Problem 1CQ: a. At this instant, is the particle in FIGURE Q4.1 speeding up, slowing down, or traveling at... Problem 2CQ: a. At this instant, is the particle in FIGURE Q4.2 speeding up, slowing down, or traveling at... Problem 3CQ: Tarzan swings through the jungle by hanging from a vine. a. Immediately after stepping off a branch... Problem 4CQ: A projectile is launched at an angle of 30°. a. Is there any point on the trajectory where and are... Problem 5CQ: For a projectile, which of the following quantities are constant during the flight: x, y, r, vx,... Problem 6CQ: A cart that is rolling at constant velocity on a level table fires a ball straight up. a. When the... Problem 7CQ: A rock is thrown from a bridge at an angle 30° below horizontal. Immediately after the rock is... Problem 8CQ: Anita is running to the right at 5 m/s in FIGURE Q4.8. Balls I and 2 are thrown toward her by... Problem 9CQ: An electromagnet on the ceiling of an airplane holds a steel ball. When a button is pushed, the... Problem 10CQ: Zack is driving past his house in FIGURE Q4.1O. He wants to toss his physics book out the window and... Problem 11CQ: II. In FIGURE Q4.11. Yvette and Zack are driving down the freeway side by side with their windows... Problem 12CQ: In uniform circular motion, which of the following quantities are constant: speed, instantaneous... Problem 13CQ: FIGURE Q4.13 shows three points on a steadily rotating wh1. a. Rank in order, from largest to... Problem 14CQ: FIGURE Q4.14 shows four rotating wheels. For each, determine the signs (+ or -) of w and a. Problem 15CQ: FIGURE Q4.15 shows a pendulum at one end point of its arc. a. At this point, is w positive,... Problem 1EAP: Problems I and 2 show a partial motion diagram. For each: a. Complete the motion diagram by adding... Problem 2EAP Problem 3EAP: Answer Problems 3 through 5 by choosing one of the eight labeled acceleration vectors or selecting... Problem 4EAP: Answer Problems 3 through 5 by choosing one of the eight labeled acceleration vectors or selecting... Problem 5EAP: Answer Problems 3 through 5 by choosing one of the eight labeled acceleration vectors or selecting... Problem 6EAP: A rocket-powered hockey puck moves on a horizontal friction- less table. FIGURE EX4.6 shows graphs... Problem 7EAP: A rocket-powered hockey puck moves on a horizontal frictionless table. FIGURE EX4.7 shows graphs of... Problem 8EAP Problem 9EAP: A particle moving in the xy- plane has velocity v =(2 ti + (3 t2)j ) m/s, where t is in s. What is... Problem 10EAP: You have a remote-controlled car that has been programmed to have velocity v = (-3 ti + 2t2j ) m/s,... Problem 11EAP: A ball thrown horizontally at 25 m/s travels a horizontal distance of 50 m before hitting the... Problem 12EAP: A physics student on the Planet Exidor throws a ball, and its follows the parabolic trajectory shown... Problem 13EAP: A supply plane needs to drop a package of food to scientists working on a glacier in Greenland. The... Problem 14EAP: A rifle is aimed horizontally at a target 50 m away. The bullet hits the target 2.0 cm below the aim... Problem 15EAP: In the Olympic shotput event, an athlete throws the shot with an initial speed of 12.0 m/s at a... Problem 16EAP: On the Apollo 14 mission to the moon, astronaut Alan Shepard hit a golf ball with a 6 iron. The... Problem 17EAP: A baseball player friend of yours wants to determine his pitching speed. You have him stand on a... Problem 18EAP: A boat takes 3.0 hours to travel 30 km down a river, then 5.0 hours to return. How fast is the river... Problem 19EAP: When the moving sidewalk at the airport is broken, as it often seems to be, it takes you 50 s to... Problem 20EAP Problem 21EAP: A kayaker, needs to paddle north across a 100-m-wide harbor. The tide is going out, creating a tidal... Problem 22EAP: Susan, driving north at 60 mph, and Trent, driving east at 45 mph, are approaching an intersection.... Problem 23EAP: FIGURE EX4.23 shows the angular-velocity-versus-time graph for a particle moving in a circle. How... Problem 24EAP: FIGURE EX4.24 shows the angular-position-versus-time graph for a particle moving in a circle. What... Problem 25EAP: FIGURE EX4.25 shows the angular-velocity-versus-time graph for a particle moving in a circle,... Problem 26EAP: The earth’s radius is about 4000 miles. Kampala, the capital of Uganda, and Singapore are both... Problem 27EAP: An old-fashioned single-play vinyl record rotates on a turntable at 45 rpm. What are (a) the angular... Problem 28EAP: As the earth mates, what is the speed of (a) a physics student in Miami. Florida. at latitude 26°,... Problem 29EAP: How fast must a plane fly along the earth’s equator so that the sun stands still relative to the... Problem 30EAP: A 3000-rn-high mountain is located on the equator. How much faster does a climber on top of the... Problem 31EAP: Peregrine falcons are known for their maneuvering ability. In a tight circular turn, a falcon can... Problem 32EAP: To withstand “g-forces” of up to 10 g’s, caused by suddenly pulling out of a steep dive, fighter jet... Problem 33EAP: The radius of the earth’s very nearly circular orbit around the sun is 1.5 X 1011m. Find the... Problem 34EAP: A speck of dust on a spinning DVD has a centripetal acceleration of 20 m/s2. a. What is the... Problem 35EAP: Your roommate is working on his bicycle and has the bike up side down. He spins the 60-cm-diameter... Problem 36EAP: I FIGURE EX4.36 shows the angular velocity graph of the crank shaft in a car. What is the... Problem 37EAP: I FIGURE EX4.37 shows the angular acceleration graph of a turn table that starts from rest. What is... Problem 38EAP: FIGURE EX4.38 shows the angular-velocity-versus-time graph for a particle moving in a circle. How... Problem 39EAP: A wheel initially rotating at 60 rpm experiences the angular acceleration shown in FIGURE EX4.39.... Problem 40EAP: A 5.0-rn-diameter merry-go-round is initially turning with a 4.0 s period. It slows down and stops... Problem 41EAP: An electric fan goes from rest to 1800 rpm in 4.0 s. What is its angular acceleration? Problem 42EAP: A bicycle wheel is rotating at 50 rpm when the cyclist begins to pedal harder, giving the wheel a... Problem 43EAP: Starting from rest, a DVD steadily accelerates to 500 rpm in 1.0 s, rotates at this angular speed... Problem 44EAP: A spaceship maneuvering near Planet Zeta is located at r = (600î — 400j + 200k) × 103 km, relative... Problem 45EAP: equation reference goes here45. A particle moving in the xy-plane has velocity v0= v0xî + voyj at t... Problem 46EAP: A projectile’s horizontal range over level ground is v02sin 201g. At what launch angle or angles... Problem 47EAP: a. A projectile is launched with speed v0and angle . Derive an expression for the projectile’s... Problem 48EAP: A projectile is launched from ground level at angle and speed v0into a headwind that causes a... Problem 49EAP: A gray kangaroo can bound across level ground with each jump carrying it 10 m from the takeoff... Problem 50EAP: A ball is thrown toward a cliff of height h with a speed of 30 m/s and an angle of 600 above... Problem 51EAP: A tennis player hits a ball 2.0 m above the ground. The ball leaves his racquet with a speed of 20.0... Problem 52EAP: You are target shooting using a toy gun that fires a small ball at a speed of 15 m/s. When the gun... Problem 53EAP: A 35 g steel ball is held by a ceiling-mounted electromagnet 3.5 m above the floor. A compressed-air... Problem 54EAP: You are watching an archery tournament when you start wondering how fast an arrow is shot from the... Problem 55EAP: You’re 6.0 m from one wall of the house seen in FIGURE P4.55. You want to toss a ball to your friend... Problem 56EAP: Sand moves without slipping at 6.0 m/s down a conveyer that is tilted at 15°. The sand enters a pipe... Problem 57EAP: A stunt man drives a car at a speed of 20 m/s off a 30-m-high cliff. The road leading to the cliff... Problem 58EAP: A javelin thrower standing at rest holds the center of the javelin behind her head, then accelerates... Problem 59EAP: A rubber ball is dropped onto a ramp that is tilted at 20°, as shown in FIGURE P4.59. A bouncing... Problem 60EAP: You are asked to consult for the city’s research hospital, where a group of doctors is investigating... Problem 61EAP: Ships A and B leave port together. For the next two hours, ship A travels at 20 mph in a direction... Problem 62EAP: While driving north at 25 m/s during a rainstorm you notice that the rain makes an angle of 38° with... Problem 63EAP: You’ve been assigned the task of using a shaft encoder—a device that measures the angle of a shaft... Problem 64EAP Problem 65EAP Problem 66EAP: Astronauts use a centrifuge to simulate the acceleration of a rocket launch. The centrifuge takes 30... Problem 67EAP: Communications satellites are placed in a circular orbit where they stay directly over a fixed point... Problem 68EAP Problem 69EAP: A high-speed drill rotating ccw at 2400 rpm comes to a halt in 2.5s. a. What is the magnitude of the... Problem 70EAP: A turbine is spinning at 3800 rpm. Frication in the bearings is so low that it takes 10 min to coast... Problem 71EAP Problem 72EAP: The angular velocity of a process control motor is =2012t2 rad/s, where t is in seconds. a. At what... Problem 73EAP: A Ferris wheel of radius R speeds up with angular acceleration starting from rest. Find an... Problem 74EAP Problem 75EAP: A painted tooth on a spinning gear has angular acceleration =20t rad/s2, where t is in s. Its... Problem 76EAP: A car starts from rest on a curve with radius of 120 m and accelerates tangentially at 1.0 m/s2.... Problem 77EAP Problem 78EAP: In Problem 78 through 80 you are given the equations that are used to solve a problem. For each of... Problem 79EAP Problem 80EAP: In Problem 78 through 80 you are given the equations that are used to solve a problem. For each of... Problem 81EAP: In one contest at the country fair, seen in FIGURE CP4.81, a spring-loaded plunger launches a ball... Problem 82EAP Problem 83EAP Problem 84EAP Problem 85EAP format_list_bulleted

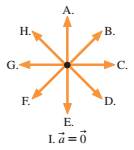

 5. At this instant, the particle is speeding up and curving downward. What is the direction of its acceleration?
5. At this instant, the particle is speeding up and curving downward. What is the direction of its acceleration? 

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning