
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780073511191
Author: Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.74AP
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The heating curve obtained for water has to be drawn and the sections of the curve that corresponds to molecular art A, B, and C has to be given.
The given molecular art is,
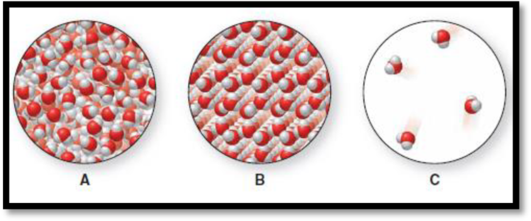
Figure 1
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please help me figure out the mechanism with arrows of the following reaction
Organic Functional Groups
Predicting the reactants or products of acetal hydrolysis
termine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction:
H*
H*
+ H₂O
Y
☑
Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure.
In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic molecules X, Y, and Z. You may draw
that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Molecule X shows up in multiple steps, but you only have to draw its structure
Explanation
Check
@2
W
Click and drag to start drawing a structure.
#4
# 3
LU
E
%
67 olo
5
66
R
T
Y
&
7
AcGraw Hill LLC. All Rights R
X
8. (16 pts) Provide the stepwise mechanism for the synthesis of the following compound via an enamine
Chapter 4 Solutions
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.1PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.2PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.3PCh. 4.1 - Prob. 4.4PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.5PCh. 4.2 - Prob. 4.6PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.7PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.8PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.9PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.10P
Ch. 4.3 - Which of the compounds in each pair has stronger...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 4.12PCh. 4.4 - Prob. 4.13PCh. 4.5 - A student has two containers one with 10 g of...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.15PCh. 4.5 - How much energy is required to heat 28.0 g of iron...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 4.17PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.18PCh. 4.5 - Prob. 4.19PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.20PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.21PCh. 4.6 - Label each process as endothermic or exothermic...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 4.23PCh. 4.7 - Answer the following questions about the graph. a....Ch. 4.7 - Prob. 4.25PCh. 4.7 - If the cooling curve in Figure 4.5 represented a...Ch. 4.7 - How much energy (in calories) is released when...Ch. 4.7 - Prob. 4.28PCh. 4 - What phase change is shown in the accompanying...Ch. 4 - What phase change is shown in the accompanying...Ch. 4 - Consider the cooling curve drawn below. a. Which...Ch. 4 - Which line segments on the cooling curve in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.33UKCCh. 4 - Prob. 4.34UKCCh. 4 - Prob. 4.35UKCCh. 4 - Prob. 4.36UKCCh. 4 - Prob. 4.37UKCCh. 4 - Prob. 4.38UKCCh. 4 - Prob. 4.39APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.40APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.41APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.49APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.50APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.54APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.55APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.56APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.57APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.58APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.59APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.60APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.61APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.62APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.63APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.64APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.65APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.66APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.67APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.68APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.69APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.70APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.71APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.72APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.73APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.74APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.75APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.76APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.77APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.78APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.79APCh. 4 - Why does steam form when hot lava falls into the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.81APCh. 4 - Prob. 4.82AP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the titration curve of (i) weak acid vs. strong base; (ii) weak acid vs. weakbase; (iii) diprotic acid with strong base (iii) triprotic acid with strong base.arrow_forwardComplete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. More... No reaction. my ㄖˋ + 1. Na O Me Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe H+ + 1 2 H H work up You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X $ dmarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. NaH (20°C) 2. CH3Br ? Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G Crarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LDA (-78°C) ? 2. Br Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. . • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardPlease draw the structuresarrow_forward
- Draw the missing intermediates 1 and 2, plus the final product 3, of this synthesis: 0 1. Eto 1. Eto- 1 2 2. MeBr 2. EtBr H3O+ A 3 You can draw the three structures in any arrangement you like. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardDraw the missing intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this synthesis: 1. MeO- H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the differences between: Glyceride and phosphoglyceride Wax and Fat Soap and Fatty acid HDL and LDL cholesterol Phospho lipids and sphingosine What are the types of lipids? What are the main lipid components of membrane structures? How could lipids play important rules as signaling molecules and building units? The structure variety of lipids makes them to play significant rules in our body, conclude breifly on this statement.arrow_forward
- What is the differences between DNA and RNA for the following: - structure - function - type What is the meaning of: - replication - transcription - translation show the base pair connection(hydrogen bond) in DNA and RNAarrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618562763
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl
Publisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
GCSE Chemistry - Differences Between Compounds, Molecules & Mixtures #3; Author: Cognito;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jBDr0mHyc5M;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY