
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
Thus, this saturated molecule has 8 additional hydrogen atoms as compared to the given molecular formula. IHD for the given molecular formula is calculated by dividing that number of additional hydrogen atoms by 2. Thus, IHD is
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
(b)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
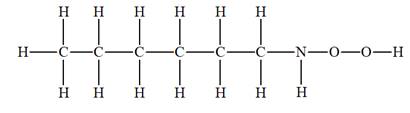
It takes a total of 15 hydrogen atoms to saturate each carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen in this compound. Thus, this saturated molecule has 10 additional hydrogen atoms as compared to the given molecular formula. IHD for the given molecular formula is calculated by dividing that number of additional hydrogen atoms by 2. Thus IHD is
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
(c)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
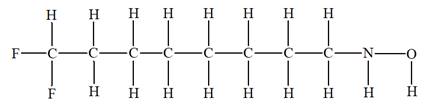
It takes a total of
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
(d)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
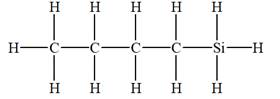
It takes a total of
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
(f)
Interpretation:
IHD for the compound having the molecular formula
Concept introduction:
In order to determine the IHD of a given molecular formula, first draw any saturated molecule that has the same number of each non-hydrogen atom as in the given formula. The general formula of a saturated hydrocarbon is
Answer to Problem 4.49P
IHD for the compound having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula is
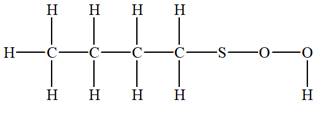
It takes a total of
The IHD for the compound with a given molecular formula is calculated by applying the steps above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- Complete the mechanismarrow_forwardV Biological Macromolecules Drawing the Haworth projection of an aldose from its Fischer projection Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H C=O HO H HO H H OH CH₂OH Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



