
a. At this instant, is the particle in FIGURE Q4.1 speeding up, slowing down, or traveling at constant speed?
b. Is this particle curving to the right, curving to the left, or traveling straight?
a.
The state of the particle: speeding up, slowing down or traveling at constant speed.
Answer to Problem 1CQ
Solution:
The particle is slowing down in the vertical axis and speeding up in the horizontal axis.
Explanation of Solution
The acceleration vector has a component that it is pointing in the opposite direction to velocity vector; this means the particle will slow down on this axis. The component in the horizontal axis will make the particle to speed up.
Given Info:
There is a constant speed vector at the vertical axis and a constant acceleration vector with a component at both axes.
Formula Used The particle has the next velocity vector equation:
Where:
It is negative because it is pointing to the left.
It is negative because it is pointing downward.
Where a and v are the magnitudes of acceleration and velocity vector respectively.
Calculation
Substituting these values in the equation of velocity vector:
Conclusion
As we can see in the equation of velocity vector, the horizontal component is continuously increasing in the negative direction and the vertical component is slowing down since the initial velocity vector and the component of the acceleration vector are pointing in opposite directions.
b.
The shape of the particle trajectory.
Answer to Problem 1CQ
Solution:
The particle curves to the left.
Explanation of Solution
Given Info:
There is a constant speed vector at the vertical axis and a constant acceleration vector with a component at both axes.
Every second, the velocity vector changes the position vector as well as the acceleration vector changes the velocity direction and magnitude. As we can see the acceleration vector is partially pointing to the left, therefore the velocity vector will be changing in that direction and so the position vector.
Formula We can obtain the position equation from the previous problem:
Calculation
We can graph the last equation, and assuming the values:
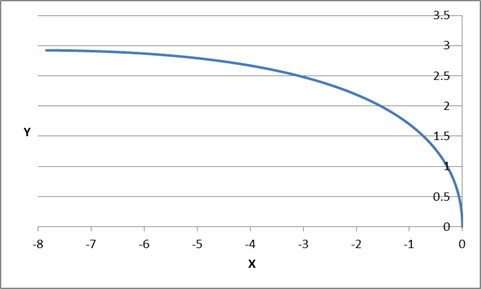
Conclusion
As we can see, the particle trajectory curves to the left because the acceleration vector has a component on the horizontal axis which points the same way.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (Chs 1-42) Plus Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- What is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardair is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- a cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
