
Concept explainers
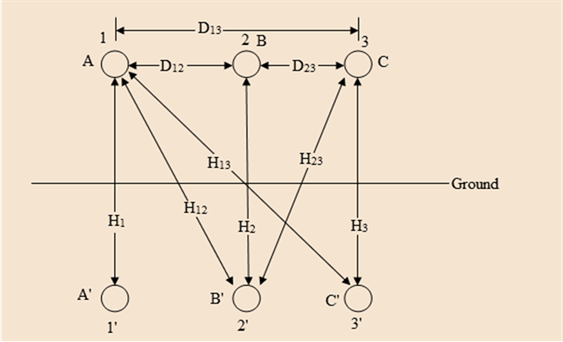
The capacitance of a single-circuit, three-phase transposed line with the configuration shown in Figure 4.38, including ground effect, and with conductors not equilaterally spaced is given by
F/m line-to-neutral
where
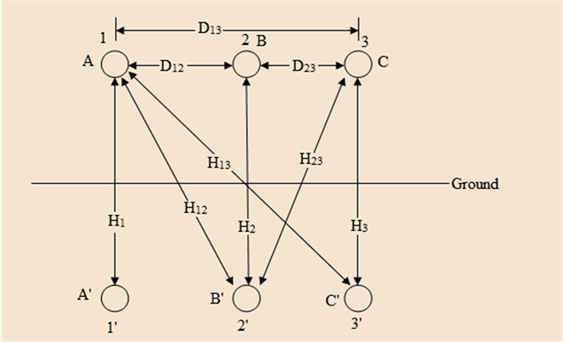
- Now consider Figure 4.39 in which the configuration of a three-phase, single circuit, 345-kV line with conductors having an outside diameter of 1.065 in. is shown. Determine the capacitance to neutral in F/m, including the ground effect.
- Next, neglecting the effect of ground, see how the value changes.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Power System Analysis & Design
- 9.56 Using JK flip-flops, design a synchronous counter that counts in the sequence 1, 3, 0, 2, 1, ... The counter counts only when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter is idle.arrow_forward9.65 Using T flip-flops, design a synchronous counter that counts in the sequence 0, 2, 4, 6, 0, ... The counter counts only when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter is idle.arrow_forward2 Using D flip-flops, design a synchronous counter that counts in the sequence 1, 4, 7, 1, The counter counts only when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter is idle.arrow_forward
- Q1: Write a VHDL code to implement the finite state machine described in the state diagram shown below. Clk D 0 CIK Q D 0 Cik Q =arrow_forwardQ1: Consider the finite state machine logic implementation in Fig. shown below: Construct the state diagram. Repeat the circuit design using j-k flip flop. r" Clk Y D' Y, Clk Q D Clk 10 0 22 3'2arrow_forwardQ: Write a VHDL code to implement the finite state machine described in the state diagram shown below. T 2 Clk Q Clk T₂ 0 la Clk T3 Q Cik 0arrow_forward
- Do you happen to know what is the complete circuit?arrow_forwardb) Draw the magnitude and phase bode plot c) Given Cdb=0.02pF, how will the frequency response change, draw the resulting magnitude and phase bode plotplz help me to solve part b and c.arrow_forwardMedium 1 is a lossless dielectric (ε₁, μ₁ = μo, σ₁ = 0) Medium 2 is a perfect electric conductor (PEC) ( 2 = 0, μ2 = μo, σ₂ = ∞) [ Moσ = 0] [ε0 μ₁ σ₂ = ∞ ] (J=σE is finite, E = 0) E(z) Exe² +Пe₁²] 1. For the case εr] = λι = = E2(z)-0 - 1 (vacuum), E₁x 1 V/m and a frequency f = 500 MHz determine: n₁ = 12= 2. Determine: r = T= 3. Using this I show that the total electric field E₁0(z) in region 1 can be written as: E(z) = -2jE, sin(2лz/λ)✰ 4. The magnitude E10(z) will show an interference pattern. The SWR (standing wave ratio) is the Emax/Emin ratio of the magnitude of the total electric field in region 1. What is the SWR? E (z) = 2|E|sin(2лz/2₁)| E" (z) SWR A Imax E(z) Imin 1+r 1-|| tot 5. Roughly SKETCH the magnitude of E10(z) and E20(z) on the graph below. E₁tot(z) tot E20(z) -0.40 -0.30 -0.ło z=0 +0.1b +0.20arrow_forward
- would anyone be able to tell me the amount of wire needed for this electrical plan in this house? and if possible would anyone be able to tell me the amount of any other materials needed (wire sizes, box sizes/styles)arrow_forwardPlease show all stepsarrow_forwardA plane wave propagating in the +z direction in medium 1 is normally incident to medium 2 located at the z=0 plane as below. Both mediums are general, characterized by ( ε i, Mi, Ơi ). tot = [ ει μη σ] [ε, μη σε ] Ex Ex tot E₁₂ (z) = Ee Ex z=0 From conservation of energy: P₁AV'(z=0) + Piav'(z=0) = P2av²(z=0). Using the above show for lossless media that: ( 1 - ||²) = (1/M2 )|T|² .arrow_forward
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
