
(a)
Interpretation: The mechanism for monochlorination with the help of iodobenzene dichloride should be proposed.
Concept introduction: The monochlorination performed with ultraviolet light proceeds via radical chain mechanism. Chlorine transforms
The mechanism for monochlorination comprises of three stages illustrated as follows:
Step1- Initiation via homolytic cleavage of
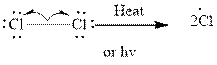
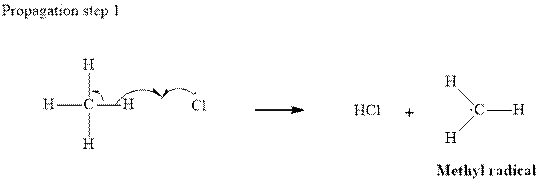
Step2-: Propagation: In first of the propagation steps,
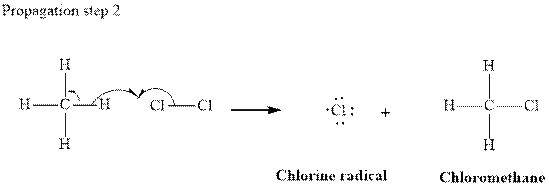
In subsequent propagation step chloromethyl radical abstracts
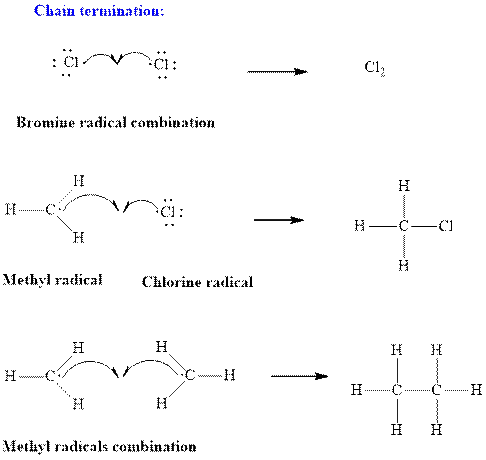
Step3: Termination: Radicals generated in propagation steps get quenched upon combination with one another. Thus termination steps are essentially the radical− radical combination illustrated as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: The three major sites of monochlorination present over steroidsshould be predicted.
Concept introduction: The monochlorination performed with ultraviolet light proceeds via radical chain mechanism. Chlorine transforms
The mechanism for monochlorination comprises of three stages illustrated as follows:
Initiation via homolytic cleavage of
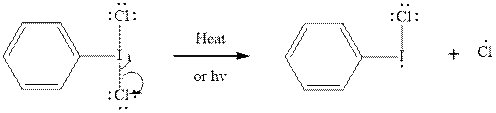
Step2-: Propagation: In first of the propagation steps

In subsequent propagation step alkyl radical abstracts
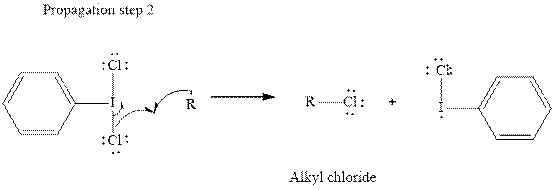
Step3: Termination: Radicals generated in propagation steps get quenched upon combination with one another. Thus termination steps are essentially the radical− radical combination illustrated as follows:
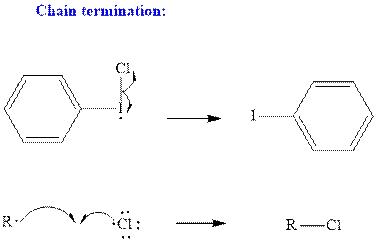
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- H-Br Energy 1) Draw the step-by-step mechanism by which 3-methylbut-1-ene is converted into 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. 2) Sketch a reaction coordinate diagram that shows how the internal energy (Y- axis) of the reacting species change from reactants to intermediate(s) to product. Brarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 H-CI CH2Cl2 CIarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. དའི་སྐད”“ H3C OH H3C CH CH3 KEq Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C NH2 NH2 KEq H3C-CH₂ 1. Product acid Product basearrow_forwardWhat alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- 2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- 2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). H-Br CH2Cl2arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole




