
Study Guide/solutions Manual For Organic Chemistry
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781260475678
Author: Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 55P
For each compound drawn below:
a. Draw representations for the cis and trans isomers using a hexagon for the six-membered ring and wedges and dashed wedges for substituents.
b. Draw the two possible cahir conformations for the cis isomer. Which conformation, if either, is more stable?
c. Draw the two possible chair conformations for the trans isomer. Which conformation, if either, is more stable?
d. Which isomer, cis or trans, is more stable and why?
[1] 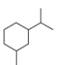 [2]
[2] 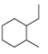 [3]
[3] 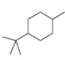
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1) Draw the control charts for the following data and
interpret the result and also develop control limts for
future use. 24 samples are taken each with a subgroup
size of 3.
Don't Use the standard excel template and analyze.
1) Draw the control charts for the following data and interpret the result and also develop
control limts for future use. 24 samples are taken each with a subgroup size of 3.
Problem to be solved both as an assignment and laboratory.
Subgroup
X₁
X2
X3
1
7
8
10
2
9
9
14
3
15
16
10
4
14
13
15
5
12
11
10
6
10
11
9
I
7
10
9
9
8
15
17
13
9
10
7
8
10
9
8
9
11
8
8
10
12
17
13
10
13
10
12
11
14
9
9
10
15
10
8
8
16
11
10
9
17
10
10
8
18
8
9
7
19
9
8
9
22222
10
10
11
9
10
9
11
9
10
12
12
11
14
2012 4
How much of each solution should be
used to prepare 1L of a buffer
solution with a pH of 9.45 using 3M
Na2CO3 and 0.2M HCI? Given: Ka
1 = 4.3 × 10-7, Ka2 = 4.69 × 10-11
Chapter 4 Solutions
Study Guide/solutions Manual For Organic Chemistry
Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 4.1 - Problem 4.2 Which of the following is not another...Ch. 4.1 - Problem 4.3 Draw the five constitutional isomers...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 5PCh. 4.2 - Draw the five constitutional isomers that have...Ch. 4.4 - Problem 4.7 Give the IUPAC name for each...Ch. 4.4 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. a....Ch. 4.4 - Problem 4.9 Give the structure corresponding to...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 4.5 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound.Ch. 4.5 - Give the structure corresponding to each IUPAC...Ch. 4.8 - Arrange the following compounds in order of...Ch. 4.9 - Problem 4.14 Draw the staggered and eclipsed...Ch. 4.9 - Prob. 15PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 16PCh. 4.10 - Problem 4.17 a. Draw the three staggered and...Ch. 4.10 - Problem 4.18 Rank the following conformations in...Ch. 4.10 - Problem 4.19 Consider rotation around the...Ch. 4.10 - Calculate the destabilization present in each...Ch. 4.12 - Problem 4.21 Classify the ring carbons as up or...Ch. 4.12 - Problem 4.22 Using the cyclohexane with the C’s...Ch. 4.13 - Draw a second chair conformation for each...Ch. 4.13 - Problem 4.24 Draw both conformations for and...Ch. 4.13 - Problem 4.25 Draw the structure for each compound...Ch. 4.13 - Prob. 26PCh. 4.14 - Prob. 31PCh. 4.14 - Prob. 32PCh. 4.15 - Prob. 33PCh. 4 - Name each alkane using the ball-and-stick model,...Ch. 4 -
4.40 Draw the structure corresponding to each...Ch. 4 - 4.42 Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
a....Ch. 4 - Prob. 42PCh. 4 - 4.46 Considering rotation around the bond...Ch. 4 - 4.50 Calculate the barrier to rotation for each...Ch. 4 - 4.51 The eclipsed conformation of is less...Ch. 4 - (a) Draw the anti and gauche conformations for...Ch. 4 - For each compound drawn below: a.Label each OH,Br...Ch. 4 - Draw the two possible chair conformations for...Ch. 4 - For each compound drawn below: a. Draw...Ch. 4 - Classify each pair of compounds as constitutional...Ch. 4 - Prob. 66PCh. 4 - 4.64 Draw the products of combustion of each...Ch. 4 - 4.65 Hydrocarbons like benzene are metabolized in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 69PCh. 4 - Prob. 70PCh. 4 - Cyclopropane and cyclobutane have similar strain...Ch. 4 - Prob. 72PCh. 4 - Haloethanes (CH3CH2X,X=Cl,Br,I) have similar...Ch. 4 - Prob. 74PCh. 4 - Prob. 75PCh. 4 - Consider the tricyclic structure B (a) Label each...Ch. 4 - Read Appendix B on naming branched alkyl...Ch. 4 - Read Appendix B on naming bicyclic compounds. Then...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How could you separate a mixture of the following compounds? The reagents available to you are water, either, 1...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
2. Which of the following is the best example of the use of a referent? _
a. A red bicycle
b. Big as a dump tru...
Physical Science
Describe the evolution of mammals, tracing their synapsid lineage from early amniote ancestors to true mammals....
Loose Leaf For Integrated Principles Of Zoology
Label each statement about the polynucleotide ATGGCG as true or false. The polynucleotide has six nucleotides. ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
What were the major microbiological interests of Martinus Beijerinck and Sergei Winogradsky? It can be said tha...
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Add substituents to draw the conformer below (sighting down the indicated bond), then rotate the back carbon to provide the anti staggered conformer. + H3C H Ph H Problem 25 of 30 Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Tap a node to see suggestions H H H Undo Rasat Remove Done Finish update Rotate Submitarrow_forwardwhat temperature does a 50% (mole fraction) of ammonia/water liquid mixture boil at 1 atmarrow_forward1) Suppose 0.1 kg ice at 0°C (273K) is in 0.5kg water at 20°C (293K). What is the change in entropy of the ice as it melts at 0°? To produce the original "water gas" mixture, carbon (in a combustible form known as coke) is reacted with steam: 131.4 kJ + H20(g) + C(s) → CO(g) + H2(g) From this information and the equations in the previous problem, calculate the enthalpy for the combustion or carbon to form carbon dioxide. kindly show me how to solve both parts of the same long problem. Thanksarrow_forward
- we were assigned to dilute 900ppm in to 18ppm by using only 250ml vol flask. firstly we did calc and convert 900ppm to 0.9 ppm to dilute in 1 liter. to begin the experiment we took 0,225g of kmno4 and dissolved in to 250 vol flask. then further we took 10 ml sample sol and dissolved in to 100 ml vol flask and put it in to a spectrometer and got value of 0.145A . upon further calc we got v2 as 50ml . need to find DF, % error (expval and accptVal), molarity, molality. please write the whole report. thank you The format, tables, introduction, procedure and observation, result, calculations, discussion and conclusionarrow_forwardQ5. Predict the organic product(s) for the following transformations. If no reaction will take place (or the reaction is not synthetically useful), write "N.R.". Determine what type of transition state is present for each reaction (think Hammond Postulate). I Br₂ CH3 F2, light CH3 Heat CH3 F₂ Heat Br2, light 12, light CH3 Cl2, light Noarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- In the phase diagram of steel (two components Fe and C), region A is the gamma austenite solid and region B contains the gamma solid and liquid. Indicate the degrees of freedom that the fields A and B have,arrow_forwardFor a condensed binary system in equilibrium at constant pressure, indicate the maximum number of phases that can exist.arrow_forwardPart V. Label ad match the carbons in compounds Jane and Diane w/ the corresponding peak no. in the Spectra (Note: use the given peak no. To label the carbons, other peak no are intentionally omitted) 7 4 2 -0.13 -0.12 -0.11 -0.10 -0.08 8 CI Jane 1 -0.09 5 210 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 -8 90 f1 (ppm) 11 8 172.4 172.0 f1 (ppr HO CI NH Diane 7 3 11 80 80 -80 -R 70 60 60 2 5 -8 50 40 8. 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 -0 80 70 20 f1 (ppm) 15 30 -20 20 -60 60 -0.07 -0.06 -0.05 -0.04 -0.03 -0.02 -0.01 -0.00 -0.01 10 -0.17 16 15 56 16 -0.16 -0.15 -0.14 -0.13 -0.12 -0.11 -0.10 -0.09 -0.08 -0.07 -0.06 -0.05 -0.04 17.8 17.6 17.4 17.2 17.0 f1 (ppm) -0.03 -0.02 550 106 40 30 20 20 -0.01 -0.00 F-0.01 10 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Lesson 2; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AL_CM_Btef4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Lesson 1; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PPIa6EHJMJw;License: Standard Youtube License