
Concept explainers
A person stands on a scale, which then reads 600 N. (a) What force is exerted on the scale by the person? (b) What force is exerted on the person by the scale? (c) What would happen to the reading as the person began to jump straight up?
(a)
The magnitude of the force applied on the scale by the person if he stands on a scaleand the readingis
Answer to Problem 9SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The weight of the person is
The scale is at rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of force equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the scale when the person stands on it:
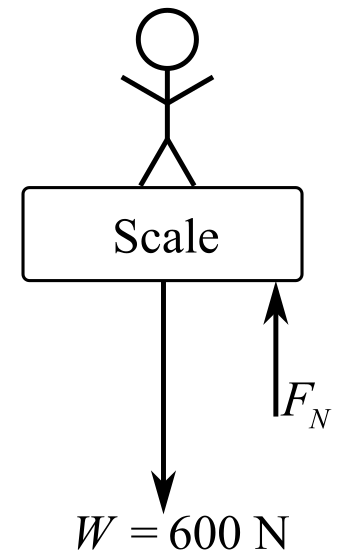
In the diagram,
Recall the expression for the first condition of force equilibrium:
Consider that the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Therefore,
Substitute
From Newton’s third law, the force exerted on the scale by a person is equal and opposite to the weight of the person and it acts in the downward direction because the force applied by the person is in the downward direction. So, the magnitude of force applied by the person to the scale should be equal to the normal reaction force applied by the contact surface of the scale to the person.
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the force applied on the scale by the person is
(b)
The magnitude of the force applied on the person by the scale if he stands on a scale and the scale reads
Answer to Problem 9SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The weight of the person is
The scale is at rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of force equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the scale:

In the above diagram,
Recall the expression for the first condition of force equilibrium:
Consider that the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Therefore,
Substitute
From Newton’sthird law, the force exerted on the person by the scale is equal and opposite to the weight of the person and it actsin the upward direction because the force exerted by the scale is in the upward direction.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the force applied on the person by the scale is
(c)
The reading on a scale when the person begins to jump straight up on a scale.
Answer to Problem 9SP
Solution:
Increase
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The weight of the person is
The scale is at rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for Newton’s second law of motion:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the person when he begins to jump:
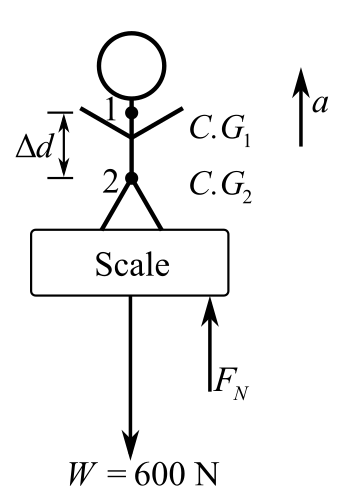
In the diagram given above,
Recall the expression for Newton’s second law of motion along the vertical direction:
Consider that the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Therefore,
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, as the person starts to jump straight up, the reading of the scale would increase.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
- A circular capacitor has 6mm radius. Two parallel plates are 2mm apart. Between the capacitors magnetic field is B=410^-2 Tesla in theta direction at a given time. Calculate the displacement current and change in electric field at thatmomentarrow_forwardA light source is incoming with 30 degrees with the normal force to an equilateral prism made out of a material withn=1.2 and it exits the prism. Draw the ray diagramarrow_forward1 Cartpole System Analysis The cartpole system (Fig. 1) consists of a cart of mass M moving along a frictionless track, and a pendulum of mass m and length 1 pivoting around the cart. The mass of the pendulum is assumed to be equally distributed along the rigid rod. The system is actuated by a horizontal force F applied to the cart. m Ө X F M Figure 1: Cart-pole as the combination of a cart and a pendulum. 1.1 Tasks 1. Draw the free-body diagram of the pendulum and cart, showing all forces acting on them. Note: Point the reaction force Fx as the coupling force between the pendulum and the cart in positive x-direction in the free-body diagram of the pendulum.arrow_forward
- A light beam with intensity I=40W/m^2 passes through two polarizers. First polarizer makes 30 degrees with the y-axis and the second one makes 40 degrees with the x-axis. Find the final intensity as it exits both polarizers fora) Original beam is umpolarized b) Original beam is polarized in x direction c) Original beam is polarized in y-directonarrow_forwardFind the critical angle between ruby and glass. Ruby has n=1.75 and glass has n=1.5Draw an approximate raydiagram for a beam coming 5 degrees less than the critical anglearrow_forwardCalculate the value of the force F at which the 20 kg uniformly dense cabinet will start to tip. Calculate the acceleration of the cabinet at this force F. Must include the FBD and KD of the system. Ignore friction.arrow_forward
- 1) A 2.0 kg toy car travelling along a smooth horizontal surface experiences a horizontal force Fas shown in the picture to the left. Assuming the rightward direction to be positive and if the car has an initial velocity of 60.0m/s to the right, calculate the velocity of the car after the first 10.0s of motion. (Force is in Newtons and time in seconds). (Hint: Use impulse-momentum theorem) F 5.0 10 0 -10arrow_forward3) Two bumper cars of masses 600 kg and 900 kg travelling (on a smooth surface) with velocities 8m/s and 4 m/s respectively, have a head on collision. If the coefficient of restitution is 0.5. a) What sort of collision is this? b) Calculate their velocities immediately after collision. c) If the coefficient of restitution was 1 instead of 0.5, what is the amount of energy lost during collision?arrow_forwardThe rectangular loop of wire shown in the figure (Figure 1) has a mass of 0.18 g per centimeter of length and is pivoted about side ab on a frictionless axis. The current in the wire is 8.5 A in the direction shown. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane. Find the direction of the magnetic field parallel to the y-axis that will cause the loop to swing up until its plane makes an angle of 30.0 ∘ with the yz-plane.arrow_forward
- Give a more general expression for the magnitude of the torque τ. Rewrite the answer found in Part A in terms of the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment of the current loop m. Define the angle between the vector perpendicular to the plane of the coil and the magnetic field to be ϕ, noting that this angle is the complement of angle θ in Part A. Give your answer in terms of the magnetic moment mm, magnetic field B, and ϕ.arrow_forwardCalculate the electric and magnetic energy densities at thesurface of a 3-mm diameter copper wire carrying a 15-A current. The resistivity ofcopper is 1.68×10-8 Ω.m.Prob. 18, page 806, Ans: uE= 5.6 10-15 J/m3 uB= 1.6 J/m3arrow_forwardA 15.8-mW laser puts out a narrow beam 2.0 mm in diameter.Suppose that the beam is in free space. What is the rms value of E in the beam? What isthe rms value of B in the beam?Prob. 28, page 834. Ans: Erms= 1380 V/m, Brms =4.59×10-6 Tarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





