
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
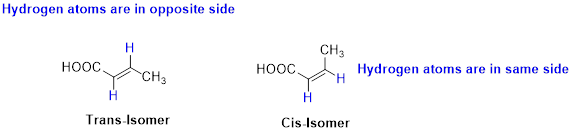
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of
Example:
(b)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

(c)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

(d)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

(e)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

(f)
Interpretation:
E or Z configuration has to be identified for the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
- 5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward
