
Concept explainers
a.
Arrange the data and obtain Xmin and Xmax.
a.
Answer to Problem 99CE
The value of Xmin is 0.9.
The value of Xmax is 11.9.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The data state to choose a dataset to prepare a brief descriptive report.
Here, the data chosen is Data set A.
The Data set A represents the percentage of sales in selected industries.
The data set A of sales percent can be sorted either ascending or descending.
Here, the data is sorted in the ascending order.
Sorting:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to sort the data using the MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Data > Sort.
- In columns to sort by, enter Percent.
- Under Columns to sort , Choose specified columns.
- In columns, enter the percent and choose increasing option.
- In storage location for current columns, choose “specified columns of the current worksheet”.
- In columns, enter “sorted percent”.
- Click ok.
Thus, the sorted data has been stored in the column of sorted percent.
Minimum and Maximum:
Step-by-step procedure to find the minimum and maximum using the MINITAB software using the given below:
- Choose Calc>calculator.
- In store result in variable box, enter Minimum.
- Under Expression, enter “MIN(Percent)”.
- Click ok.
- Choose Calc>calculator.
- In store result in variable box, enter Maximum.
- Under Expression, enter “MAX(Percent)”.
- Click ok.
Data display:
Step-by-step procedure to display the data using the MINITAB software using the given below:
- Choose data> display data.
- Select the columns to display as Minimum, Maximum.
- Click ok.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
Thus, the value of Xmin is 0.9 and the value of Xmax is 11.9.
b.
Construct a histogram.
b.
Answer to Problem 99CE
Histogram:
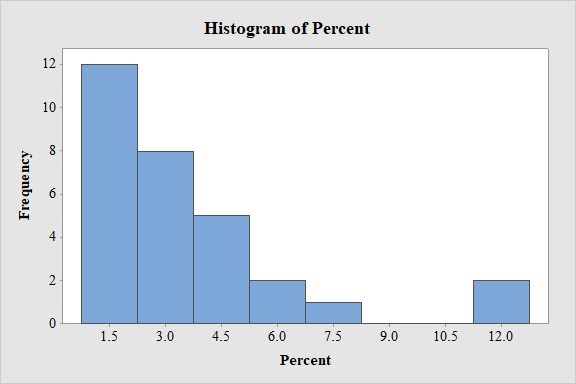
Output obtained from MINITAB software is:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software procedure:
- Step by step procedure to draw the Histogram using MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Graph > Histogram.
- Choose Simple, and then click OK.
- In Graph variables, enter the Percent.
- Click OK.
Thus, the histogram has been obtained.
By observing the graph, it is clear that the curve is right skewed. Hence, it is appropriate to conclude that the data is approximately right skewed. Thus, the data set A for percent of sales is approximately right skewed.
c.
Find the
c.
Answer to Problem 99CE
The mean score is 3.55.
The median score is 3.
Explanation of Solution
Mean and median:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to find the mean, the median using the MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display
Descriptive Statistics . - In Variables enter the columns Percent.
- Choose option statistics, and select Mean, Median.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
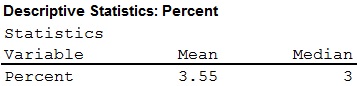
- Thus, the mean and the median for the data set A are 3.55 and 3 respectively.
Shape of the distribution:
- For symmetric data, the mean, the median and the
mode are equal. - For positively skewed data, the mean exceeds the median.
- For negatively skewed data, the mean is lower than the median.
From the value of mean, median, it is observed that the value of mean is greater than that of the median.
Thus, the data is said to be right skewed or positively skewed.
d.
Find the standard deviation for data set A.
d.
Answer to Problem 99CE
The standard deviation for data set A is 2.749.
Explanation of Solution
Standard deviation:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to find the mean and standard deviation using the MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display Descriptive Statistics.
- In Variables enter the columns Percent.
- Choose option statistics, and select Standard deviation.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
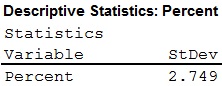
- Thus, the standard deviation have been obtained.
e.
Standardize the data and identify the outliers and unusual observations.
e.
Answer to Problem 99CE
The standardized values of dataset A are given below:
| -0.9640 | -0.6366 | 0.3456 | 0.3820 | -0.6730 | 0.0909 |
| 0.7093 | -0.0182 | -0.0182 | -0.9276 | -0.1637 | -0.2001 |
| 1.4005 | -0.9640 | -0.8912 | -0.0182 | 3.0375 | -0.6002 |
| -0.8185 | 1.0367 | -0.2001 | -0.4547 | 0.2728 | -0.6366 |
| -0.8912 | -0.5638 | -0.5638 | 0.4911 | -0.3820 | 2.8192 |
There are one outlier in the dataset.
Explanation of Solution
Standardized values:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain standardized values using EXCEL software is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- Enter the data in the column A in cells A1 to A32.
- In cell B1, enter the formula “=STANDARDIZE(A1, 3.55, 2.749)”.
- Select “ENTER” option.
- Select and copy the cell B1 and drag till the 30nd cell.
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
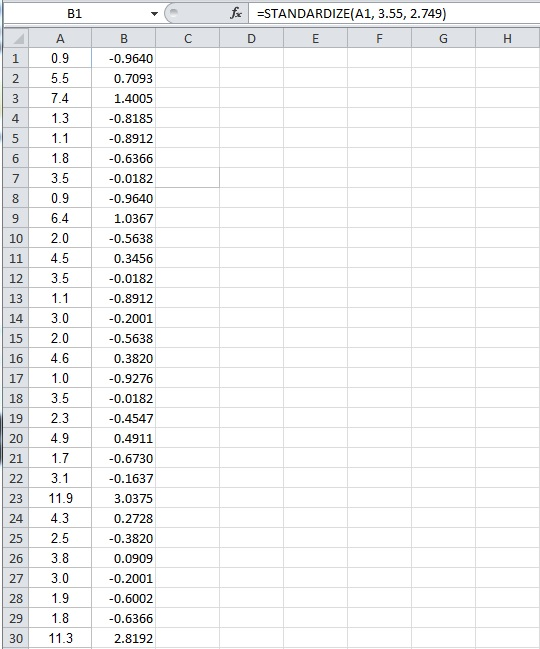
Thus, the standardized values have been obtained using EXCEL.
The outliers in the data set A can be identified using
Empirical Rule:
The Empirical Rule for a Normal model states that:
- Within 1 standard deviation of mean, 68.26% of all observations will lie.
- Within 2 standard deviations of mean, 95.44% of all observations will lie.
- Within 3 standard deviations of mean, 99.73% of all observations will lie.
Empirical rule using MEGASTAT:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain Empirical rule using Mega Stat software is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- Enter the data in the column A in cells A1 to A30.
- From the Add-Ins, Select Mega Stat >Descriptive statistics.
- A dialogue box appears.
- In Input
range box, select the input range from Sheet1!$A$1:$A$30. - From the list box, select Empirical rule.
- Click “OK”.
Output obtained using MEGA STAT is as follows:
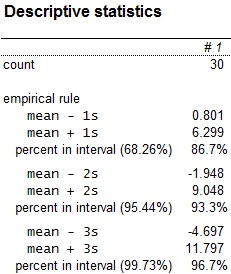
The upper and lower bounds for the intervals indicated by the Empirical rule have been obtained.
Based on the z-scores, the observation has one outlier, that is, the observations with values 11.9 do not lie within the 3-standard deviations limits (–4.697 to 11.797). there is no unusual observation in the data set A.
f.
Find the
f.
Answer to Problem 99CE
The Q1 (25th percentile) is 1.775, Q2 (50th percentile) is 3 and Q3 (75th percentile) is 4.525.
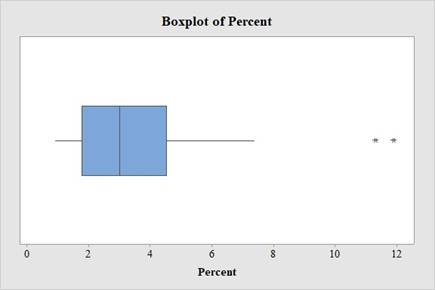
The boxplot for the data set A is:
Explanation of Solution
Quartiles:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to find the Quartiles using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display Descriptive Statistics.
- In Variables enter the columns Percent.
- Choose option statistics, and select First Quartile, Median and Third Quartile.
- Choose option Graphs, and select boxplot of data.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
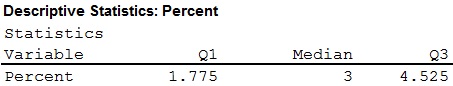

- Thus, the Quartiles and boxplot have been obtained.
Observation:
From the boxplot, it is observed that the data set has two outliers within it. The boxplot disclosed that the median is closer to the first quartile, Q1 than it is to the third quartile, Q3, suggesting that the data is right skewed. The whiskers on the two sides are close in length, although it appears that the left whisker is slightly longer.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Gen Combo Ll Applied Statistics In Business & Economics; Connect Access Card
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forward3. Consider the following regression model: Yi Bo+B1x1 + = ···· + ßpxip + Єi, i = 1, . . ., n, where are i.i.d. ~ N (0,0²). (i) Give the MLE of ẞ and σ², where ẞ = (Bo, B₁,..., Bp)T. (ii) Derive explicitly the expressions of AIC and BIC for the above linear regression model, based on their general formulae.arrow_forwardHow does the width of prediction intervals for ARMA(p,q) models change as the forecast horizon increases? Grows to infinity at a square root rate Depends on the model parameters Converges to a fixed value Grows to infinity at a linear ratearrow_forward
- Consider the AR(3) model X₁ = 0.6Xt-1 − 0.4Xt-2 +0.1Xt-3. What is the value of the PACF at lag 2? 0.6 Not enough information None of these values 0.1 -0.4 이arrow_forwardSuppose you are gambling on a roulette wheel. Each time the wheel is spun, the result is one of the outcomes 0, 1, and so on through 36. Of these outcomes, 18 are red, 18 are black, and 1 is green. On each spin you bet $5 that a red outcome will occur and $1 that the green outcome will occur. If red occurs, you win a net $4. (You win $10 from red and nothing from green.) If green occurs, you win a net $24. (You win $30 from green and nothing from red.) If black occurs, you lose everything you bet for a loss of $6. a. Use simulation to generate 1,000 plays from this strategy. Each play should indicate the net amount won or lost. Then, based on these outcomes, calculate a 95% confidence interval for the total net amount won or lost from 1,000 plays of the game. (Round your answers to two decimal places and if your answer is negative value, enter "minus" sign.) I worked out the Upper Limit, but I can't seem to arrive at the correct answer for the Lower Limit. What is the Lower Limit?…arrow_forwardLet us suppose we have some article reported on a study of potential sources of injury to equine veterinarians conducted at a university veterinary hospital. Forces on the hand were measured for several common activities that veterinarians engage in when examining or treating horses. We will consider the forces on the hands for two tasks, lifting and using ultrasound. Assume that both sample sizes are 6, the sample mean force for lifting was 6.2 pounds with standard deviation 1.5 pounds, and the sample mean force for using ultrasound was 6.4 pounds with standard deviation 0.3 pounds. Assume that the standard deviations are known. Suppose that you wanted to detect a true difference in mean force of 0.25 pounds on the hands for these two activities. Under the null hypothesis, 40 0. What level of type II error would you recommend here? = Round your answer to four decimal places (e.g. 98.7654). Use α = 0.05. β = 0.0594 What sample size would be required? Assume the sample sizes are to be…arrow_forward
- Consider the hypothesis test Ho: 0 s² = = 4.5; s² = 2.3. Use a = 0.01. = σ against H₁: 6 > σ2. Suppose that the sample sizes are n₁ = 20 and 2 = 8, and that (a) Test the hypothesis. Round your answers to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76). The test statistic is fo = 1.96 The critical value is f = 6.18 Conclusion: fail to reject the null hypothesis at a = 0.01. (b) Construct the confidence interval on 02/2/622 which can be used to test the hypothesis: (Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).) 035arrow_forwardUsing the method of sections need help solving this please explain im stuckarrow_forwardPlease solve 6.31 by using the method of sections im stuck and need explanationarrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning





