
Write the formulas of the following compounds and decide which are soluble in water.
(a) sodium sulfate
(b) iron(lll) nitrate
(c) silver chloride
(d) chromium(lll) hydroxide
(a)
Interpretation:
The formula for sodium sulfate should be written along with identify whether it is soluble in water or not.
Concept introduction:
First, the symbol of the metal (cation) with its ion charge as a superscript should be written.
The symbol of the non-metal (anion) with its ion charge or polyatomic ion as a superscript should be written.
After that, the charges should be crisscross so that they become subscript for the opposite element and + and - charges should be removed.
| Group-1 cations and |
||||||
| Group-2 cations | - | - | ||||
| Transitions metal cations |
- | - | - |
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with hyphen will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Answer to Problem 1QAP
The formula is
It is soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is sodium sulfate
Symbol of sodium is
Symbol of sulfate is
Sodium belongs to group 1 and carries +1 charge.
Sulfate is a polyatomic ion carries -2 charge.
The symbol of sodium and sulfate is written with their charges and charges are crisscrossed.
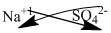
Thus, the formula is
Ions present in the solution is
According to solubility, attractive forces present between ion and ion is less than the water to ion. Thus, it is soluble in water.
(b)
Interpretation:
The formula for iron(III) nitrate should be written along with identify whether it is soluble in water or not.
Concept introduction:
First, the symbol of the metal (cation) with its ion charge as a superscript should be written.
The symbol of the non-metal (anion) with its ion charge or polyatomic ion as a superscript should be written.
After that, the charges should be crisscross so that they become subscript for the opposite element and + and - charges should be removed.
| Group-1 cations and |
||||||
| Group-2 cations | - | - | ||||
| Transitions metal cations |
- | - | - |
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with hyphen will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Answer to Problem 1QAP
The formula is
It is soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is iron(III) nitrate
Symbol of iron is
Symbol of nitrate is
Here, iron(III) implies iron carries +3 charge.
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion carries -1 charge.
The symbol of iron and nitrate is written with their charges and charges are crisscrossed.
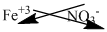
Thus, the formula is
Ions present in the solution is
According to solubility chart, all nitrates are soluble. Thus, iron(III) nitrate is soluble in water.
(c)
Interpretation:
The formula for silver chloride should be written along with identify whether it is soluble in water or not.
Concept introduction:
First, the symbol of the metal (cation) with its ion charge as a superscript should be written.
The symbol of the non-metal (anion) with its ion charge or polyatomic ion as a superscript should be written.
After that, the charges should be crisscross so that they become subscript for the opposite element and + and - charges should be removed.
| Group-1 cations and |
||||||
| Group-2 cations | - | - | ||||
| Transitions metal cations |
- | - | - |
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with hyphen will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Answer to Problem 1QAP
The formula is
It is insoluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is silver chloride
Symbol of silver is
Symbol of chloride is
Here, silver is a metal carries + 1 charge.
Chloride is a non-metal carries -1 charge.
The symbol of silver and chloride is written with their charges and charges are crisscrossed.
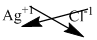
The formula is
Make the above formula simplify, thus the formula of given compound is
Ions present in the solution is
According to the solubility chart, it will form precipitate, thus insoluble in water.
(d)
Interpretation:
The formula for chromium(III) hydroxide should be written along with identify whether it is soluble in water or not.
Concept introduction:
First, the symbol of the metal (cation) with its ion charge as a superscript should be written.
The symbol of the non-metal (anion) with its ion charge or polyatomic ion as a superscript should be written.
After that, the charges should be crisscross so that they become subscript for the opposite element and + and - charges should be removed.
| Group-1 cations and |
||||||
| Group-2 cations | - | - | ||||
| Transitions metal cations |
- | - | - |
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with hyphen will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Answer to Problem 1QAP
The formula is
It is insoluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is chromium(III) hydroxide
Symbol of chromium is
Symbol of hydroxide is
Here, chromium(III) implieschromium carries +3 charge.
Hydroxide ion carries -1 charge.
The symbol of chromium and hydroxide is written with their charges and charges are crisscrossed.
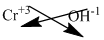
The formula is
Ions present in the solution is
According to the solubility chart, it will form precipitate, thus insoluble in water.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
PRINCIPLES+REACTIONS
- 4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a) NHBoc ⚫OBn HO. H3C CO2CH3 -OBn H3C H3C. H3C. NHBOC CI CO2CH3arrow_forwardDraw structures of the following compounds and identify their role: mCPBA (MCPBA) DMS Py 9-BBN LAH Sia₂BH TsCI PCC t-BuOK LDA MeLi n-BuLi DMSO DMF Sodium Borohydride Lithium DiisopropylAmide 2arrow_forwardUsing Luther's rule, calculate the reference potential of the Hg2+/Hg redox electrode. DATA: Electrode potentials E° = 0,854 V y E 0,788 V Hg2+/Hg 2+ Hg2/Hgarrow_forward
- For the following compound: HO -H Draw a mechanism for the tautomerization process under BASIC conditions: Mechanism A: H-O: H-OH H-O HH H-OO Mechanism B: H-Q Mechanism C: Θ OH H-O: Mechanism D: H-O H- H-OO C H-OO H- H- H-OO HH OH -H - HON H :OH H-Harrow_forwardidentify the product (or multiple products) for each of the following reactions: CI 1) NaNH2 (excess) ठ Cl 2) H₂O Hz H₂SO₂, H₂O HgSO Lindlar's catalyst 1) n-BuLi 2) 1)9-BBN 2) H₂O, NaOH ? Br H A B C afó gó H OA B O c OD E OF D E F H H Na, NHarrow_forwardIdentify the product (or multiple products) for each of the following reactions: ? or CI CI 1) NaNHz (excess) 2) H₂O OA OB O C OD OE OF H₂SO₂, H₂O Hq50. 1) n-BuLi 2) Br 1) 9-BBN 2) H₂O₂, NaOH A B H H متته D E H H H H C H H F H H H₂ Lindlar's catalyst Na NHarrow_forward
- Identify the product (or multiple products) for each of the following reactions: O A OB Oc OD OE OF CI CI 1) NaNH2 (excess) 2) H₂O H₂ H₂SO2, H₂O HgSO Lindlar's catalyst 1) n-BuLi 2) Br 1)9-BBN 2) H₂O₂, NaOH ? Na, NH3 C H A H H مننه مننه منن مننه H F H H E مند H D H Harrow_forwardFor the following compound: HO H Draw a mechanism for the tautomerization process under BASIC conditions: Mechanism A: + H-O: H-OH₂ H Mechanism B: H-Ö: HO-H H-OO -H H HH H H HH H-O: H-OO H-OO -H H e -H : OH Θ Mechanism C: Θ A : OH H-O: H H H-O-H 0. Mechanism D: e.. : OH :0 H H-O-H H-O: H-OO :O H -H H H сём H 0 :0 + H Θ H H H-arrow_forwardFor the following compound: H OH Draw a mechanism for the tautomerization process under ACIDIC conditions: Mechanism A: Θ :OH O O-H HO 0: Mechanism B: :O-H e.. Θ :OH Mechanism C: H HO-H :0: Θ 0: H H e.. : OH 0: "Θ HH O. :OH :OH O-H O-H Mechanism D: :OH H-OH₂ :OH HO-H 0: © O-H H HH 0: HHarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





