
Write a net ionic equation for any precipitation reaction that occurs when 1 M solutions of the following are mixed.
(a) copper(II) sulfate and sodium chloride
(b) manganese(II) nitrate and ammonium hydroxide
(c) silver nitrate and hydrochloric acid
(d) nickel(II) sulfate and potassium hydroxide
(e) ammonium carbonate and sodium nitrate
(a)
Interpretation:
The net ionic equation should be written when copper(II) sulfate and sodium chloride are mixed.
Concept introduction:
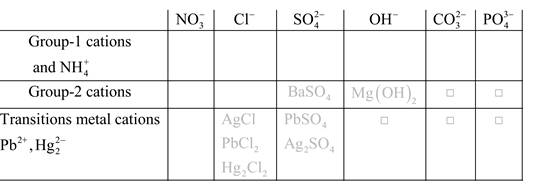
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 9QAP
No precipitation occurs.
Explanation of Solution
Copper(II) sulfate:
Sodium chloride:
Reaction for the solution of copper(II) sulfate and sodium chloride is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
(b)
Interpretation:
The net ionic equation should be written when manganese(II) nitrate and ammonium hydroxide are mixed.
Concept introduction:
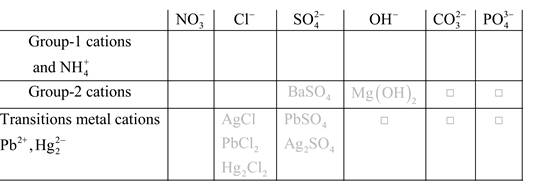
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 9QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Manganese(II) nitrate:
Ammonium hydroxide:
Reaction for the solution of manganese(II) nitrate and ammonium hydroxide is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
(c)
Interpretation:
The net ionic equation should be written when silver nitrate and hydrochloric acid are mixed.
Concept introduction:
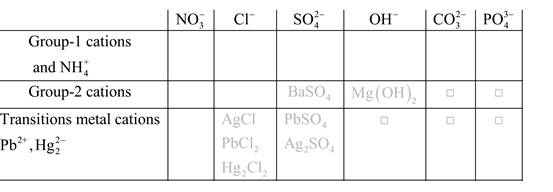
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 9QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Silver nitrate:
Hydrochloric acid:
Reaction for the solution of silver nitrate and hydrochloric acid is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
(d)
Interpretation:
The net ionic equation should be written when nickel(II) sulfate and potassium hydroxide are mixed.
Concept introduction:
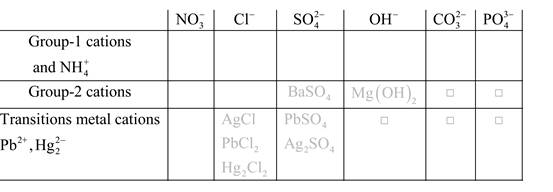
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 9QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Nickel(II) sulfate:
Potassium hydroxide:
Reaction for the solution of silver nitrate and hydrochloric acid is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
(e)
Interpretation:
The net ionic equation should be written when ammonium carbonate and sodium nitrate are mixed.
Concept introduction:
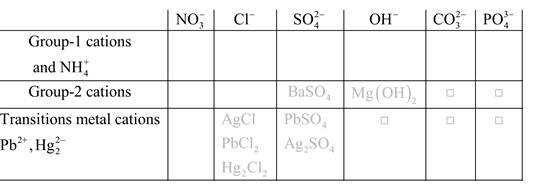
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 9QAP
No precipitation occurs.
Explanation of Solution
Ammonium carbonate:
Sodium nitrate:
Reaction for the solution of silver nitrate and hydrochloric acid is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
PRINCIPLES+REACTIONS
- Write the amididation reaction mechanism of a-aminophenol and acetic acid to produce acetaminophenarrow_forwardFor the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. arrow_forwardHow to draw the reaction mechasnism belowarrow_forward
- Name the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forward
- How to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forwardPlease help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





