Four-Color Problem for South America
Model the map of South America by a graph and use this graph to color the map using at most four colors.
Solution: In this problem, we have a set of countries, some of which are related in that they share a common border. Therefore, we can model this situation by a graph.
We will represent each country by a vertex; if two countries share a common border, we draw an edge between the corresponding vertices. This graph appears in Figure 4.17 .
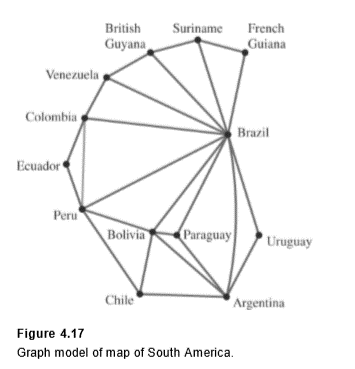
Note that we connect the vertices representing Peru and Colombia with an edge because they share a common boundary. We do not connect the vertices representing Argentina and Peru, because they have no boundary in common.
We can rephrase the map-coloring question now as follows: Using four or fewer colors, can we color the vertices of a graph so that no two vertices of the same edge receive the same color? It is easier to think about coloring a graph than it is to think about coloring the original map.
We show one coloring using four colors in Figure 4.18 and another coloring that I generated on my iPad using a graph theory app called Graphynx. Notice that Graphynx again had to use four colors to color the graph.
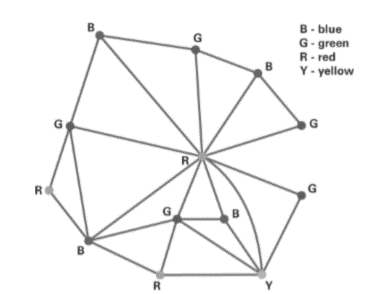
Figure 4.18 Coloring of graph of South America.
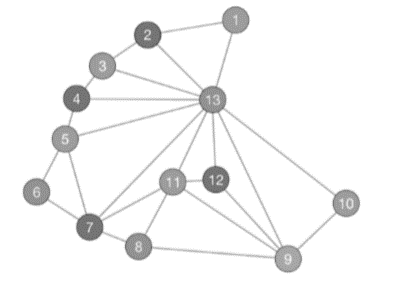
Graphynx coloring of graph of South America.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
MYLAB MATH WITH PEARSON ETEXT FOR MATHEM
- B G R + K Match each equation with a graph above - 3(0.9)* 1 a. green (G) 3(1.5)* b. black (K) 3(0.73)* c. blue (B) d. red (R) I ✪ 4(1.21)* - 3(1.21)* e. orange (O)arrow_forwardSuppose the planet of Tattooine currently has a population of 6500 people and an annual growth rate of 0.35%. Use this information for all the problems below.arrow_forwardConsider the weighted voting system [16: 15, 8, 3, 1]Find the Banzhaf power distribution of this weighted voting system.List the power for each player as a fraction: P1: P2: P3: P4:arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls willarrow_forwardConsider the weighted voting system [9: 7, 4, 1]Find the Shapley-Shubik power distribution of this weighted voting system.List the power for each player as a fraction:P1: P2: P3:arrow_forwardConsider the weighted voting system [11: 7, 4, 1]Find the Shapley-Shubik power distribution of this weighted voting system.List the power for each player as a fraction: P1: P2: P3:arrow_forward
- Consider the weighted voting system [18: 15, 8, 3, 1]Find the Banzhaf power distribution of this weighted voting system.List the power for each player as a fraction: P1: P2: P3: P4:arrow_forwardConsider the weighted voting system [16: 15, 8, 3, 1]Find the Banzhaf power distribution of this weighted voting system.List the power for each player as a fraction: P1: P2: P3: P4:arrow_forwardConsider the weighted voting system [18: 15, 8, 3, 1]Find the Banzhaf power distribution of this weighted voting system.List the power for each player as a fraction: P1 = P2 = P3 = P4 =arrow_forward
- Consider the weighted voting system [18: 15, 8, 3, 1]Find the Banzhaf power distribution of this weighted voting system.List the power for each player as a fraction: P1: P2: P3: P4:arrow_forwardConsider the weighted voting system [18: 15, 8, 3, 1]Find the Banzhaf power distribution of this weighted voting system.List the power for each player as a fraction: P1: P2: P3: P4:arrow_forwardFind the Banzhaf power distribution of the weighted voting system[26: 19, 15, 11, 6]Give each player's power as a fraction or decimal value P1 = P2 = P3 = P4 =arrow_forward
 Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
 Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





